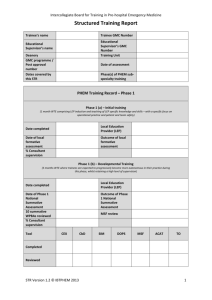
Organizing Training Programs
advertisement

ORGANIZING TRAINING PROGRAM Presented By: GROUP 4 Lets us answer a couple of questions • What is the basic objective of Training? • What are the main areas in which training can operate ? • • • • • Knowledge Skills Attitudes Techniques Experience` Principles of Organizing Training Programs (National Industrial Conference Board) • Purpose: to meet Organizational objectives, by providing opportunities for employees at all organizational levels to acquire the requisite knowledge, skills and attitude • The first step in training is to determine needs and objectives • The objectives and scope of a training program should be defined before its development is begun in order to provide a basis for common agreement and co-operation Principles of …. ( contd) • The techniques and processes of a training program should be related directly to the needs and objectives of the organizations • The function of training personnel is to assist line management in determination of training needs and in the development, administration, conduct and follow up of training plans • To be effective, training must use the tested principles of learning to make it most effective to the trainees. Important points(general) while organizing a Training Programme • • • • • • • • • Briefing Letter to Participants Timing Number of Participants Staffing Involvement of Participants Social events Handouts Visual Aids and Films Meeting Room Steps in Organizing Identifies needed functions and activities Structure of the Training Department (grouping of activities) Duties, Functions & Authority (of each sub element) Job Descriptions & Organizations and Functions Manual (of all jobs) Organizational Survey Assumptions • The training department must be able to deal effectively with the environment in which it operates. • The structure of training and development must aim at improved performance. • A sound organizational structure is no guarantee that the training organization will function properly. MANAGEMENT TRAINEE SCHEME • In every industry there is a need for managerial staff. • From first-line supervisors to top executives, managers plan and direct the work of the organization, set policy, establish channels of communication, and evaluate the work that is done. • These functions require knowledge, skills, and judgment that are most effectively developed on the job. • To prepare individuals for management responsibilities, many companies use MANAGEMENT TRAINEE positions. These positions are most often found in finance, trade, manufacturing, and in government agencies. Who is a Management Trainee? • According to The Apprentices Act 1961 Section 8 (3A) “management trainee” means a person who is engaged by an employer for undergoing a course of training in the establishment of the employer ( not being apprenticeship training under this Act) subject to the condition that on successful completion of such training, such person shall be employed by the employer on a regular basis. • Management trainees are low ranking managers who are in the process of learning management methods. They undergo formal training to carry management operations. • Management trainee works under the supervision of an experienced manager while learning. They receive formal training in a variety of management areas. • The Management Trainee position is designed to prepare trainees to work as administrators or managers. First step of Management Trainee scheme : Induction INDUCTION SCHEDULE February 16,2011 S.No. Program April 6,2011 1 Safety Practices April 6,2011 Time 10:30:00AM Facilitator* Mr. ABC, HeadSafety VTC Administration Block 3 Overview of Financial Services 2:00PM Mr. DEF, HeadFinance 4 IT 3:10 PM Mr. GHI, Head IT 6 HR 8 April 7,2011 Time Office 9 Interaction with the UNIT HEAD 4:00 PM Rendezvous Point Signature Mr. JKL Head- HVSC HVSC 8:00 AM Mr.MNO 10:00 AM Mr.PQR 10:30 AM Human Resources Mr. STU, Associate Department, Manager-HR Administration Block 14 Feed Back 7 11:00 AM Commercial Mr.VWX Orientation at respective department. Mining Block Administration Block Note= * HODs may depute other executives for the program STU Associate Manager- HR FEEDBACK FORM GET - INDUCTION Name of the Trainee: Name of HR Co-ordinator: Date : Rating scale:1-Very Satisfied, 2-Satisfied, 3-Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied, 4.Dissatisfied ,5-Very dissatisfied Kindly rate the sessions on a scale of 1 to 5. Rating Session Conducted (Yes or Name of Facilitator No ) Facilitator Content Mining Technical Session Mine visit Geology HEMM Safety Mill Technical Session Plant Visit Environment HR Finance Commercial FEEDBACK FORM 1 Was the induction process well managed ? 