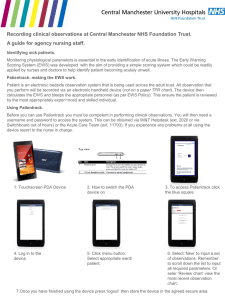
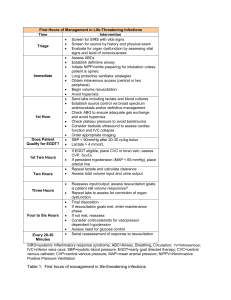
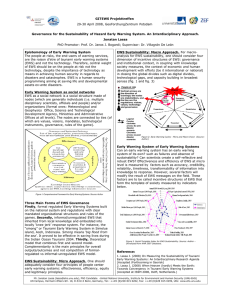
EWS Powerpoint presentation
advertisement

James Griffiths Consultant EM Barnsley CEM FOAMed Network @YorksHumberFoam Objectives Evolution of Early Warning Scores Rapid Emergency Medicine Score (REMS) National Early Warning Score (NEWS) EWS in the ED Future work? Conclusion Background First EWS Developed in 1997 by Morgan et al Based on five physiological parameters: SBP Pulse Resp rate Temp AVPU Morgan et al. Clin Intensive Care 1997;8:100 M(odified)EWS Surgical patients Deviation from normal BP Urine output Potential benefit from critical care Stenhouse et al. Br J Anaesth 2000;84:663 Patients at risk Score SBP 3 2 0 1 2 3 71-80 81-100 101-199 HR <40 41-50 51-100 101-110 111-129 ≥130 RR <9 9-14 15-20 21-29 ≥30 Temp <35 35-38.4 AVPU <70 1 Alert Subbe et al. Q J Med 2001;94:521-526 ≥200 ≥38.5 Voice Pain Unrespo nsive REMS 0 1 2 3 4 Age <45 45-54 55-64 HR 70-109 55-69 110-139 40-54 140-179 <40 >179 RR 12-24 6-9 35-49 >49 SBP 90-129 70-89 130-149 150-179 <69 >179 GCS >13 11-13 8-10 5-7 <5 O2 >89 86-89 75-85 <75 10-11 25-34 Olsson & Lind. Acad Emerg Med 2003;10:1040-1048 5 6 65-74 >74 NICE The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) have recommended that physiological track and trigger systems should be used to monitor all adult patients in acute hospital settings NICE Clinical Guideline 50 (2007) DoH Clinical Indicators The new Department of Health Quality Indicators that will replace the four-hour standard record a time to full initial assessment of patients attending EDs which includes a pain score and early warning score in patients arriving by 999 ambulance Department of Health 2011 NEWS Royal College of Physicians working party July 2012 Based on a large number of vital signs from an electronic patient database Prytherch et al. Resuscitation 2010. 81:932-937 Smith et al. Resuscitation 2013. 84:465-470 The Future? Finally... Smith et al. Resuscitation 2013. 84:465-470