tryagainshesays
advertisement

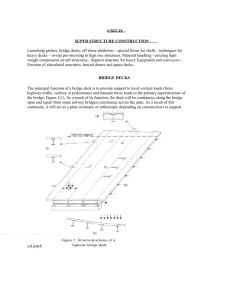
Offshore Natural Resource Extraction Overview History Exploration Platform models Seismic surveys Drill ships Fixed Platforms Compliant Towers Semi-submersible Platforms Jack-up Platforms Tension-leg Platforms Spar Platforms Subsea Systems Recent Affairs History 1986 - Companies drilled from piers extending off the beach at Summerland California 1911 - Gulf Oil drilled the worlds first truly “offshore” well detached from the shore at Caddo Lake, Louisiana/Texas border 1947 - Although drilling in the Gulf of Mexico has been taking place for some time, Kerr McGee completed first offshore well out of sight of land 1965 – The 5600 ton drilling barge “Sea Gem” was first to discover hydrocarbons in the British North Sea sector Exploration Seismic Surveys Maps rock layers without drilling a well Send shockwaves using air guns and record echoes The time for each echo to return as it bounces depends on depths and properties of rock layers Problem: presence of hydrocarbons can only be confirmed by drilling Drill Ships Ship with oil derrick on deck Used to quickly drill and check for hydrocarbons Not as stable as other rigs Very mobile Early ships used anchors to maintain position Modern vessels use Dynamic Positioning Platform Models Fixed Platform Used in shallow waters up to 520m Legs constructed of concrete or steel Rest on their own masses, very stable in strong winds or rough waters Designed for long term use Concrete legs serve as storage tanks Gravity base platform being built in Norway Jack-up Platforms Moving legs attached to platform Legs can be lowered like jacks and rested on seabed Designed to easily move from place to place Used in relatively low depths (up to 150m) Problem: cannot be used in extremely deep waters Compliant Towers Similar to fixed platforms Used in deeper waters ( 450 – 900m) Slender tower attached to foundation slab on seabed Very flexible compared to fixed platforms Can sustain significant lateral deflection cause by water movement Strong enough to withstand hurricanes despite it’s flexibility Semi-submersible Platforms Supported by hulls or pontoons Can be ballasted up and down by regulating flooding in buoyancy tanks Can be moved from place to place Anchored by cable or dynamic positioning Very stable in rough, deep seas Used in depths from 180 – 1,800m Tension-leg Platforms Similar to semi-submersible, consisting of a floating rig Attached to seabed by tethers Tethers have high axial stiffness which eliminates most vertical movement Used in depths of up to 2000 m Miniature version called Seastar platforms are used in depths between 200 - 1100m Examples of Seastar platforms Spar Platforms The largest of all platforms Consist of a large cylinder used to stabilize the platform Does not extend to the floor Tethered by lines and cables Unlike the TLP platforms it has conventional cables but is more stable due to the large ballast -The Genesis hull, travelling past condominium complex in Port Arkansas, Texas Subsea Systems Do no have ability to drill Extract and transport only Used in depths of up to 2000m Tied in to underwater pipeline or production platform Avoids the need of production platform for each well Summary Recent Affairs Hurricane Rita and Katrina Facts 394 platforms in the path of the storms 18 rigs suffered major damage or were totally lost 16 rigs damage to varying degrees, up to 2 weeks to repair Furthest rig drifted 80 miles during the storms No loss of life - Billiton Oil Platform Beached by Rita, just off of Dauphin Island, Alabama Chevron’s TLP platform before the storms - What remains of Chevron’s TLP platform after being hit by hurricane Rita References http://www.offshore-technology.com/projects/shtokman/images/image2.jpg http://www.sv.vt.edu/classes/MSE2034_NoteBook/MSE2034_kriz_NoteBook/design_pro j/ten_leg/tlp.gif http://www.solentwaters.co.uk/Vessel%20Types/Vessel%20Types%204/_wp_generated/w p94c9b6c4.jpg http://www.offshore-technology.com/projects/siri/ http://www.mossww.com/mossmaritime/ http://www.km.kongsberg.com/ks/web/NOKBG0239.nsf/obj/kristin_rig_200.jpg/$File/k ristin_rig_200.jpg?OpenElement http://www.jraymcdermott.com/images/jrme/compliant.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Condeep http://www.mms.gov/tarprojectcategories/deepwate.htm http://dsc.discovery.com/fansites/oilsweatrigs/photo/photo_05.html http://thomko.squarespace.com/display/ShowJournal?moduleId=209208&categoryId=353 73 http://www.solarnavigator.net/oil_rigs.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oil_platform http://www.naturalgas.org/naturalgas/extraction_offshore.asp http://www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/sources/non-renewable/offshore.html http://science.howstuffworks.com/oil-drilling.htm http://www.mms.gov/tarprojectcategories/Assets/Photos/abb.jpg http://www.rigzone.com/data/rig_report.asp?rpt=reg http://www.solentwaters.co.uk/Vessel%20Types/Vessel%20Types%204/page7.html http://www.gomr.mms.gov/homepg/regulate/environ/louisiana_coast.html http://www.schoolscience.co.uk/content/4/chemistry/petroleum/knowl/4/2index.htm?pla tforms.html http://www.offshore-technology.com/projects/mensa/index.html#mensa6 http://www.mustangeng.com/content.aspx?upstream_compliantpiledtowers http://www.offshore-technology.com/projects/genesis/genesis3.html