ENT - West Lakes GP Training
advertisement
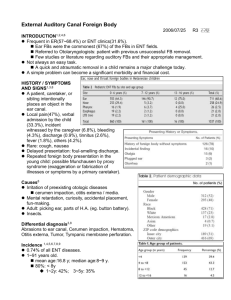
ENT UPDATE FOR PRIMARY CARE WEST CUMBERLAND HOSPITAL 05/06/2013 Mohamed Ouda ST1 WHY ENT? • very common • comprising 20% of presenting complaints to a primary care provider • limited training in undergraduate and postgraduate medical education for primary care • What are the most common conditions ? Sore throat tonsillitis ear ache Otitis media Dysphagia lump in the throat dizziness tinnitus deafness neck lump hoarseness anosmia ear discharge Facial palsy Facial swelling thyroid disease F.B EAR F.B nose F.B throat ,Nose bleeding ,wax nasal blockage Snoring Stridor Otitis externa nasal polyps sinusitis Rhinitis Anatomy External Ear • • • • • Cellulitis Erysiplas Perichondritis,chondritis Eczema ,Psoriais Trauma (heamatoma) • • • • • Exostosis Malignancy (BCC , SCC,Melanoma) Bat ear Preauricular sinus Otitis externa Bat ears 1 Preauricular sinus ??????????? Otitis externa • Ask about :swimming, D.M, Eczema, Psoriasis. • Causative organism? • Treatment: Aural toilet Ear drops Ear wick Oral antibiotics ?IV antibiotics *Analgesia ???? Necrotizing otitis externa =Malignant O. E • NON Neoplastic • Osteomyelitis (canalskull base) • DM • Severe pain, granulations. • Diagnosis :history +C/P+ CT SCAN • Treatment Admit DM control Systemic Abx(Oral or IV) FOR 6-12 WEEKS Aural toilet Surgery Topical anti psudomonal Death SOFRADEX GENTISONE HC ` Otitis media • Inflammation of the middle ear caused by infective organism. • <3 weeKs =Acute Otitis Media • > or = 3 episodes in 6 months =Recurrent AOM. • INFECTION> 3 MONTHS =CSOM. Self limiting . Oral antibiotics(controversial) Acute OM • • • • COMMON Pain relief with perforation 80% resolve in 4/7 days without treatment Antibiotics (Amoxycillin):no improvement in 4 days, B/L OM,OM with otorrhoea, systemically unwell. • Delayed approach • ENT Referral : -Recurrent( >4 episodes in 6 months), -poerforation has not healed after 1 month. Acute mastoiditis Urgent ENT Referral Otitis media with effusion (OME) Serous OM=Secretory OM=Glue ear • • • • NO infection Fluid in the middle ear E T dysfunction Most common cause of hearing loss in children. • Down syndrome, cleft palate. • Adults :post URTI ,Resolve in 6/52 if not Refer?PNS tumour (NICE GUIDELINES) 2008 Children who will benefit from surgical intervention Children with persistent bilateral OME documented over a period of 3 months with a hearing level in the better ear of 25– 30 dBHL or worse averaged at 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 kHz . Adjuvant adenoidectomy is not recommended in the absence of persistent and/or frequent upper respiratory tract symptoms Active monitoring (watchful waiting)* • Essential • 50% will recover with no treatment in the first three months. The following treatments are not recommended for the management of OME: − antibiotics − topical or systemic antihistamines − topical or systemic decongestants − topical or systemic steroids Browning GG. Watchful waiting in childhood otitis media with effusion.Editorial.Clin Otolaryngology 2001;26:417-424 Otitis media with effusion (OME) Serous OM=Secretory OM=Glue ear Investigations – PTA ...Conductive deafness – Tympanometry....Type B curve(Flat) Treatment Watchful waiting (Valsalva maneovre) Hearing aid Ventilation tubes CSOM without cholestatoma • Chronic otorroea (mucopurulent) + perforation (can be dry in inactive disease). • Pseudomonas aeruginosa,staph aureus • Otalgia is uncommon . • Peforation (safe versus unsafe) • Treatment: aural toilet, topical antibiotics ,surgical repair CSOM with cholestatoma • Skin in the wrong place. • • • • • • • Sudden SNHL IF UNILATERAL OR ONLY GOOD EAR...Refer SAME day referral if within 24 hours Acoustic neuroma=Vestibular schwanoma Benign ,slow growing tumour. 80% CPA tumour B/L in NF2 MRI ACOUSTIC NEUROMA • Acoustic neuromas (more correctly called vestibular schwannomas) account for approximately five percent of intracranial tumours and 90 percent of cerebellopontine angle Features can be predicted by the affected cranial nerves cranial nerve VIII: hearing loss, vertigo, tinnitus • cranial nerve V: absent corneal reflex • cranial nerve VII: facial palsy • Bilateral acoustic neuromas are seen in neurofibromatosis type 2 MRI of the cerebellopontine angle is the investigation of choice ????????????????????