Kristin_Final
advertisement

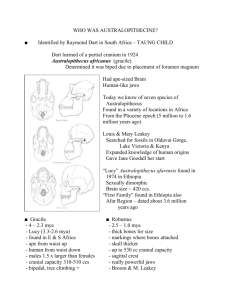
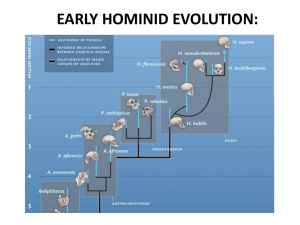
Climate and Human Evolution; the last 4.6 billion years By Kristin Hepper Time gone by… Earth is 4.5 billion years old Archaean Era 3800 to 2500 million years ago Proterozoic Era 2500 to 544 million years ago Stromatolites Ice Ages Huronian Ice Age- 2.3 billion years ago Gnejso Ice Age- 950 million years ago Sturtian Ice Age- 750 million years ago Varangian Ice Age- 600 million years ago Muir Glacier at Glacier Bay, 1971 Phanerozoic Eon Archaean Era, Proterozoic Era, Phanerozoic Eon 544 million years ago to the present Divided into three Eras Cenozoic 65 million years ago to the present Mesozoic 248 to 65 million years ago Paleozoic 544 to 248 million years ago Pangaea- one supercontinent 300-200 million years ago Laurasia and Gondwanaland Triassic200 mya Say Goodbye to Pangaea… Jurassic Cretaceous But, they are still moving…. The question is…where are they going? Just one hypothesis… Now that we are at the present, let’s jump back 5 million years… To the Pliocene 5-1.8 million years ago What is going on? Antarctic ice sheet melts back significantly Climate is oscillating Tethy’s Seaway What about our ancestors? Earliest known hominoid- Proconsul africanus 16 mya East Africa Divergence from the great ape lineage 5 mya Timing estimated from molecular clock Ardipithecus ramidus (Pliocene) From Aramis in Ethiopia 5.5-4.4 mya Primitive dentition Oldest taphonomically determined example of australopithecines Maybe the missing link??? Ardipithecus ramidus: upper right molar Australopithecus anamensis (Pliocene) Lake Turkana, Kenya 4 mya More adaptations to bipedality Australopithecus afarensis (Pliocene) Known to the world as “Lucy” Brain size415 cc’s Hadar, Ethiopia Varied from 1-1.7 m in height and 25-50 kg in weight Ate fruits and nuts and some meat while living in a wooded environment Laetoli Footprints- Tanzania Preserved in volcanic tuff erupted out of Mt. Sadiman to the east, which is dated back to 3.7 mya. 75 ft long 69 total prints Australopithecus africanus (Pliocene) The Taung Baby Material comes from all over Africa Sterkfontein, Makapansgat, and Taung 3-2.4 mya Has more derived characteristics Lived in a more open environment and maybe used underground resources such as roots Brain size- 450 cc’s Pleistocene- 2 mya-10,000 ya Biotas were similar to modern ones Characterized by distinctive large animals Global oscillations of ice sheets Global oscillations of productivity Humans…here we come!!! Glacial maximum Homo habilis (Pleistocene) First appearance of Homo 2.4 mya Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania Brain size- 590-710 cc’s Specimens show high variability of traits Stone tools Homo ergaster (Pleistocene) Lake Turkana, Kenya; Olduvai Gorge, northern Tanzania 1.8 mya Big brain- 900 cc’s Very human-like body Associated with tools Homo ergaster 600,000 to 400,000 years ago Homo heidelbergensis Around 600,000 ya hominids start Showing some differences from H. ergaster Had larger brains 12001250 cc’s Out of Africa Remember… Out of Africa- what was happening in Africa in the Plio-Pleistocene Habitats were unstable Grasslands were expanding and contracting Climate is oscillating Homo neanderthalensis Neander Valley, Germany 200,000 to 35,000 ya in Europe and W. Asia Tools Burial Had thick brow ridges Brain Size1300 cc’s Human Neanderthal Homo sapiens Anatomically modern Homo Africa: 100,000 to 90,000 ya 50-45,000 ya evidence of culture Reach Australia between 50,000 and 35,000 ya Homo sapiens 35,000 ya adapted to cold Siberia and Alaska 14,000 ya crossed the land bridge into the Americas Islands of Pacific were settled around 3,000 ya New Zealand was the last 1200 A.D. Features of Homo sapiens Big brains 1500 cc’s High foreheads Face is flat and pushed in Small brow ridge Long limbs