Hematologic & Lymphatic System
Chapter 19-20
Hematologic
• BONE MARROW
– Location
• Spongy center of bones
– Function
• RBCs production
• WBC production
• Platelets production
Hematologic
• LIVER
– Function:
• Manufactures
clotting factors
• Filter old & damaged
RBC’s from circulation
Hematologic
• SPLEEN
– Function
• Works with the liver
removes old RBC’s
from circulation
• Stores platelets
Hematologic
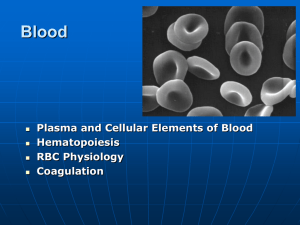
• BLOOD
Blood
• Function
– Transport
• Oxygen
• Nutrients
• Essential
substances
• Waste products
To cells/tissue
Away from cells / tissue
Blood composition
• Plasma
• Red blood cells
– Erythrocytes
• White blood cells
– Leukocytes
• Platelets
– Thrombocytes
Plasma
• Color
– Clear yellow
• Contains
– Protein
• Formed in the
– LIVER
Red Blood Cells
• AKA:
– Erythrocytes
• Function
– Carry O2 to body tissues
• Formed
– Bone marrow
– Erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis
• The process of red
blood cell formation
Tissue hypoxia
h RBC
production
Kidney
3-5
days
Bone marrow
erythropoietin
Hemoglobin
• Function
– Carry oxygen
• Main ingredient
– Iron
Hemolysis
• Hemo =
– Blood
• Lysis
– -breakdown
• Breakdown of RBC
•Death of a
RBC
Hemolysis
• Life span of RBC
– @120 days
• Old / damaged cells
– Liver filters blood
– Iron – saved & reused
– Heme bilirubin bile
sm. intestine
Platelets
• AKA
– Thrombocytes
• Function
– Blood clotting
• Storage
– Spleen
Hemostasis
• Blood clotting process
5 stages of hemostasis
1. Vessel spasm
• Damage to blood
vessel
• Vessel spasm
• Vasoconstriction
• i blood flow
5 stages of hemostasis
2. Formation of the
platelet plug
• Platelets stick to the
wall & one another
5 stages of hemostasis
3. Clot formation
• Fibrin cements
components together
5 stages of hemostasis
4. Clot retraction
• Platelets contract
–
•
(Pulls broken walls
closer together)
Release growth factors
tissue repair
5 stages of hemostasis
5. Clot dissolution
• Fibrinolysis removes the
clot after tissue is
repaired
Hemostasis
•
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2002_general/Esp/folder_structure/tr/m1/s7/trm1s7_3.h
tm
Hematologic & Immune System
• White Blood Cells
White Blood Cell
• AKA:
– Leukocytes
• Leukocytosis
– h WBC count
• Leukopenia
– i WBC count
Leukocytes
• Can migrate out of the
blood vessel other
tissue
Leukocytes: Neutrophils
• Function
– Phagocytic
• Life span
– 10 hours
Leukocytes: Eosinophils
• Allergic reactions
Leukocytes: Basophils
• Stress
Leukocytes: Monocytes
• Monocytes
• Macrophages
• Phagocytic cells
Leukocytes: Lymphocytes
• Specific immune
response
– B lymphocytes
• B-cells
– T lymphocytes
• T-cells
B-cells
• Production of
– Plasma cell
• Antibody factories
– Memory cell
• Future quick response
T-cells
• T-helper cells
– Activate other
components of the
immune system
• T-cytotoxic cells
– Directly destroy the
invader
Immune System
• BONE MARROW
– Function
• WBC production
Immune System
• THYMUS
– Incubator for T-cells
– Not needed after
puberty
Immune System
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
• Lymph Fluid
– Plasma
– WBC
• Lymph nodes
– Housing for T & B-cells
– Filter micro-organism
Immune System
LIVER
• Function
– Filter blood
– Stores phagocytes
Immune System
• SPLEEN
– Function
• Filters blood
• Stores Phagocytes
Natural immunity
• A person’s resistance to
foreign substances d/t
– Gender
– Heredity
– Age
– Health status
Naturally acquired immunity
• Resistance acquired
by developing the
disease
Artificially acquired immunity
• Resistance develops
through
immunization
Physical Exam
• Skin & mucus
membranes
– Color
• Pallor
– Anemia
• Cyanosis
– i Oxygen to tissue
– Hypoxia
• Jaundice
– Yellow
– h bilirubin
• Jaundice
Physical Exam
• Skin & mucus
membranes
– Color
• Erythemia
– Inflammation
• Petechiae
– Small red spots caused
by a minor hemorrhage
– i platelet count
• Petechiae
Physical Exam
• Skin & mucus
membranes
– Color
•
•
•
•
•
•
Pallor
Cyanosis
Jaundice
Erythemia
Petechiae
Bruising
– Ecchymosis
• Ecchymosis
Physical Exam
• Skin & Mucus
Membranes
– Temperature
– Capillary refill
– Edema
• Lymph nodes
• Palpate abd for
tenderness
Physical Exam
• Vital signs
– Temp
• h
– Infection / bacterial
• i
– Infection viral
– Anemia
– Apical pulse
– Pedal pulse
Dx Tests
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
• RBC count
• Hemoglobin
• Hematocrit
