Chapter 4 – Control Structures Part 1
advertisement

ASP .Net, Web Forms and Web Controls
Outline
Introduction
Simple HTTP Transaction
System Architecture
Creating and Running a Simple Web Form Example
Web Controls
Text and Graphics Controls
AdRotator Control
Validation Controls
1
Introduction
• Web-Based Application Development
• Creates Web content for Web browser clients, includes
• HyperText Markup Language (HTML)
• Client-side scripting
• Images and binary data
• Uses Web Forms, Web Controls, and C# programming
• Web Forms (Web Form pages)
• Represent what the Web page sent to client will look like
• File extension .aspx
• ASPX (Web Form files) contain written code, event handlers, utility
methods and other supporting code
• Every ASPX file has a corresponding class written in .NET language
(C#) called the code-behind file
2
Simple HTTP Transaction
• HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
• Defines methods and headers which allows clients and servers
exchange information in uniform way
• Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
• IP address indicating the location of a resource
• All HTML documents have a corresponding URL
• Domain Name Server (DNS)
• A computer that maintains a database of hostnames and their
corresponding IP addresses
• Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS)
• Web server that programmers use when developing ASP.NET Web
applications in Visual Studio
3
A Simple HTTP Transaction
Client interacting with Web server.
Step 1: The GET request, GET /books/downloads.htm HTTP/1.1.
4
A Simple HTTP Transaction
Client interacting with Web server.
Step 2: The HTTP response, HTTP/1.1 200 OK or HTTP/1.1 404 Not found
5
System Architecture
• Most Web-based applications are multi-tier applications
• Tiers are logical groupings of functionality
• Information Tier (data tier or bottom tier)
• Maintains data pertaining to the applications
• Usually stores data in a relational database management systems
(RDBMS)
• Middle Tier
• Implements the business logic, controller logic and presentation logic
• Acts as an intermediary between data in the information tier and the
application's clients
• Client Tier – application’s user interface (Web browser)
6
System Architecture
Three-tier architecture.
7
Creating and Running a Simple
Web-Form Example
• Program consists of two related files
• ASPX file
• C# code-behind file
• Example
• Show the output
• Step-by-step process to create the program
• Present the code (much of which is generated by Visual Studio)
8
WebTime ouput
WebTime.cs
Program Output
9
Creating and Running a Simple
Web Form Example
Adding Web Form for project WebTime (Right click on project in Solution Explorer)
10
Creating and Running a Simple
Web Form Example
Click on Add New Item and Add a Web Form for project WebTime .
11
Creating and Running a Simple
Web Form Example
ASPX file
code-behind
file
12
Creating and Running a Simple
Web Form Example
codebehind file
ASPX file
13
Solution Explorer window for project WebTime .
Creating and
Running a
Simple Web
Form Example
Toolbox in
Visual Web
Developer.
14
Creating and Running a Simple
Web Form Example
Design
mode
button
15
Source mode of Web Forms designer.
Creating and Running a Simple
Web Form Example
Cursor
Cursor’s
current
location
16
Design mode of Web Forms designer.
Creating and Running a Simple Web
Form Example
17
Split mode of Web Forms designer.
Creating and Running a Simple
Web Form Example
18
Code-behind file for WebTime.aspx.cs generated by Visual Web Developer.
Designing the Page
• Designing a Web Form as simple as a Windows Form
• Use Toolbox to add controls to page in Design mode
• Unlike working with Windows Form, type text directly on a
Web Form at the cursor location or insert XHTML elements
using menu commands
• Control and other elements are placed sequentially on a Web
Form
• position is relative to Web Forms upper left corner
• Alternate type layout (absolute positioning) is discouraged
19
Designing the Page
label
Web Form
WebForm.aspx after adding Label and setting its properties.
20
Adding Page Logic
• Open WebTime.aspx.cs
• Add to Page_Load event handler
//display the server's current time in timeLabel
timeLabel.Text =
DateTime.Now.ToString("hh:mm:ss");
21
Running the Program
• Can view the Web Form several ways
• Select Debug > Start Without Debugging
• runs the app by opening it in a browser window
• If created on a local file system URL
http://localhost:PortNumber/WebTime/WebTime.aspx
• Debug>Start Debugging
• view web app in a web browser with debugging enabled
• Do you want IDE to modify the web.config file to enable debugging?
