(atheroma) Coronary heart disease
advertisement

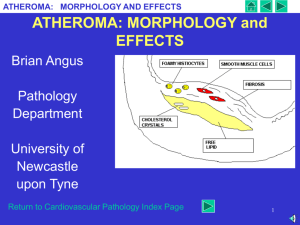
5.3 Heart disease Learning outcomes Students should understand the following: Atheroma as the presence of fatty material within the walls of arteries. The link between atheroma and the increased risk of aneurysm and thrombosis. Myocardial infarction and its cause in terms of an interruption to the blood flow to heart muscle. Diseases of the heart and circulation are called cardiovascular disease: Atheroscelrosis – build up of fatty deposits on the inner linings of arteries (atheroma) . Coronary heart disease (CHD)- an atheroma in coronary arteries. Aneurysm – a weakened and ballooning area of an artery. Cerebrovascular accident – blockage of a blood vessel in the brain (stroke). Condition Atherosclerosis (atheroma) Coronary heart disease (CHD) Aneurysm Cerebrovascular accident (Stroke) Description Diagram Atherosclerosis Build up of fatty deposits on the inner linings of arteries (atheroma). Fat is transported in the body as lipoproteins: Low density lipoproteins (LDL) from saturated fats more likely to cause atheroma. High density lipoproteins (HDL) from polyunsaturated fats are less likely to be deposited. Atheroma Most commonly form in larger arteries and are made up of deposits of cholesterol, fibres and dead muscle cells. They bulge into the lumen and cause a narrowing and therefore restriction of blood flow. Atheroma increase the chance of a blood clot forming. Thrombus – stationary blood clot Embolism – mobile blood clot Coronary heart disease (CHD) An atheroma in coronary arteries. Narrowing of the coronary arteries may restrict blood flow and starve an area of cardiac muscle of oxygen – angina Blood clots may form in these narrowed blood vessels causing a blockage and depriving cardiac muscle of it’s blood supply. These areas of heart muscle do not function properly and my die. If the cardiac muscle does not contract this can lead to a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Coronary Heart disease 1.swf Aneurysm A weakened and ballooning area of an artery, due to damage or loss of elastic tissue. A burst aneurysm may cause serious internal bleeding. Aneurysm occur most frequently in the cerebral arteries and brain. Aneurysms can only be treated by surgery. Cerebrovascular accident (stroke) Blockage of a blood vessel in the brain or a burst aneurysm in a cerebral artery. The effects are: confined to one side of the brain; range from slight to severe paralysis; speech is often effected; damage may be permanent or may make gradual recovery Strokes are more common in older people. Stroke.swf Learning outcomes Students should understand the following: Atheroma as the presence of fatty material within the walls of arteries. The link between atheroma and the increased risk of aneurysm and thrombosis. Myocardial infarction and its cause in terms of an interruption to the blood flow to heart muscle.