Reproductive System Disorders
Pathophysiology
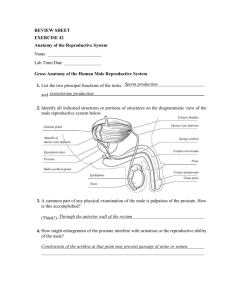
Male Reproductive System
• Anatomy
– Gonads = Testes
– Ductile system =
epididymis, vas deferens,
ejaculatory duct, urethra
– Supportive glands =
seminal vesicles, prostate,
bulbourethral (Cowper’s)
– External genitals =
scrotum, penis
• Testes
– tunica vaginalis = parietal peritoneum that remains surrounding testis after
its descent
– tunica albuginea = tough connective tissue membrane that surrounds testis
and enters the gland to form septa
– seminiferous tubules = where sperm are developed; approx. 100 yards in in
testis; contain Sertoli cells; between tubules are inter-stitial spaces that contain Leydig cells
• Testes (cont)
– Physiology
• Spermatogenesis
– mature sperm formed by process
of Meiosis
» Key = getting mature
gamete with ½ number of
chromosomes
» mature sperm = head
(nucleus & acrosome), neck
(mitochondria), and tail
» takes 60 days +/- to make a
sperm
– primary spermatocyte, secondary
spermatocyte, spermatids, sperm
• Testosterone Production
– 2 key functions
» masculinization
» anabolism
•
Male Ductal System
– Epididymis
– storage tank for sperm
– sperm get final maturation
– Vas Deferens
– becomes Ejaculatory Duct after it joins
seminiferous tubule duct
– Urethra
•
Accessory Glands
– Seminal Vesicles
– contributes 60% of semen
» rich in fructose ; provides energy for
the sperm
– Prostate
– contributes 30% of semen ; provides
nutrients for the sperm; antibiotic
secretion
– Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s)
– contribute 5-10% of semen ; provides
lubrication & sterilization
•
External Genitalia
– Penis
– 3 columns of erectile tissue
» corpora cavernosa (2) & corpora
spongiosum (1)
– glans covered by foreskin (prepuce)
– Scrotum
– skin-covered (has hair follicles) pouch
suspended from groin
• Hormones and male reproductive function
Female Reproductive
System
• Anatomy
– gonads = ovaries
– ductal system = fallopian
tubes, uterus, vagina
– accessory glands =
Bartholin's, breasts
– external genitalia = clitoris,
labia majora & minora,
perineum
• Ovaries
– contain gametes (oocytes) surrounded by
some cells (follicular cells)
– these called Primary Follicles
» each ovary has appox. 1 million
at birth
– life cycle of oocyte after puberty: primary
oocyte, secondary oocyte, ovum
– functions
• gamete production
• hormone production
– Estrogen = causes feminization ;
from granulosa cells
– Progesterone = prepares for
pregnancy ; from corpus luteum
• Female Ductal System
– Fallopian Tubes
• distal end = fimbria
• Outer 1/3 = fertilization
– Uterus
• composed of fundus, body, & cervix
• has myometrium & endometrium]
– Vagina
• Accessory Glands
– Bartholin’s (greater vestibular)
• exocrine gland
• provides lubrication
– Breasts
• composed of glands & ducts surrounded by fat tissue
• External Genitalia
– clitoris, labia majora & minora (no hair follicles), vestibule, perineum
•
The Menstrual Cycle
– begins after menarche ; ends
with menopause
– 4 basic parts:
– Menses
– Proliferative
Phase = first half of
cycle
» deals with
maturation of
follicle &
development of
more granulosa
cells thus
producing more
estrogen
– Ovulation = usually
at midcycle
– Secretory Phase =
second half of cycle
» deals with
conversion of
ruptured follicle
to corpus
luteum
» corpus luteum
produces
progesterone
• hormonal control
• hypothalamus--------GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone)
• anterior pituitary---- FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
LH (luteinizing hormone)
• Ovary --------------- Estrogen
Progesterone
Male reproductive tract disorders
overall outline
• Disorders of testes & scrotum
• Disorders of prostate
• Disorders of the penis
Disorders of the Testes & Scrotum
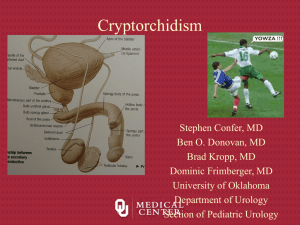
• Cryptorchidism
– undescended testis
– By age one, 80% are in scrotum
– incidence: 3% of term babies; 20% of premies
– increases the incidence of carcinoma (Seminoma)
– treat early-------the longer you wait, the greater the chance of
decreased sperm & testosterone production
•
Remember:
– Tunica Albuginea = thick connective tissue
that covers testes & divides
substance of testes into lobules
– Tunica Vaginalis = peritoneum that remains around
testes after descent
– 2 layers: visceral (on testis) & parietal (around testis)
• Hydrocele
– most common disease of testes
