strategy
advertisement

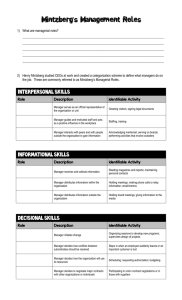
Strategy: an overview Jonny Holmström Web: jonnyholmstrom.com Email: jonny.holmstrom@informatik.umu.se Twitter: jonnyholmstrom IT Management Group www.itmanagementgroup.se Outline Definitions Forms of Strategy Coherence in Strategic Direction Information Systems Vs Information Technology The importance of vision/mission The organizational context for strategies: Mintzberg’s structure in fives “Strategies are both plans for the future and patterns from the past” - Henry Mintzberg Definition of Strategy A strategy is a plan of action designed to achieve a vision. It derives from the Greek "στρατηγία” (strategia), "office of general, command, generalship” (Wikipedia). Aspects of Strategy Statement of ends, purposes and intent High level plan Element of leadership Positioning for the future Building capability Fit between capabilities and opportunities Pattern of behaviour resulting from embedded culture 6 Strategic Management • Strategic management is the study of why some firms outperform others • How to create a competitive advantage in the market place that is unique, valuable, and difficult to copy • “Total organization” perspective, integrating across functional areas • Strategies put together an understanding of the external environment with an understanding of internal strengths and weaknesses Definition of Strategic Management Strategic management consists of the analysis, decisions, and actions an organization undertakes in order to create and sustain competitive advantages (Dess, Lumpkin, & Eisner, Strategic Management: Creating Competitive Advantage, 3rd Ed., p. 9). Attributes of Strategic Management • Directs the organization toward overall goals and objectives • Includes multiple stakeholders in decision making. • Needs to incorporate short-term and long-term perspectives • Recognizes trade-offs between efficiency and effectiveness • Efficiency describes the extent to which time or effort is well used for the intended task or purpose; Effectiveness is the capability of producing a desired result Mintzberg’s Views of Strategy • Plan - consciously intended course of action • Ploy - maneuver to outwit opponent • Pattern - consistency in behavior • Position - location in environment • Perspective - way of perceiving the world Forms of Strategy • Formal versus informal - associated with size of firm and stage of development • Intended versus realized - intended strategies are the plans managers develop; realized strategies are the actions that actually take place over time Forms of Strategy Source:H. Mintzberg and J. A. Waters, “Of Strategies, Deliberate and Emergent,” Strategic Management Journal 6 (1985), pp. 257-72. Coherence in Strategic Direction Company vision • Massively inspiring • Overarching Company vision • Long-term • Driven by and evokes passion • Fundamental statement of the organization’s • Values • Aspiration • Goals Hierarchy of Goals Coherence in Strategic Direction Mission statements • Purpose of the company Company vision • Basis of competition and competitive advantages Mission statements • More specific than vision • Focused on the means by which the firm will compete Hierarchy of Goals Coherence in Strategic Direction Strategic objectives • Operationalize the mission statement Company vision • Measurable, specific, appropriate, realistic, timely, challenging, resolve conflicts that arise, and yardstick for rewards and incentives Mission statements Strategic objectives Hierarchy of Goals Example: Coca Cola’s Vision and Mission • Vision: ”The Coca-Cola Company exists to benefit and refresh everyone it touches. The basic proposition of our business is simple, solid, and timeless. When we bring refreshment, value, joy and fun to our stakeholders, then we successfully nurture and protect our brands, particularly Coca-Cola. That is the key to fulfilling our ultimate obligation to provide consistently attractive returns to the owners of our business.” • Mission: “Everything we do is inspired by our enduring mission: • To Refresh the World… in body, mind, and spirit. • To Inspire Moments of Optimism… through our brands and our actions. • To Create Value and Make a Difference… everywhere we engage.” IS Vs IT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Inventory System Hardware Software Databases Networks Other related components Payroll System are used to build INFORMATION SYSTEMS Marketing System Customer Service System IT vs IS Strategy Carr (2003): IT doesn’t matter – Since everybody can buy the same technology strategic advantages cannot be found in having IT in the organization IS matter! – Merely having IT is not enough; what matters is what you do with it Mintzberg’s ‘Structure in fives’: An organisation has five main parts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 19 Strategic apex Middle line Support staff Technostructure Operating core Five main configurations Mintzberg proposes five main configurations, or kinds of organisations These are contexts where strategies are played out! 20 Simple structure 21 A small shop A new agency A start-up company led by a very dominant person Machine bureaucracy 22 A traditional airline A paper and pulp factory Professional bureaucracy 23 University Hospital Divisional form 24 A major corporation Umeå municipality Adhocracy 25 A project based consulting or R&D company Some highly innovative companies or agencies (e.g. North Kingdom) When analyzing strategies in organizations We will meet mixed configurations Thus, in your project, in the two seminars, and in the essay assignments: you may see cases that tend to confirm, falsify or call for elaboration of Mintzberg’s five types 26 When analyzing IT strategies in organizations (Peppard et al., 2014)