Prenatal Care – Module A
NUR 106
Spring, 2005
Anatomical Landmarks
Female
Male
External Structures
Internal Structures
Midsagital View
Uterus
Uterine Ligaments
Pelvic Bones
Female Pelvis
Pelvic Types
Muscles of the Pelvic Floor
Male: External and Internal
Structures
Testis
Testis
Sperm
Female Reproductive Cycle
Ovulation
Menstruation
Menarche
Climacteric
Menopause
Female Reproductive Cycle
Conception and Fetal
Development
Nine Month Miracle
Miracle of Life
Internet sites
Conception
Fertility
Sexual intercourse
Pregnancy
Genetics
Chromosomes
Autosomal
Sex
Chromosomal syndromes
Modes of inheritance
Patterns of Inheritance
Dominant
Recessive
X-linked
Nursing Responsibilities
Identify families at risk
Education
Liaison
Support / Crisis intervention
Continuity of care
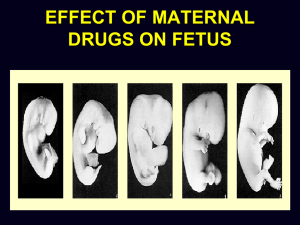
Teratogens
Tobacco
Alcohol
Marijuana
Cocaine
Heroin
Anticonvulsants
Anticoagulants
Acne medications
Reproductive Ethics
Maternal-fetal conflict
Abortion
Intrauterine fetal surgery
Reproductive assistance
Embryonic stem cell research
Human genome project
Cord blood banking
Fertilization
One spermatozoon enters the ovum
Two nuclei containing the parents’
chromosomes merge
Occurs in the outer third of the fallopian
tube
Sex is determined
Multifetal Pregnancy
Dizygotic twinning -- fraternal
Monozygotic twinning -- identical
Implantation
Nidation
Gradual process
Occurs between 6th / 7th and 10th days
Upper part of posterior uterine wall
Placenta develops
Fertilization and Implantation
Amniotic Membranes
Amnion (inner)
Chorion (outer)
Enclose fetus in amniotic fluid
Protects fetus from infectious organisms
Amniotic Sac
Amniotic Fluid
Clear, slightly yellow, alkaline fluid
Approximately 1 liter at term
Derived from
Maternal plasma
Cells of the amnion
Fetal fluids from lung, skin, fetal urine
Functions of Amniotic Fluid
Cushions fetus from trauma
Facilitates fetal movement
Facilitates symmetrical growth
Regulates intrauterine temperature
Provides source of oral fluid
Cushions umbilical cord
Receptacle for fetal substances
Placenta / Function
Fully functional by week 12
Respiration
Nutrition
Waste removal
Protection
Endocrine
Placenta
Placenta After Delivery
Umbilical Cord
One vein
Two arteries
Wharton’s jelly
Amnion
Placenta and Cord
Umbilical Cord
12 weeks
18 Weeks
4 Months
5 Months
30 Weeks
40 Weeks
Fetal Development
Preembryonic or ovum
Embryonic
Fetal
Fetal Circulation
Ductus venosus
Ductus arteriosus
Foramen ovale
Fetal Circulation
Factors Affecting Fetal
Development
Exposure to teratogens
Maternal health habits and lifestyle
Paternal health habits and exposure to
environmental influences
Physiological Changes During
Pregnancy
Uterus
Ligaments
Cervix
Chadwick’s
Goodell’s
Hegar’s
Breast
Montgomery tubercles
Skin
Circulatory System
Increases up to 50%
Pseudoanemia
Iron requirements increased
Increase in size
Blood pressure changes
Fibrinogen increases
Mechanical circulatory effects
Supine Hypotension Syndrome
Respiratory System
Thoracic cage
Oxygen consumption increases
Hyperventilation
Respiratory alkalosis
Mucosal edema
Digestive System
Nausea / vomiting
Constipation
Flatulence / heartburn
Gallstones
Urinary System
Kidneys
Function increases
Renal threshold for sugar reduced
Bladder and ureters
Blood supply increased
Pressure
Atonia
Joints, Bones, Teeth, and Gums
Pelvic cartilages
Gait
Uterus
Posture changes
Teeth
Gums
Endocrine System
Placenta
HCG
HPL
Estrogen
Progesterone
Pituitary
Adrenal
Thyroid
Signs of Pregnancy
Presumptive – Subjective
Probable – Objective
Positive -- Diagnostic
Signs of Pregnancy: S, O, or D
Amenorrhea
Goodell’s sign
Fetal heart sounds
Urinary frequency
Positive pregnancy test
Nausea and vomiting
Enlargement of the abdomen
Quickening
Palpable fetal movements
Braxton Hicks contractions
How would you explain the
differences between the
subjective (presumptive),
objective (probable), and
diagnostic (positive) signs of
pregnancy to an expectant
mother?