– it’s fluid in cavity bound by the 2 layers of tunica vaginalis
– this may communicate with peritoneal cavity via congenital patency
of process vaginalis
– this may cause size to vary from time to time
• Infertility Problems
– deals with decreased production and/or quality of sperm
– 2 distinct reasons
– poor production in sperm development
» One correctable cause = varicocele
– blockage of ductile system
– low count = oligospermia
– zero count = azospermia
• Varicocele
– varicosities around the testis (usually left testis)
– left spermatic vein into renal vein (10 cm higher
than insertion of right spermatic
vein into inferior vena cava)
– usually begins at puberty
– may be relieved by lying down
• Torsion of the testis
– Etiol:
• Spontaneous
• Post trauma
– Timing
• Usually puberty
– Path: necrosis & infarction
• Testicular Cancer
– range from VERY aggressive to least aggressive
• Germ cell tumors
» Seminoma = least aggressive (most common)
» Nonseminomas
* embryonal carcinoma
* teratomas
* choriocarcinoma = most aggressive
• Non- germ cell tumors
» May be hormonally active (secrete androgen or estrogen)
» Exp: leydig cell, Sertoli cell
– tumors of young men ( age 15 - 35)
– diagnosis : tumors are solid masses - no transillumination
– Usually unilateral
– predisposing factors:
– undescended testes
– inguinal hernia during childhood
– prior history of mumps orchitis
» Note: in mumps orchitis, 50% of cases result in testicular atrophy
– Cure rate = 95%
Prostate Diseases
• Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH)
– enlargement of the prostate common in older men
– Involves central area of gland
– complications include:
• pyelonephritis
• hydronephrosis
• uremia
• Cancer
– primarily occurs in men over age 50
– third leading cause of cancer death
– Involves periphery of gland
– Usually begins as nodule on posterior surface of gland
– Many are androgen dependent
– If metastases, first usually to bone
– diagnosis
» DRE
» 2 serum markers
» PSA (prostatic specific antigen)
» Prostatic acid phosphatase
» Ultrasound
Pathology of the Penis
• Foreskin (prepuce)
– phimosis
– paraphimosis
– redundant foreskin
• Glans
– Balantitis
STD from Yeast (Candida)
• Carcinoma
–
–
–
–
Rare
Risk factors: HPV (now have vaccination)
First sign = usually leukoplakia
circumcision in child prevents it
• adult circumcision does not prevent it
• Impotency
– approx. 50% of men age 40 - 70 have, at times, some degree or complete
impotency ( failure to get an erection)
– sexual stimulation causes release of nitric acid from nerves in penis
– an enzyme breaks down the product of nitric acid that causes the erection
– this enzyme’s effect is loss of the erection
– this is where Viagra works ; it prevents loss of the erection
Female reproductive tract disorders
overall outline
• Structural abnormalities
• Menstrual disorders
– Endometriosis
– Menopause
• Infections
• Tumors
– Benign
– Malignant
• Breast
• Pregnancy
• STD’s
Structural abnormalities
• Pelvic relaxation disorders
– Normal variations of uterine position
• Uterine mobility is key to normalcy
– Uterine prolapse
– First, second, & third degrees
– Cystocele
– Rectocele
Normal variations of
uterine position
– Uterine mobility
is key to
normalcy
– midline
– Anteverted &
anteflexed
– Retroverted &
retroflexed
Uterine Prolapse
• def = downward
displacement of uterus
• etiol = fascial tissue defect
• First degree
• Get vaginal shortening
• Second degree
• Cervix at introitus
• Third degree
• Vagina completely
everted
• Uterus hanging outside
vagina
• Cystocele
• downward displacement of bladder
into vagina
• Can get retention & frequent
cystitis
• urethra may or may not accompany
it
» called cysto-urethrocele
» frequently get symptom of
urinary stress
incontinence
• Rectocele
• displacement of rectum into vagina
• Usually asymptomatic
• If very large may get constipation &
inability to completely evacuate
rectum
• May get ulceration of vaginal wall
• See picture
Menstrual Disorders
• Dysmenorrhea
– Primary dysmenorrhea = when no obvious pathology found
– ? Hormonal cause
» prostaglandins
» hormonal changes secondary to teenage ovulatory cycles
– Secondary dysmenorrhea = when obvious pathology found as the cause
• Amenorrhea
– Primary Amenorrhea = never having a menstrual flow
– Secondary Amenorrhea = having menstrual cycles & then they stop
– causes = many !!!
