Building Construction
advertisement

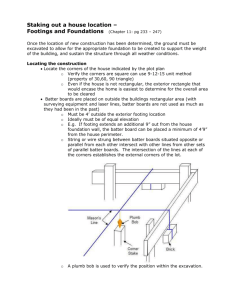
Chemical department Topic.construction Guided by J.M.J SIR D.M.P SIR 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Zavin gajera(group leader) Jaydeep rangani Ninma chandu Nadan shah Subham ch-07 ch-10 ch-09 ch-12 ch-11 Introduction Types of building Design load/building load Common building components Introduction building bye-laws 1. 2. Two types of building Based upon occupancy Based on structure 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Building include based upon occupany. Residential building Educational building Institutional building Assembly building Business building Mercantile building Industrial building Storage building 1.Load bearing structure It has lod bearing walls which receive the loads and transmit the same to the ground though their foundation. 20,30,40,cm thick walls are load bearing walls. R.c.c slab is provided directly on load bearing walls. 2.Framed structure In the buildings with frammed structure,load is transferred through a frame of R.C.C slab,beam,colomn. In this type of structures,there are partition walls of 10 cm thick,which divide and enclosethe space. Construction time is less. Various loads are taken into account while designing the foundation of a structure loads coming on a structure are: No. Type of floor Minimum live lord ( Kg/𝑚2 ) 1 Dwelling house, hospitals , hostels 2 Office ,light work room 3 6 Bank, office, reading room Shops, classrooms, assembly halls, restaurants, power station Warehouse, workshop, factory, store room , dancehall Light garage 7 Heavy garage 8 Stairs 300-500 9 Balcony 300-500 4 5 200 250-400 300 400 500-1000 250-400 750 Number of floors carried by member (column, foundation, wall etc.) Total L.L on all floors above the member 1 100% 2 90% 3 80% 4 70% 5 60% 6 or more 50% NO Material/structure Unit weight 3 Wall : brick masonry 10 cm thick 20 cm thick 30 cm thick Roof :G.I sheet 0.5 mm thick 1.63 mm thick A.C sheet Slab R.C.C 192 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 384 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 576 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 5 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 13 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 12.15.6 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 2400 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 4 PCC (plain cement concrete ) 2300 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 5 6 Mangalore tiles Clay 63 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 1440-1760 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 7 Sand 1540-2000 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 8 Fresh water 1000 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 9 Steel 7850 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 10 11 Cement Timber 1440 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 650-720 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 12 Bricks 1600-1920 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 1 2 Basic building components SUPER STURCTURE Plinth D.P.C Walls and colums Floors Beams Roofs and slabs Lintels and Aechers Doors and Window Chajjas Parapet Steps and Stairs Cupboard and Shelves Substructer Foundation A typical cross section through door and window showing all Building components Defination of building Components Foundetion - It is a sturcture below the G.L . It is the lowest part of a building Plinth – It is the portion of a building above ground up to the finished floor level. It is the loer most part of building Walls – It costructed by the use of bricks, stone, concrete , blocks , etc. Column – It is a load bearingg member of smaal section of bricks or stone or concreate Stair – It is series of steps to connect the different floors of building Roof – It is the uppermost part of a building to cover the space below Floors – The floors of each storey, above ground level are none as upper floors Lintel – It is defined as a horizontal structural member provided across the opening the doors and window Beam – It is defined as a horizontal structural member provided rested Types of Foundation Shallow Deep Pile Spread footing For walls Simple Strap footing for columns Stepped Pier Combind footing Rectangular Grillage Single Well or Cassion Mat footing Trapezodial Stepped Sloped If depth of foundation is equal to or less than its width, it is called shallow fo Generally it is 3 to 4 m. Spread footing -- which spread the super improsed load of wall over larger area. Masonary walls have ste with a concrete base. STRAP FOOTING -- If the independent footing of two columns are connecte it is called a strap footing. COMBINED FOOTING -- A spread footing which support two or more colomuns RAFT or MAT foundation GRILLAGE Foundation – It is a combined footing that covers the ent beneat a structure and supports all w – Grillage foundation is a special type of isolated and it is provided for heavily loaded steel -The depth of foundation is 1 to 1.5m (1)Plinth (2) Wall (i) Load bearing ( 20,30,40 cm) (ii) Non-load bearing (Partition wall – 10 ) - Brick Masonry Wall (3) Roof -- Types of roof Flat Lean-to-roof Sloped Domes King post trussQueen post truss Cylindrical Spherical (4) FLOOR -- A floor provides a plane surface to support the occupant and any equipment. •TYPES OF FLOOR (1) Ground floors (2) Upper floors The different types of floor which are commonly used for floor constuc (1) Mud and Muram (9) Brick (2) Flag stone (10) C.C (3) Terrazzo (11)Marble (4) Tiles (12)Asphalt (5) Timber (13)Glass (6) Rubber (14)Granite (7) Cor (15)Mosaic tiles (8) Plastic or PVC (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) Battened and ledged door Framed and panelled door Flush door Revolving door Swing door Collapsible steel door Mild steel sheet door Glazed door