Maternal Psychosocial Changes
First trimester
Ambivalent
Second trimester
Baby becomes real
Maternal introspection
Third trimester
Begins to think of baby as separate
being
Restless
Self-centered
Rubin’s Maternal Tasks
Seeking safe passage
Securing acceptance
Learning to give of self
Committing self to child
Paternal Psychosocial Changes
First trimester
Excitement over virility
Financial concerns
Energetic
Exhibit symptoms with wife
Second trimester
More confident
Concerns about wife’s changes /
introspection
Third trimester
Rivalry with fetus
Interest in himself
Fantasizes about child
Factors Affecting Psychological
Response
Body image
Personal characteristics
Financial situation
Cultural expectations
Emotional security
Support from significant others
Changes in sexuality
Role of the father and siblings
Preparation for Parenthood
Preconception
Childbearing decisions
Prenatal education
Childbirth preparation
Childbirth Education
Provides information on pregnancy and
childbirth to facilitate optimal decision
making
Classes for special groups
Importance of exercise during pregnancy
Selection of birthing process
Infant care
First Trimester
Physical and psychosocial changes of
pregnancy
Self-care in pregnancy
Protecting and nurturing the fetus
Choosing a care provider and birth setting
Prenatal exercise
Relief of common early pregnancy
discomforts
Second Trimester
Planning for breast-feeding
Sexuality in pregnancy
Relief of common later-pregnancy
discomforts
Third Trimester
Preparation for childbirth
Development of a birth plan
Relaxation techniques
Postpartum self-care
Infant stimulation
Infant care and safety
Goals of Prenatal Care
Safe birth
Health promotion
Self-care
Provide physical care
Provide anticipatory guidance
Risk Factors / Reproductive
Outcomes
Maternal age
Parity
Socioeconomic status
Ethnicity
Geographic factors
Behavioral and Lifestyle risks
Health risks
Previous pregnancies
Role of Nurse
Physical assessment
Identify and reevaluate risk factors
Teach self-care
Nutrition counseling
Promote family’s adaptation to pregnancy
Prenatal Visits
Every 4 weeks for first 28 to 32 weeks
Every 2 weeks from 32 to 36 weeks
Every week from 36 to 40 weeks
Terminology
Gravida
Multipara
Nulligravida
Nullipara
Primigravida
Abortion
Multigravida
Gestational age
Para
Fertilization age
Primipara
Nomenclature
G
T
P
A
L
M
=
=
=
=
=
=
number of pregnancies
number of term deliveries
number of preterm deliveries
number of abortions
number of living children
number of multiple births
Nägele’s Rule
First Day of Last Menstrual Period
Minus 3 months
Plus 7 days
Identify the causes and interventions
for each discomfort of pregnancy:
Heartburn
Hemorrhoids
Urinary frequency
Nausea / vomiting
Leg cramps
Vaginal discharge
Fatigue
Backache
Constipation
Varicose veins
Edema
Dyspnea
Why is a positive
pregnancy test not a
positive sign of
pregnancy?