» Treatment directed at the underlying cause
• Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)
– abnormal menstrual flow when no obvious cause is known
– frequently thought to be secondary to some type of hormonal
imbalance, but specific diagnosis not necessary to have DUB
– Types:
»
»
»
»
»
oligomenorrhea
polymenorrhea
menorrhagia
metrorrhagia
meno-metrorrhagia
• Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
– group of symptoms that occur in the woman’s secretory phase of cycle
– Currently called : PMDD (premenstrual dysphoric disorder)
• Def of dysphoria = excessive pain, anguish, & agitation
– usually secondary to inappropriate ovulation
– Key = too much estrogen & not enough progesterone in the
second half of the cycle
• Endometriosis
– A condition when you get
endometrial tissue located outside
its normal position, which is the
inside lining of the uterus
– symptoms depend on where the
ectopic tissue is located
– the tissue has function, i.e.
bleeds with menstruation
– Sx : pain
– Complications
• Fibrosis
• Scarring
• Adhesions
• Infertility
• Dyspareunia
•
menopause
– Get cessation of menses & drop in estrogens which can cause:
– general symptoms
» irritability
» short term memory loss
» Insomnia
» Vasomotor instability = hot flashes & night sweats
– gynecological symptoms
» vaginal dryness & dyspareunia
» urinary stress incontinence
– Cardiovascular problems
» ASHD
» coronary artery disease
» strokes
– Osteoporosis
– Dx:
– High FSH; low estrogens
Infections of the Female Reproductive Tract
• Vaginitis
– 3 types:
• Yeast Vaginitis
– caused by fungus from genus Candida or Monilia
• Trichomonas
– caused by a protozoa
– may be sexually transmitted
• Bacterial Vaginosis
– caused by different bacterial overgrowth
– used to be called non-specific vaginitis or Gardnella
• Generally most cases of vaginitis are NOT sexually transmitted, but
at times they ALL may be sexually transmitted !!
• Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
– usually acute, but may be chronic
– may involve some or all of the pelvic
organs
– get tissue inflammatory reaction with
resultant symptoms
– Key symptom = pelvic pain
– Pain worsens with movement
& sex
– frequently secondary to untreated or
inadequately treated STD
– Complications
– Infertility (pyosalpinx)
– Adhesions
– Dysuria
– Irregular vaginal bleeding
See next slide
•
Note PID spread:
–
–
–
–
Vaginitis
Cervicitis
Endometritis
Oophoritis
• Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
– vaginal infection with systemic symptoms
– caused by staphlococci toxin which comes from
nidus of infected tampon
– prevention by proper tampon toilet
– Symptoms begin immediately post menses
Bartholin cyst (Bartholinitis)
Etiol = pathogens that cause inflammation
Duct become obstructed
Get “large pimple”
Tumors of the Female Reproductive Tract
• Cervix
– Benign
• Cervical polyps
– malignant
• key ages: 20 - 40
• pap smear
• Etiol: HPV
– Vaccine available
• Uterus
– benign
• fibroids = commonest tumor of
female repo. System
– leiomyomas
– only in premenopause
– See next slide
– malignant
• ? Estrogen related
• Age: 50 – 70
• Dx: pmb
•
•
Estimated that half the women get them during the reproductive years
Clinically symptoms depend on size & location
• Submucous = bleeding problems, infertility
• Intramural = sx only if large
• Subserous = pressure sx from surrounding structures
• Ovary
– Benign
• Functional (commonest)
– Follicular cyst
– Corpus luteum cyst
• Non-functional (benign germ cell)
(e.g. Teratoma)
– Malignant
Solid teratoma
• Factors that suppress ovulation
decrease the risk
• Avg age = 40
• 2 basic types
– Epithelial (line ovary or
follicles)
– Germ cell – aggressive
» Mainly in children &
adolescents
• See next slide re:
– Late diagnoses
– seeding
Functional (follicular) cyst
Breast disorders
• Fibrocystic breasts
• Was called fibrocystic “disease”
• “lumpy” breasts
• Fibroadenoma
• Benign
• In young girls (age 15-25)
• nontender
• Intraductile papilloma
