POTS
advertisement

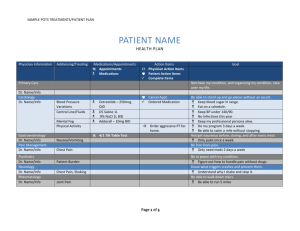
POTS Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome Lorna Busmer Nurse Practitioner Rotherham Definition • Increase heart rate of > 30 bpm within 10 min of standing • The standing heart rate is often > 120 bpm • Without hypotension • Low resting heart rate • Aged 12–19 years- increment of > 40 bpm (Freeman et al 2011) POTS • Incidence in the UK unknown • Increased frequency in females • Often misdiagnosis • Many given anxiety diagnosis • 25-50% of people with CFS may have POTS Hoad et al 2008 Case Study 1 • Female health professional in 30s • Symptoms – Fatigue – exercise intolerance – relieved by sitting down • PMH – tachycardia • ECG – Normal sinus rhythm • 24 hour tape – Sinus Rhythm with heart rates up to 150 bpm Case Study 1 Cont. • 1st Diagnosis - Anxiety and depression • 2nd diagnosis – Inappropriate sinus tachycardia (IST) • Further investigations – tilt test - drop in BP on tilt after 40 minutes – autonomic function test • Supine HR 90 bpm • Standing HR 126 • 3rd diagnosis – POTS, IST, Vasovagal syncope (VVS) • Meds – Diltiazem, Sertraline 160 140 REST HEART RATE 120 AFTER 5 mins of standing 100 After getting dressed 80 60 40 20 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Day 7 8 9 10 Case Study 2 • Female health care professional - 50s • Symptoms over 20 years – – – – – – – – – Dizziness (20 years hx) Fatigue Nausea Diarrhoea Headaches Palpitations sweating Tremulous collapse • PMH – Recurrent musculoskeletal problems, migraine Case Study 2 Cont. • 1st diagnosis – Inner ear/Balance problem • 2nd diagnosis - Benign positional vertigo, irritable bowel syndrome and anxiety • 3rd diagnosis – JHS, POTS, VVS • Treatment - Fludrocortisone, midodrine, beta blockers, SSRIs Symptoms CARDIOVASCULAR Lightheaded Dizziness Rapid Heart rate Palpitations Near fainting or fainting Short of breath Chest Pain GASTROINTESTINAL Nausea Diarrhoea Abdominal cramps Constipation Bloating NEUROLOGICAL Headaches Tremulous MUSCULAR SKELETAL Restless Leg syndrome Myofascial pain Neuropathic pain GENERAL Fatigue Tiredness Weakness Exercise intolerance OTHER Excess Sweating Loss of sweating Bladder problems Sleep disturbance Onset • Sudden or gradual • After – Virus/febrile illness – Trauma – Pregnancy – Surgery Severity • Mild, moderate, severe • 25% of patients may be unable to work and be wheel chair dependant • Disability can be equivalent to that found in heart failure (Benrud-Larson et al 2002) Autonomic Nervous System Disorders of the ANS Reflex Syncope POTS Autonomic Failure POTS Primary JHS Partial Dysautonomia Developmental Secondary Hyperadrenergic Hypovolemia Other Deconditioning Overlapping Syndromes IST POTS CSF Recognition in primary care • Good history • Stand test • Acrocyanosis • Secondary causes • Refer - cardiologist Investigations Investigations • Stand test / Tilt Table Test • Bloods – FBC, Ferritin, UE, LFT, TFT • Bloods - Lying and standing Noradrenaline • Urinary Catecolamines (Pheochromocytoma) • Urinary sodium • ECG/ 24 hour monitoring • Echo Treatment Treatment – Non pharmacological • Fluids • Salt (except in H.Pots) • Compression stockings • Counter manoeuvres • Psychological support and....... Exercise Pharmacological • Trial and error • Tiny doses • Lack of research • Off licence Pharmacological • Fludrocortisone • Midodrine • Ivabradine • Beta Blockers- Propranolol, Bisoprolol • SSRI/SNRI – Sertraline, Duloxetine • Clonidine • Octreotide Psychological Support Working together with individuals, families and medical professionals to offer information and support on syncope, reflex anoxic seizures and POTS www.stars.org.uk www.stars-international.org info@stars.org.uk Helpline: 01789 450 564