Red Blood Cell Count: RBC count
• Men
– 4.6- 6.0 million /mm3
• Women
– 4.0 – 5.0 million / mm3
• Magic number
–5
RBC count
Elevated
Decreased
• COPD
• Hemorrhage
• Anemia
• Kidney disease
Hemoglobin: Hgb
• Men
– 13.5 – 18 g/dL
• Women
– 12-15 g /dL
• Magic Number
– 15
Hemoglobin
Elevated
Decreased
• COPD
• Hemorrhaging
• Kidney failure
• Nutritional deficit
Hematocrit
• Men
– 40 – 54%
• Female
– 36 – 46%
• Magic Number
– 45
Hematocrit
Elevated
Decreased
• COPD
• Dehydration
• Anemia
• Kidney failure
• Nutritional deficiency
Prothrombin time: PT or Protime
Partial thromboplastin time: PTT
• Clotting time
– h
• Risk of hemorrhaging
– i
• Risk of blood clots /
thrombi
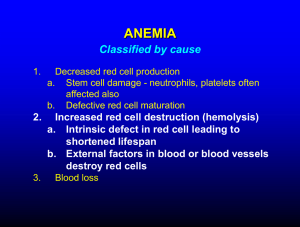
Anemia
• Definition
– i Red blood cells
Anemia: S&S
• i Oxygen-carrying
capacity
• Respiratory
– Tachypnea
– Dyspnea
Anemia: S&S
• i Oxygen-carrying
capacity
• C/V
– Tachycardia
– Palpitations
– Angina
Anemia: S&S
• i Oxygen-carrying
capacity
• Neurological
–
–
–
–
H/A
Fatigue
i Concentration
Dizzy
Anemia: S&S
• i Oxygen-carrying
capacity
• Integumentary
– pallor
Anemia: S&S
• i Oxygen-carrying
capacity
• M/S
– Leg cramps
– Bone pain
– Weakness
Anemia
• Causes
– Blood loss
– Nutritional
– Hemolytic
– Aplastic
Blood Loss Anemia
• Cause
– Hemorrhaging
Nutritional Deficit Anemias
• D/T lack nutrient
– Iron
– Vitamin B12
– Folic Acid
Iron Deficiency Anemia
• Iron is a necessary
component of
– Hemoglobin
• Specific S&S
– Pica
• Craving to eat
unusual
substances
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia
• AKA
– Pernicious Anemia
• Specific S&S
– Paresthesia
Folic Acid Deficiency Anemia
• Required for normal
production and
maturation of RBCs
Hemolytic Anemias
• Premature destruction
of RBC
Sickle Cell
• Genetically transmitted
• Abnormal hemoglobin
Anemia
i O2
Hemolysis
Damaged
RBC
RBC stress
Blocks sm
vessels
RBC Sickles
Sickle cells
clump
S&S of sickle Cell Anemia
• Pain
–hands and feet
• Vision problems
• Jaundice
• Increased risk:
–Infections
–Stroke
Aplastic Anemia
• Bone marrow
does not make
enough RBCs
IDT Care: Anemia
• Dx Tests
– CBC
– Iron levels
IDT Care: Anemia
• Medications
– Iron
– Vitamin B12
– Folic Acid
IDT Care: Anemia
• Dietary
– Iron
• Meat
• Beans
• Green veg
– Folic Acid
• Green Veg
• Beans
– B12
• Meat
• Fish
• Milk
IDT Care: Anemia
• Blood Transfusions
Leukemia
• Malignant disorders
of WBC’s
In Leukemia…
• Normally the ratio of
RBC:WBC
– 3:1
• In leukemia the ratio
changes
– >WBC’s
Pathophysiology
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Stem cell mutates
Proliferation
NON-function WBC’s
Fill bone marrow
Spill into blood
Crowd out RBC’s & Platelets
Anemia, Infection & bleeding
Death
Leukemia: etiology
• Unknown
Leukemia: S&S
• Anemia
• Infection
• Bleeding
Leukemia: S&S
• Anemia
–
–
–
–
Pallor
Fatigue
Tachycardia
Dyspnea
Leukemia: S&S
• Infections
–
–
–
–
–
Fever
Skin infections
Respiratory infections
UTI
Septicemia
Leukemia: S&S
• Bleeding
– Bruising
• Ecchymosis
Leukemia: S&S
• Bleeding
– Bruising
• Ecchymosis
– Petechiae
Leukemia: S&S
• Bleeding
– Bruising
• Ecchymosis
– Petechiae
– Occult stool
Leukemia: S&S
• Bleeding
– Bruising
• Ecchymosis
–
–
–
–
Petechiae
Occult stool
Tarry stool
Coffee ground emesis
Leukemia: Dx
• CBC
• WBC w/ differential
Leukemia: Tx
• Chemotherapy
– Destroy leukemic cells
• Radiation therapy
– Use to shrink
• Bone Marrow
Transplants
• Stem cell transplant
Clients with HIV
• Page 249-260
HIV pathophysiology
• Mode of transmission
– Direct person to person
through sex
– Direct injection with
contaminated blood,
blood products or
needles
– Mother to fetus
Manifestations of HIV
• 3 stages:
– Primary infection
– Asymptomatic period
– AIDS & opportunistic
disorders
HIV: Primary infection
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Fever
Sore throat
General malaise/fatigue
H/A
Rash
N&V
Night sweats
Wt loss
HIV: Asymptomatic period
• Chronic
– @ 10 years
HIV:
AIDS & Opportunistic disorders
• Respiratory
– Pneumocystis carinii
pneumonia
• Gastrointestinal
– wasting syndrome
• Integumentary
– Kaposi's Sarcoma
Small group questions
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Identify 3 major S&S of leukemia.
What lab results indicate leukemia?
How are HIV and AIDS related?
What are the three phases of HIV infection?
How can you protect yourself as a nurse
while caring for a client with end stage HIV
infection?