• Get nipple discharge
• Mammary duct ectasia
– Get lumpiness beneath areola
– Seen in
– Postmenopausal
– Pregnancy
– Lactation
– Get thick nipple discharge
– Pathophysiology: ducts dilate & fill with cellular debris; get
inflammation
• Breast cancer
–
–
–
–
–
1 out of 8 women in USA
Most are intraductile carcinomas
50% in upper outer quadrant
Ca in situ = mammary dysplasia
Risk factors:
– Family history
– Menstrual history
– Reproductive history
Pathology in Pregnancy
• Morning Sickness
– severe form = Hyperemesis Gravidarum
• Spontaneous Abortion
– 3 Types : Complete, Incomplete, Missed
• Ectopic Pregnancy
• Toxemia of Pregnancy = syndrome of hypertension, proteinuria, &
edema
• called Preeclampsia
• If severe & accompanied by convulsions, called Eclampsia
• Placental Problems
– Placenta Praevia
– Abruptio Placenta
• Hydatidiform Mole = development abnormality of conception
• may progress to Choriocarcinoma
• Preterm Birth
– 8% of all births in US
– Preterm labor
– Preterm PROM (premature rupture of membranes)
» Responsible for half of all premie deliveries in US
• Trauma during pregnancy
– Complicates 1 out of 12 pregnancies in US
– Watch for:
» Uterine contractions
» Uterine tenderness &/or irritability
» Ruptured BOW
» Nonreassuring FHR pattern
» Vaginal bleeding
• Maternal hemorrhage
– Is the leading cause of maternal mortality
– Hemorrhagic shock
– Postpartum hemorrhage
• Endometritis
– Occurs in 1-3% of vaginal births
– Occurs in 10-50% of cesarean sections
STD’s
• AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
• Def: progressive impairment of the immune system caused by
the immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
– Attacks helper T lymphocytes
• Initial infection similar to URI
• Then latency
• Then AIDS
– Begins with generalized adenopathy, weight loss, fatigue, nt.
Sweats, and diarrhea
– Get opportunistic infections:
» PCP (pneumocystis carinii pneumonia) = caused by small
protozoa (? fungus) that can normally be found in lung tissue
of certain animals (dogs) and in humans
» Toxoplasmosis = small protozoan that can infect many
mammals including cats and dogs
» Herpes simplex
» Herpes zoster (shingles)
» TB
• AIDS (continued)
– Get opportunistic cancers
» Non-Hodgkins lymphoma
» Kaposi’s sarcoma
• HIV also has predilection to attack G-I cells & CNS cells
– Get malabsorption, colitis, and proctitis
– Dementia
• Diagnosis
– ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
– Western blot test
• Treatment
– AZT = reverse transcriptase inhibitors
– Protease inhibitors
– Fusion inhibitors
• Chlamydia
– Most frequent bacterial STD
– Known as the “silent STD”
– Transmitted via oral, anal, or genital intercourse
» Oral route can lead to conjunctivitis
– If symptomatic, get urethritis
– Incubation = 1-3 weeks
• Gonorrhea
–
–
–
–
Bacterial
Incubation = 1-3 weeks (usually less than 1 week)
Very similar in signs & symptoms to chlamydia
Antibiotic resistance
• Syphilis
–
–
–
–
–
–
Bacterial
Can get primary, secondary, and tertiary forms
New cases at an all time low
Primary = hard, painless chancre in 2-3 weeks ------------ see pictures
Secondary syphilis may appear 1-3 months later
Then latency for years & then possible tertiary syphilis
• Chancroid
– Soft chancre (painful) with
bubo(necrotizing ulceration &
lymphadenopathy) in 1 week
• See pictures
– Bacterial
– Frequent in developing tropical
countries
– Increasing in urban USA
• Genital Herpes
– Type I & type II
– Short incubation of 2-7 days
– See pictures
• Hepatitis B & C
– Transmitted in body fluids
• Genital warts
– Very contagious
– First exposure incidence:
– 40% ---to--- 90%
– Viral; HPV
– 120 different serotypes
– A few cause dysplasia &
neoplasia
– Condylomata accuminatum
– Benign growths
– See picture
– Prolonged incubation of 1-6
months
– Most frequent STD
– Estimated that 60% of
sexually active young
women in USA have it
– New vaccine available
Differences in clinical appearance among genital ulcers