2.1 Energy Flow in Ecosystems
advertisement

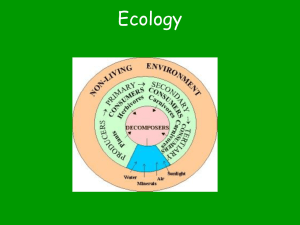
2.1 Energy Flow in Ecosystems By the end of section 2.1 you should be able to understand the following: In an ecosystem, energy flows from producers to primary consumers to secondary and tertiary consumers. Food chains and food webs show the energy flow and feeding relationships. Each step in a food chain is called a trophic level. Food pyramids model how energy is lost at each trophic level in an ecosystem. 2.1 Energy Flow in Ecosystems • Biomass is the total mass of all living things in a given area. (measured in g/m2 or kg/m2) • Organisms interact with the ecosystem by: 1.Obtaining food from the ecosystem 2.Contributing energy to the ecosystem Energy Flow in Ecosystems Plants are called producers because they make carbohydrates during photosynthesis. CO2 + H2O + sunlight C6H12O6 + O2 Consumers get their energy by feeding on producers or other consumers. - Decomposers break-down wastes & dead organisms, through the process of biodegradation. Energy Flow & Energy Loss in Ecosystems Methods to represent energy moving through ecosystems. • Food chains: show the flow of energy in an ecosystem. • Food webs: represent interconnected food chains. They model the feeding relationships in an ecosystem • Food pyramids: show the changes in available energy from one trophic level to another in a food chain. They’re also called ecological pyramids • Each step is a trophic level • • • • Producers = 1st trophic level Primary consumers = 2nd trophic level Secondary consumers = 3rd trophic level Tertiary consumers = 4th trophic level Food Chains Terrestrial & aquatic food chains • Consumers in a food chain can be classified as: 1.Detrivores (decomposers) - obtain energy & nutrients from dead organisms & waste matter. they have their own, separate food chains & they feed on every trophic level. Eg. small insects, earthworms, bacteria This dung & fungi 2.Herbivores - primary consumers eat plants (producers) only Ex. Horse eating hay beetle is a detrivore. 3. Carnivores - secondary or tertiary consumers Secondary consumers eat non-producers (herbivores) • Eg. Frog eating a grasshopper Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers • also called top predators, top carnivores or top consumers • Eg. Lions eating humans 4. Omnivores - consumers that eat both plants & animals • Eg. include humans and bears • Food Webs • Most organisms are part of many food chains. • Arrows in a food web represent the flow of energy and nutrients. • Following the arrows leads to the top carnivore(s). This food web represents a terrestrial ecosystem that could be found in British Columbia. Food Pyramids Energy enters at the first tropic level (producers), where there is a large amount of biomass & therefore a lot of energy • It takes large quantities of organisms in one tropic level to meet the energy needs of the next trophic level. • 80% - 90% of energy taken in by consumers is used in chemical reactions in the body, or is lost as heat energy. • The amount of life an ecosystem can sustain is based on the bottom level of the ecological pyramid, where producers capture energy from the sun. • Lower trophic levels have much larger populations than upper levels. • This shows the importance of maintaining large, biodiverse populations at the lowest levels of the food pyramid. Take the Section 2.1 Quiz