2 Overall, what was the most useful part , and why? 3 What was the least useful part and why? 4 Suggestions for improvement: 5 How would you rate your experience of Induction on a scale of 1 to 5 ? Components of a Management Trainee Scheme Periodical review and career counseling Buddy system Live Projects Job Rotation Training Program Self Study Organizing Management Trainee Program • Steps for organizing Management Trainee Scheme Defining Objectives Formulating Policies Duration Compensation Training Module Review Mechanism MANAGEMENT DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM • The Management Development Program (MDP) is a program designed for managers at all organizational levels who want to develop and enhance their understanding and practice of fundamental management principles in the context of today's challenging environment. • This program attracts an audience from a wide diversity of backgrounds, experience, and managerial levels who come together to discuss fundamental issues facing managers in today's complex organizations. The program is highly interactive and participant-centered. Instructors utilize a variety of teaching methods to actively involve participants and facilitate the learning process. The program focus is on the practical application of the management principles discussed. Graduates of the program return to their workplace with a written action plan to transform their learning into increased managerial effectiveness in the workplace What does MDP system training include? • Management and Leadership Excellence • Examines basic principles and practices of management as they apply to today's workforce and explores management behaviors that contribute to personal and interpersonal effectiveness. • Personal Preferences and Leadership • Provides participants an opportunity to discover personal preferences, relate them to their management styles, and maximize their advantages in the workplace. • Communication in the Workplace • Explores the art of effective communication in a diverse and ever changing workplace. Describes verbal language that promotes positive, supportive and inclusive communication. Contd.. • Working Together Effectively • Identifies the fundamentals of team development and characteristics of effective team leaders. It also explores the sources and consequences of conflict and identifies methods to approach it constructively. • Managing Performance • Introduces coaching as a management tool and identifies strategies managers can use to improve employee performance. • Managing Personal & Organizational Change • Describes the human reaction to change and the impact of response to change. This session provides a toolbox for managing change and strategies for increasing resilience. Methods and techniques used to facilitate training • Instructional DVDs • Operational Training manuals (hard copies and electronic versions) • On-line testing • In-class seminars • Product seminars (conducted by suppliers) • Consultation Services provided by Senior Management including Regional and District Managers Some of the reasons behind the management development programs are • It is managements’ responsibility of ensuring the success of the organization • It is the management who deal with people of different background, culture, language, etc • Mergers and acquisitions, downsizing, etc are all under management’s control • It is managements’ responsibility to ensure that the employees obtain the required KSAs to perform the tasks Contd.. • It is managements’ responsibility to ensure that right people is hired for the right job, at the right time for the right place. • It is the management who makes decisions on the basis of judgment and intuition • It is the manager who performs several routine duties as well as handling the exceptions in their own as well as subordinates’ routine Contd.. • It is the management that understand the organization, its vision, mission, ethics, values, strategies, capabilities, and how his organization fits into the industry, and how his behavior will influence people outside the organization • Therefore, managers must be able to get the required knowledge, skills, and attitudes (KSAs) to meet the challenges as soon as they arise SUPERVISORY TRAINING PROGRAM • A supervisor is the lowest, or most-junior, management position. It is usually a step above lead (Accounting Supervisor is senior to Lead Accounting Specialist), but below Manager. • A supervisor is responsible for the day-to-day performance of a small group. It may be a team, or a shift. The supervisor has experience in what the group does. The supervisor's job is to guide the group toward its goals, see that all members of the team are productive, and resolve problems as they arise. Supervisor, being the manager in a direct contact with the operatives, has got multifarious function to perform. The objective behind performance of these functions is to bring stability and soundness in the organization which can be secured through increase in profits which is an end result of higher productivity. Therefore, a supervisor should be concerned with performing the following functions - •Planning and Organizing •Provision of working conditions •Leadership and Guidance •Motivation •Controlling •Linking •Grievance Handling •Reporting •Introducing new work Enforcing Discipline SUPERVISOR TRAINING • • • • • • • • A new promotion means more challenges and more responsibilities. The Supervisor Training curriculum targets newly promoted foremen and supervisors or include training program in your organizational quality improvement plan and recommend it to experienced supervisors who need to brush up on fundamental skills. After an effective training program, the supervisors will be able to: Discuss the concepts and skills that a first-level supervisor uses in their daily responsibilities including: managerial concepts, how to plan, organize, and control; the process of motivation; employee relations; training, communication, and coordination; cost control and work simplification. Sharpen their verbal communication skills. Write effective letters, reports, and proposals. Be a contributing leader/member of an organizations quality improvement team, by understanding and communicating the accepted concepts