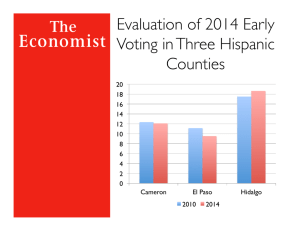
Presentation
advertisement

ICT and Election Management: The Nepalese Experience Presented By Neel Kantha Uprety Chief Election Commissioner of Nepal upretyneil@gmail.com Introduction Nepal A Federal Democratic Republic in Asia Area: 147,181 Sq. Km (Mountain and Hill 83%, Plains 17%) Eight of the world’s 14 mountains of over 8,000m are in Nepal including the EVEREST Population: Approx. 27 Million (Male 49 % , Female 51%) Literacy Rate: Approx. 66% Languages: 92 Election Commission established in 1950. Five member Election Commission a constitutional body. 2 Background of ICT Use Computers were introduced for the first time in 1986 to prepare electoral rolls. Since 1999, computer use extended beyond electoral roll preparation. ICT used for election result processing dissemination of election results. 3 CA Election 2008 and ICT Electoral Roll Preparation Periodic (annual) door to door collection and updating. Digital data entry from a manual register at 75 district election offices. Data aggregated to a centralized digital voter register. Voter list published in ECN Website with facility to search for names. Independent assessments found duplicate and erroneous registrations including deceased and underage voters. 4 CA Election 2008 and ICT Supporting ICT Systems VPN Connectivity to 41 out of 75 districts. Information transfer from district to ECN using web application and fax machines. EVM was first used in one constituency in Constituent Assembly election 2008. ECN adopted EVM in all the six constituencies for the CA by-Elections in 2009. 5 Strategic Plan (2009-2013) and ICT Establish a new voter register that includes voters’ photograph and finger prints. Record information of polling stations in a Geographic Information System (GIS). Link the Commission and all field offices through a secure ICT network. Implement election management information systems in the commission and field offices. Use the Internet to provide updated election information. Use Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) for polling. 6 Voter List with Photo Program Inception and Pilot Project Voters Registration study visits made to selected countries. Hybrid methodology adopted including both door to door enumeration and registration centers visit by electors. Project linkages established to facilitate establishment of national identity and civil registration for Nepal. Collection of voter data including photograph and four fingerprints for all citizens of 16 years and above. Pilot projects conducted in seven semi-urban and rural areas to trial and refine technologies, methodologies, and operational processes. 7 Voter List with Photo Program Project Scope and Progress Phased data collection commenced in August 2010. Approx. 10,000 Registration Centers. Approx. 90,000 temporary staff. 3,600 Voter Registration Kits comprised of backpack, laptop, camera, fingerprint scanner, and external keyboard. 800 Portable Generators. 10.3 million voters registered as at March 2012. 8 Registration Process Enumerator Visits home Voter Residence Returns with Completed Forms Voter attends registration centre at predefined time Uploading of Data District Election Office District Server Report of matches for follow-up Voter Registration Centre form checking voter authentication ECN Central Office in Kathmandu Central Storage Data Matching & Checking Voter List with Photo Program 10 Voter List with Photo Program Data Consolidation & Management Data consolidated on 75 district office desktop servers and central data center storage area network (SAN). Tape and disk based backup systems established . Text based and biometric de-duplication performed using virtualized server systems. 11 Voter List with Photo Program Data Consolidation & Management • • • Nationwide display and missed voter processes. Web based display and claims mechanisms. Continuous voter registration established through district offices and other designated locations. 12 Voter List with Photo Program Challenges Available documentation of citizens. Obstruction by some political groups. Support, maintenance, and logistics for equipment due to diverse geographic conditions. Finger print capture for manual laborers and elderly citizens. Secure data management in disparate geographic environment. Updated Legal Framework during political impasse. Development of skills and capacity to maintain systems. 13 Future Direction Long term technical and operational integration with National ID & civil registration. Full implementation of a secure network to all district offices to support continuous voter registration, administration, communications, and EMS including nominations & results. Extended use of GIS for Election Management. Technology implementation for the Electoral Education and Information. Extended use of Electronic Voting Machines. 14 Thank You The Rolls Right, The Poll Right Your vote is a valuable for democracy 15