Routine Lab Tests
Blood grouping
Rh factor and
antibody screen
CBC
H&H
VDRL, RPR, or
STS
Rubella titer
TB skin test
Hg electrophoresis
HIV screen
Hepatitis B screen
UA
PAP test
Cervical culture
MSAFP
Maternal blood
glucose
Prenatal Laboratory Tests:
Normal or Abnormal ?
Hemoglobin 13.6 g/dL
Hematocrit 35%
Rubella titer 1:6
WBC 6,200/ mm3
Sickle Cell screen negative
Prenatal Self-Care Measures
Breast tenderness
Leg cramps
Nausea
Constipation
Backache
Risk Factors
Definition
Social / Personal
Preexisting medical disorders
Obstetric considerations
Problems associated with current
pregnancy
Prenatal Diagnostic Studies
Ultrasound
Estriol: Increases with fetal growth
Amniotic Fluid
Amniocentesis
Lecithin / sphingomyelin ratio
Fern test
Nitrazine test
Kick test
Chorionic villus sampling
Alpha feto protein level
Level I Ultrasound
Basic
Detect gestational sac (5 weeks after LMP)
Identify number of fetuses
Document fetal life
Detect gross fetal structural anomalies
Estimate gestational age
Determine fetal position
Locate the placenta
Estimate amniotic fluid volume
Evaluate maternal pelvic masses
Level II Ultrasound
Evaluate gestational age
Measure fetal growth
Perform specific examinations of the brain,
heart, kidney, and cord insertion
Quantify amniotic fluid volume
Determine placental location
Performed after 18 weeks
List two advantages of
prenatal ultrasound
assessment for the
mother and fetus.
Tests of Fetal Well-Being
Ultrasound
Amniocentesis
Nonstress Test (NST)
Contraction Stress Test (CST)
Breast Self-Stimulation Test (BSST)
Danger Signs in Pregnancy
C = Chills and fever
Cerebral disturbances
A = Abdominal pain
B = Blurred vision
Blood pressure
Bleeding
S = Swelling
Sudden escape of fluid
Nutrition During Pregnancy
Choose foods from food guide pyramid
Increase of 300 calories / day
Calorie needs greater in last two trimesters
Encourage diet high in folic acid with
supplements
Calcium needs increase nearly 50%
Heavy demand for iron for fetal stores
Drink 8 to 10 glasses of water / day
Food Guide Pyramid
Vegetarianism
Need ample and complete proteins from
dairy products and eggs
Protein from brown rice and whole wheat,
legumes, nuts, cooked and fresh vegetables
and fruits
Vitamin B12 supplement
Lactose Intolerance
Abdominal distention, discomfort, nausea,
vomiting, loose stool, cramps
May tolerate milk in cooked form
Cheese and yogurt
Lactase may be prescribed
Lactase-treated milk
Lactose-free products
Pica
Non-nutritive eating
Associated with poverty and inadequate
diets
Iron deficiency anemia
Weight Gain
Normal: 25 -- 35 pounds
Underweight: 28 -- 40 pounds
Overweight: 15 -- 25 pounds
Uterine Growth During Pregnancy
F
Uterine Growth During Pregnancy
What is the average
pattern of weight gain
during each trimester of
pregnancy?
Maternal Weight Gain
Distribution
Fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid
Uterus
Increased blood volume
Breast tissue
Maternal stores
Total
11 pounds
2 pounds
3 pounds
3 pounds
5-10 pounds
25-35 pounds
Medications
Prenatal vitamins
Iron supplements
Folic Acid
Antacids
Case Study
A client, who is a primigravida in her
second trimester, has come in for a
scheduled prenatal visit. When the nurse
asks how things are going, the client
replies, “Not very well. It seems like I’m
just falling apart. I have heartburn after I
eat, my ankles swell, I’m constipated all
the time, and I think I may be getting
hemorrhoids.”