and techniques. Learn and implement the principles of statistical process control within their organization. Learn and understand the use of quality measurement tools and measurement inspection methods. Key Issues to Address • How to integrate into the entrenched culture and survive resistance to you and your authority. • How to handle the challenge of maintaining authority and building personal friendships with employees. • How to motivate people to want to show up for work. • How to motivate individual initiative and personal responsibility with respect for following procedures and regulations. • How to develop the judgment to know when to follow written procedures and when to adapt. • How to give clear instructions and verify recipient’s understanding. • How to give performance feedback to employees that motivates them to want to improve. • How to mediate and resolve most employee disputes. • How to set goals, monitor behaviors and progress, and connect these things to performance feedback and organizational Success-o-Meters. • How to manage your own stress while managing the stress of others. Other Important Issues to be Addressed • • • • • • • Contract Documents and other Legal Compliances Planning and Scheduling Cost Awareness and Production Control Accident Prevention and Loss Control Managing the Project: The Supervisor’s Role Productivity Improvement Company’s Statutes and Policies Organizing a Supervisory Training Program Selection of the participants ( voluntary /rooster/ nominated) Letter to the reporting officers of the participants Briefing Letter to Participants Topic of Training Timing ( so that it does not affect the production/service providing process) Number of Participants Staffing ( from within generally) Involvement of Participants ( with the resource person) Food Handouts Visual Aids and Films Venue WORKER’S EDUCATION AND TRAINING WHY IS IT NEEDED ? • To keep new and young workers safe on the job. • And prevent painful and costly work related injuries. Why focus on young and new workers? • Young workers, are at a much higher risk of injury than other workers. More than half of workplace accidents involving workers aged 15 to 24 occur during their first 6 month on a job: nearly 20 percent occur during the first month. • Young workers generally have less experience in recognizing hazardous situations than older workers. Many are also eager to please and afraid they will look dumb if they ask question, so they take risk that could be avoided. • It’s not just only young workers are getting hurt. starting a new job can be risky for workers of any age, including experienced workers. 1.Provide safety orientation, and train workers on the basics • Rights and responsibilities. • Workplace hazards. • Safe work procedure. 2.Train workers for tasks specific to their jobs. Specifically, you need to train workers in how to: • Perform tasks safely • Operate machines and equipment safely • Use and maintain any required PPE such as gloves or goggles • Follow safe work procedure 3.Provide supervision and ongoing training for all workers to ensure that they continue to work safely. The most important part of training is the follow-up supervision. Adequate supervision includes the following: • Ensure proper instruction and training of workers. • Follow up training with regularly scheduled observation to ensure that workers continue to follow safe work procedures. Document this observation. • Make information inspections on a daily basis to ensure that workers understand and are following safe work procedures, including proper lifting techniques and the use of protective equipment, devices, and clothing. • Enforce safety rules and work procedures. • Conduct informal discussions (crew talks) with workers to discuss specific safety issues as they arise. • Encourage worker feedback. Important items that the organizer should consider • Provision of information to participants and resource persons (before, during, and following the training session) • Logistical aspects of course preparation and implementation: Travel arrangements and transportation Accommodation Meals and breaks Social events Training rooms and infrastructure available Per diem (Daily Subsistence Allowance) Equipment, materials and supplies Name badges Certificates (Template provided upon request) Innovative approaches and methods for flexible training delivery • For workers to be able to adapt to the diverse skill needs of rapidly changing labour markets, they will need a greater capacity to learn and develop broader skills as a platform for continuous training, rather than acquiring fixed and narrow technical skills during a single period of training. • To match these needs, a diversified supply of good quality training will have to be available, offering combinations of information and guidance services and interconnected paths of initial training. • Emphasis needs to be placed on competency-based training and the development of competence standards and certification systems for the recognition of the experience and skills acquired in formal and informal training. • In this context, training content and methodologies have to be flexible to increase labour mobility and the employability of new entrants to the labour market and displaced workers. • However, to be in a position to respond to these needs, constituents require greater knowledge of the possible options, combined with assistance in analysing and identifying those that are most appropriate to their specific situation.