Presentation (PPTX 2.9MB)
advertisement

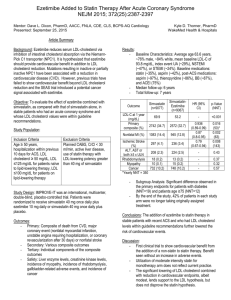
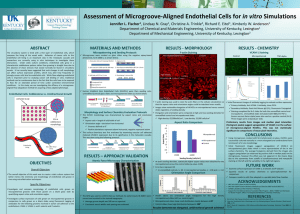
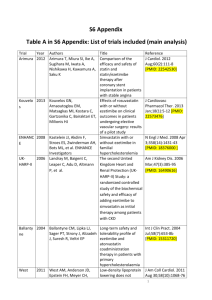
Master Class Lipid Innovations Prague, Czech Republic May 27-28, 2011 Presentation topic Vascular function as an early sign of trouble: How can the inhibition of cholesterol absorption reduce the atherogenic load of intestinal lipoproteins? Slide lecture prepared and held by: Prof Frank Visseren, MD Academic Medical Centre Utrecht The Netherlands Overview of Cholesterol Transport Cholesterol transporter Altman SW et al. Science 2004;303:1201-1204 Postprandial lipidemia Postprandial lipids (triglyceride-rich lipoprotein or lipoprotein-remnant particles) are associated with: – Endothelial dysfunction – Elevated small LDL particles – Elevated Factor VII – Elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) – Elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) Copenhagen City Heart Study Nordestgaard B, et al. JAMA 2007;298:299-308. Triglyceride levels and levels of remnant lipoprotein cholesterol since last meal Nordestgaard B, et al. JAMA 2007;298:299-308. Levels of Remnant Lipoprotein Cholesterol as a function of levels of nonfasting Triglycerides Nordestgaard B, et al. JAMA 2007;298:299-308. Non-fasting triglycerides and risk for MI, IHD and death in Women Nordestgaard B, et al. JAMA 2007;298:299-308. Non-fasting triglycerides and risk for MI, IHD and death in Men Nordestgaard B, et al. JAMA 2007;298:299-308. Women’s Health Study (WHS) Bansal S, et al. JAMA 2007;298:309-316. Association of triglyceride levels with incident CVD according to fasting status Bansal S, et al. JAMA 2007;298:309-316. Womens Health Study (WHS) Bansal S, et al. JAMA 2007;298:309-316. Tirglycerides (mmol/l) Triglyceride concentrations after an oral fatload in obese patients with metabolic syndrome 3,5 2,5 1,5 0,5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 hours post fatload Olijhoek et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2008;52:145-150 Drop in HDL-c after an oral fatload N=19 Hajer et al. Clin Endocrinol 2008;69:870-877 Increase in Cholesterol Ester Transfer (CET) after an oral fatload N=19 Hajer et al. Clin Endocrinol 2008;69:870-877 Oral Triglyceride Tolerance Test!?? Standardized Oral Triglyceride Tolerance Test (OTTT): • • • 1g dairy cream/kg body weight 50g fat plus 50 g carbohydrate Mixed meal But: No evidence for CVD risk stratification No evidence for clinical benefit of treatment of postprandial lipids Effect of statin versus fibrate on postprandial endothelial dysfunction: role of remnant-like particles Randomized, placebo controlled trial Cerivastatin 0.4mg vs. gemfibrozil 900mg 15 healthy volunteers Wilmink H et al. Cardiovasc Res 2001;50:577-582 Ezetimibe improves postprandial hyperlipemia and its induced endothelial dysfunction N=19 Yunoki K et al. Atherosclerosis 2011;epub Ezetimibe improves postprandial hyperlipemia and its induced endothelial dysfunction N=19 Yunoki K et al. Atherosclerosis 2011;epub Low-dose statin and ezetimibe compared to high-dose simvastatin on postprandial lipids in patients with the metabolic syndrome 6 weeks 4 weeks Simva 80mg washout 6 weeks Simva/eze 10/10 FMD Simva/eze 10/10 FMD washout Oral fatload Simva 80mg Oral fatload Olijhoek et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2008;52:145-150 Low-dose statin and ezetimibe compared to high-dose simvastatin on postprandial lipids in patients with the metabolic syndrome Oral fatloading test Tirglycerides (mmol/l) 3.5 2.5 No treatment Simva 80mg Simva/Eze 10/10mg 1.5 0.5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 hours post fatload Olijhoek et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2008;52:145-150 Low-dose statin and ezetimibe compared to highdose simvastatin on postprandial lipids in patients with the metabolic syndrome p<0.001 FMD after ischemia (%) 10 8 6 pre fatload 4 hrs post fatload 4 2 0 Simva 80mg Simva/eze 10/10mg Olijhoek et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2008;52:145-150 Low-dose statin and ezetimibe compared to high-dose simvastatin on postprandial lipids in patients with the metabolic syndrome 6 5 5000 IL-6 (pg/ml) Adiponectin (mg/l) 5500 4500 4000 4 No treatment N 3 Simva 80mg S Simva/Eze 10/10mg S 2 3500 1 3000 6 0 0 IL-6 (pg/ml) 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 hours post fatload hours post fatload No treatment Simva 80mg Simva/Eze 10/10mg Olijhoek et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2008;52:145-150 Conclusions HDL-c drops after an oral fatload Statins, fibrates, statin/ezetimibe lower post-fatload hyperlipidemia (triglycerides, LDL-c, remnant particles) Statin monotherapy and Ezetimibe monotherapy preserve post-fatload endothelial function Combination of low-dose statine with ezetimibe preserve post-fatload endothelial function But: small studies The PostprAndial eNdothelial function After Combination of Ezetimibe and simvAstatin (PANACEA) Study The PostprAndial eNdothelial function After Combination of Ezetimibe and simvAstatin (PANACEA) Study Primary objective: To evaluate the effect of simvastatin/ezetimibe or high-dose simvastatin alone on fasting and postprandial endothelial function as measured with FMD and EndoPat in obese patients with metabolic syndrome. The PostprAndial eNdothelial function After Combination of Ezetimibe and simvAstatin (PANACEA) Study Study design: Randomized, double blind 2 period cross-over 100 patients 5 centers in The Netherlands and Spain 6 weeks simvastatin 80mg 6 weeks simvastatin/ezetimibe 10/10mg PANACEA trial design Parallel study A B Cross-over study A A B B Conclusions Non-fasting triglycerde plasma levels are associated with increased CVD risk In the postprandial phase HDL-c plasma levels drop Postprandial hyperlipidemia can be reduced with lipidlowering therapy Postprandial endothelial dysfunction can be diminished by lipid-lowering therapy Although an appealing pathophysiological concept, the clinical usefulness of postprandial hyperlipidemia remains to be determined