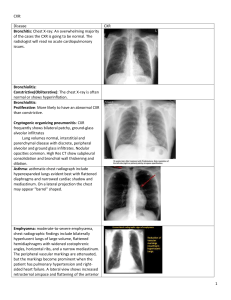
Interstitial Lung

Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
What is the lung interstitium?
• It is all the structures that support the lung tissue. The interstitium includes:
– Fibrous septae
– Alveolar walls
– Lymphatics
– Pulmonary vessels
What are the causes of abnormal
Interstitial Shadowing on a CXR?
• There are many causes!
• Two important ones are:
– Idiopathic
• leading to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis / fibrosing alveolitis
– Cardiogenic intersitial pulmonary oedema
• see pulmonary oedema presentation
• There are many other causes
– E.g. Drugs, asbestosis, farmer’s lung
What happens when there is ILD?
• Interstitial structures become thickened / inflamed
• This occurs in an irregular fashion – some structures will initially remain normal while others will become inflamed
• Interstitial structures that are normally too small to be seen with the naked eye on CXR eventually become large enough to be visible
What does ILD look like?
• ILD can include some or all of:
– Fine lines (reticular shadowing)
– Small nodules
– Larger nodules
– Lung volume loss
– Honeycombing
– Fibrosis
• A good place to look for ILD is between rib spaces; close to the chest wall, there should normally be very few lung markings, and certainly no nodules or fine lines
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Reticulonoduar shadowing
Irregular heart border
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
This patient also has lung cancer (a complication of pulmonary fibrosis)
How can ILD be investigated?
• High resolution CT chest
– Some causes have specific appearances
• Pulmonary function tests
• Lung Biopsy
• Blood tests
…the choice of tests depends on the clinical presentation
Take Home Points
• Interstitial lung disease has a characteristic appearance on a CXR
• Look between rib spaces for the presence of extra nodules and fine lines
• High resolution CT chest is a useful test to evaluate suspected cases of ILD