Click OK
• To view ASPX file
• right click either the Web Forms Designer or the ASPX file name and
select View in Browser to load the page
• Finally, can open web browser and type the web page’s URL in the
Address field
22
Directive to specify
information needed to process
file
WebTime.aspx
This attribute
determines
how event handlers are
linked to a control’s events
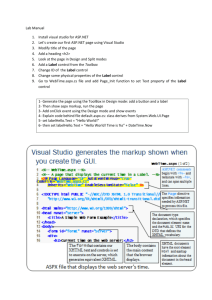
<%-- Fig. 22.4: WebTime.aspx --%>
<%-- A page that displays the current time in a Label. --%>
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="WebTime.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebTime"
EnableSessionState="False" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
AutoEventWireUp set to true
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
so ASP.NET treats method of
<head runat="server">
name Page_eventName as an
<title>Simple Web Form Example</title>
event handler for a specified
<style type="text/css">
Document type event
#form1
declaration, specifies
{
document element name
height: 255px;
and URI
Specify class in the codewidth: 655px;
behind file from which this
}
ASP .NET document
.style1
{
font-size: large;
}
</style>
</head>
23
Title for web page
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<h2>
Current time on the Web Server:</h2>
<p>
&nbsp;</p>
Body tag, beginning of Web
page’s viewable content
Attribute indicates the
server processes the form
and generates HTML for
client
</div>
<asp:Label ID="timeLabel" runat="server"
BackColor="Black" Font-Size="XX-Large"
ForeColor="Lime"></asp:Label>
</form>
</body>
The asp:Label control maps to
</html>
HTML span element – markup for
the Label Web control
24
// WebTime.aspx.cs
// The code-behind file for a page that displays the Web server's time.
using System;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
Contains classes that manage
client requests and server
responses
Contain classes for creation
of Web-based applications
and controls
// definitions for graphical controls used in Web Forms
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
public partial class WebTime : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//display the server's current time in timeLabel
timeLabel.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString("hh:mm:ss");
}
}
Event raised when Web page
loads
25
Set timeLabel’s Text
property to Web server’s time
Creating and Running a Simple Web-Form Example
• How are ASPX file and code-behind file used to create the Web
page that is sent to the client?
• WebTimeTest.aspx.cs is the base class specified in the ASPX file
• WebTimeTest
• inherits from Page, which defines general functionality of a Web page
• Also defines some of its own functionality (displaying time)
• WebTime.ASPX defines the GUI
• When client requests an ASPX file…
• Class is created behind the scenes that contains both the visual
aspect of our page (.aspx) and the logic of our page (.aspx.cs)
• New class inherits from Page
• First time Web page is requested, class is compiled, and instance
created (put in project’s bin directory)
• This instance represents the page – creates the HTML sent to the
client
26
Creating and Running a Simple
Web-Form Example
• Once the web page has been created
• Multiple clients can use that instance (w/o recompilation)
• Project is recompiled only when programmer modifies the
application; this is detected by the runtime environment
• How does it execute?
• When the Web server creates an instance of our page to serve a
client request
•
•
•
•
The Init event occurs first, invoking method OnInit
This method calls InitializeComponent
Then Load event is generated, which calls Page_Load
Page_Load executes processing
• time will be updated with every page request
• After this event handler finishes, the page processes any events raised by
page’s controls (such as button clicks).
• When ready for garbage collection, an UnLoad event is generated and
method Page_Unload is called
27
1 <!-- WebTime.html
-->
2 <!-- The HTML generated when WebTime is loaded. -->
3 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Look at HTML
response when
browser requests
WebTime.aspx
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head><title>
Simple Web Form Example
</title>
<style type="text/css">
#form1
Using Cascading Style Sheets
{
height: 255px;
width: 655px;
}
.style1
{
font-size: large;
Defines the body of the document
}
</style>
</head>
Hidden inputs from the user
<body>
<form name="form1" method="post" action="WebTime.aspx" id="form1">
<div>
<input type="hidden" name="__VIEWSTATE" id="__VIEWSTATE"
value="/wEPDwUJODExMDE5NzY5ZGTHi7f/xNriT14LWNspMfB7YfGTVA==" />
24 </div>
25 <div class="style1">
26
27
Current time on the web server:<br />
28
<span id="timeLabel" style="color:LimeGreen;background
29
color:Black;font-size:XX-Large;">03:10:03</span>
30
31 </div>
32 </form>
span
33 </body>
34 </html>
28
element to represent the text in the label
Instructions to get IIS and
ASP.NET running
•
First
•
•
Install IIS (need Windows 7 CD)
Start IIS by executing inetmgr.exe (?)
•
•
•
Expand node representing your computer
Right click Default Web Site and select Start
Run
C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.nnnn\aspnet_regiis /i
29
Summary Instructions to
Create a Web App project
1.
File>New Web Site
Type in project name in the Location field
2.
Examine the newly created project
•
•
3.
4.
View aspx file
Click on display all files icon and expand the node for ASPX page –
View code-behind file
Rename the ASPX file and the Class in the code-behind file
Design the page
•
•
•
Change page title
EnableSessionState property set to false
Add labels, rename, change BackColor, ForeColor and Font-Size
properties
5. Add page logic in code-behind file in Page_Load
30
Instructions to Run the
Program
Three ways
1. Debug>Start Without Debugging
2. Right-click Web Form designer or ASPX file name in Solution
Explorer and select View In Browser
3. Open browser and type in URL
•
http://localhost/ProjectFolder/PageName.aspx
31