Faster, better, cheaper
(PRRSV) surveillance using
oral fluid-based sampling
Jeff Zimmerman DVM PhD
Iowa State University
Ames, Iowa
Basic assumptions
• We need better surveillance of pathogens of
swine, but current methods provide inadequate
detection, are unacceptable to farmers, or are
too expensive to implement
– Good oral fluid antibody and PCR assays can be
developed for a variety of pathogens
– How well would these assays work?
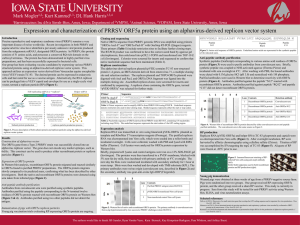
Performance of oral fluids in PRRSV
surveillance - a field study
C Olsen,1 C Wang,1 J Christopher-Hennings,2 K Doolittle,3 K Harmon,1 S
Abate,1 A Kittawornrat,1 S Lizano,5 R Main,1 E Nelson,2 T Otterson,6 Y
Panyasing,1 C Rademacher,4 R Rauh,7 R Shah,8 J Zimmerman1
1Iowa
State University, 2South Dakota State University, 3Boehringer
Ingelheim Vetmedica, Inc., 4Murphy-Brown LLC, 5IDEXX Laboratories
Inc., 6University of Minnesota, 7Tetracore®, Inc., 8Life Technologies®, Inc.
Objective
- Estimate the probability of detecting PRRSV
infection as a function of within-pen prevalence
Experimental design
• 25 pens, 25 pigs per pen
• Prevalence was established using pigs
vaccinated with PRRSV MLV vaccine
Prevalence
(pigs +)
Samples tested by RT-PCR and ELISA
Lab 1
Lab 2
Lab 3
Lab 4
Lab 5
Lab 6
0% (0+)
0%
0%
0%
2%
2%
2%
4% (1+)
12%
16%
12%
8%
20%
20%
12% (3+)
85%
95%
55%
55%
100%
90%
20% (5+)
72%
88%
40%
32%
80%
72%
36% (9+)
96%
96%
76%
76%
100%
96%
PRRSV MLV
SITE 1
SITE 2 … 14 DPV - serum antibody and virus positive
25 pigs per pen
Experimental design
● DPV 0
PRRSV-negative pigs (n = 90) in Missouri vaccinated with MLV
PRRSV MLV.
● DPV 10
PRRSV-vaccinated pigs (n = 90) in Missouri brought to Iowa farm
and placed in isolation
● DPV 12
PRRSV-negative pigs (n = 535) from Oklahoma brought to Iowa
farm, placed in 25 pens, oral fluid collected from each pen.
● DPV 13
Morning: blood sample from each of 535 negative pigs.
Afternoon: Within pen PRRSV prevalence (0%, 4%, 12%, 20%, or
36%) established by placing 0, 1, 3, 5, or 9 PRRSV-vaccinated
pigs in the 25 pens. Each pen held a total of 25 pigs after
placement.
● DPV 14
5 successive oral fluid samples were collected from each pen,
i.e., a total of 125 samples.
● DPV 14
Serum samples were collected from each of the 90 vaccinated
pigs to establish PRRSV status.
Probability of detection as a
function of prevalence?
PRRSV RT-PCR results on oral fluids
PRRSV RT-PCR results on oral fluids
PREV
(pigs +)
*n
Percent of RT-PCR positive oral fluid samples
Lab 1
Lab 2
Lab 3
Lab 4
Lab 5 Lab 6
p-value
0% (0+)
50
0%
0%
0%
2%
2%
2%
0.700
4% (1+)
25
12%
16%
12%
8%
20%
20%
0.443
8% (2+)
5
80%
100%
80%
20%
100%
80%
0.015
12% (3+)
20
85%
95%
55%
55%
100%
90%
<0.001
20% (5+)
25
72%
88%
40%
32%
80%
72%
<0.001
36% (9+)
25
96%
96%
76%
76%
100%
96%
0.002
*n = number of oral fluid samples
PRRSV ELISA results on oral fluids
PRRSV ELISA results on oral fluids
PREV
(pigs +)
*n
Percent of ELISA positive oral fluid samples
Lab 1
Lab 2
Lab 3
Lab 4
Lab 5 Lab 6
p-value
0% (0+)
50
2%
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
0.416
4% (1+)
25
24%
16%
12%
8%
24%
8%
0.067
8% (2+)
5
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
1.000
12% (3+)
15
67%
60%
80%
47%
73%
53%
0.048
20% (5+)
25
68%
88%
92%
80%
92%
88%
0.015
32% (8+)
10
90%
100%
90%
90%
100%
90%
0.722
36% (9+)
15
87%
93%
93%
87%
100%
87%
0.352
*n = number of oral fluid samples
COMPARISON
PREV
(pigs +)
*n
Percent of RT-PCR positive oral fluid samples
Lab 1
Lab 2
Lab 3
Lab 4
Lab 5
Lab 6
0% (0+)
50
0%
0%
0%
2%
2%
2%
4% (1+)
25
12%
16%
12%
8%
20%
20%
8% (2+)
5
80%
100%
80%
20%
100%
80%
12% (3+)
20
85%
95%
55%
55%
100%
90%
20% (5+)
25
72%
88%
40%
32%
80%
72%
36% (9+)
25
96%
96%
76%
76%
100%
96%
PREV
(pigs +)
Percent of ELISA positive oral fluid samples
*n
Lab 1
Lab 2
Lab 3
Lab 4
Lab 5
Lab 6
0% (0+)
50
2%
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
4% (1+)
25
24%
16%
12%
8%
24%
8%
8% (2+)
5
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
0%
12% (3+)
15
67%
60%
80%
47%
73%
53%
20% (5+)
25
68%
88%
92%
80%
92%
88%
32% (8+)
10
90%
100%
90%
90%
100%
90%
36% (9+)
15
87%
93%
93%
87%
100%
87%
One oral fluid sample
One serum sample
X
x
x
Within-pen prevalence
Increased probability of
PRRSV detection with one
oral fluid samples vs. one
serum sample
X
x
x
Within-pen prevalence
Conclusions
• Oral fluid-based detection of PRRSV infection using
either ELISA or RT-PCR is effective, efficient, and easy.
• The estimates in this study are conservative:
1. Vaccine-induced viremia and antibody response is "weaker"
than natural infection (Johnson et al., 2004)
2. Vaccinated pigs were introduced into pens ~16 hours prior
to collection. Lack of socialization adversely affects
sampling behavior.
3. Results from all laboratories were included in the estimates.
4. Oral fluid-based surveillance could facilitate faster, better,
cheaper surveillance of PRRSV and other pathogens
Thank you!
jjzimm@iastate.edu