Chinese IP Rights
advertisement

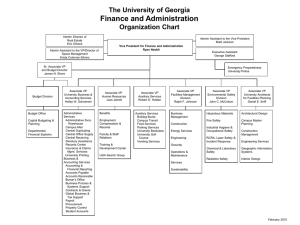
Chinese Intellectual Property Rights and Enforcement Antony Craggs Associate Intellectual Property Wragge & Co LLP Wragge & Co LLP: General Background: – We are a leading European law firm providing legal services to clients worldwide. – We have over 110 partners and more than 500 qualified legal staff. – We advise on all aspects of corporate and commercial work. – We are specialists in all aspects of intellectual property including patents, designs, trade marks, unfair competition / passing off, copyright, database rights, marketing and advertising. Antony Craggs, Associate Wragge & Co LLP: Intellectual Property General Intellectual Property Specialists: – European High-tech Law Firm of the Year 2009 - Managing Intellectual Property. – No 1 UK National Firm – Legal Week Client Satisfaction Report 2009 – Runner-Up TMT Team of the Year 2009 – The Lawyer Awards 2009 – UK Intellectual Property Law Firm of the Year 2007 – Managing Intellectual Property Antony Craggs, Associate Wragge & Co LLP: Intellectual Property China Cradle-to-Grave Intellectual Property Management – Registration – Management & Exploitation – Licensing – Assigning – Tax – Enforcement – Administrative Action – Civil Litigation – Criminal Sanction – Customs Action Antony Craggs, Associate Agenda Chinese IP Rights: – Overview – Copyright – Trade Marks / Unfair competition – Designs – Patents Licensing Enforcement of Chinese IP Rights Antony Craggs, Associate Chinese IP Rights: Overview System: – “Teenage” system: 15-25 years old – Compliant with TRIPS and WTO (in most areas) Antony Craggs, Associate Chinese IP Rights: Copyright Features: – The subject is not always “artistic” – product leaflets, website designs, advertising slogans and product packaging – Arises automatically – Voluntary recordal – Sample of the work to be registered – Description of the work (including the purpose of its creation, the creation process and the 'creativeness' of the work) – Obtain information about the author and the work including: a) the author's name; b) the author's passport; c) the date and place for completion of the work; and d) the date and place of first publication; – Obtain any relevant documents regarding the ownership of copyright including: a) the employment contract or other copyright assignment; b) (if possible) a letter from the author stating that he/she created/modified the work and that you are the owner of the copyright; and c) any other copyright registration certificates for other countries – Obtain a copy of the certificate of incorporation for the copyright owner. Antony Craggs, Associate Chinese IP Rights: Trade Marks (1 of 2) Types of sign protected: – A sign that identifies the goods or services of a producer or service provider and allows the consumers to distinguish these goods or services from those of others. – A sign may be composed of words, devices, letters, numerals, three-dimensional shapes Translations of non-Chinese signs: – It is extremely important to register common translations and transliterations of non-Chinese signs. The registration of a sign in roman characters does not automatically protect the trade mark against the use of the same or similar sign written in Chinese. Term: – Renew every 10 years Antony Craggs, Associate Chinese IP Rights: Trade Marks (2 of 2) Class: – Filing: – Absolute and relative grounds Process: – 2 years to register a mark (but aiming for one year) Examination: – “First-to-file” system: prior use affords little protection unless your mark is well-known Time: – Nice Classification with sub-classes Approve – advertise – 3 months opposition – registered Cancellation: – 3-year non-use, absolute/relative grounds, but slow and uncertain Antony Craggs, Associate Chinese IP Rights: Designs Features: – Design patents (no unregistered designs) – No substantive examination – 10 years protection term – Design registration is relatively simple and inexpensive, and is very useful for enforcement Antony Craggs, Associate Chinese IP Rights: Patents Types of patents: – “Invention” patent: Innovations in the field of technology that are new and inventive and that are practically applicable. – “Utility model” patent: Technical solutions relating to the shop and / or structure of an object that are new. – “Design” patent: Original designs relating to the shape, pattern, colour or a combination of an object. Term of patents: – Invention patents: 20 years from filing date – Utility model patents: 10 years from filing date – Design patents: 10 years from filing date Antony Craggs, Associate Licensing Confidentiality agreement Due Diligence – Identify the company’s Chinese name (not pinyin), registered address and date of incorporation – Identify the company’s legal representative, directors and shareholders – Accounts / credit check / export licence – Referees / private investigator – Inspection / Audit Contract – Written contract which is short, bi-lingual and subject to Chinese law – State clearly who owns the intellectual property developed/licensed – State clearly payment terms – Chinese courts / arbitration body Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Overview Three main enforcement options: – Administrative Action – Civil Litigation – Criminal Sanctions Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Administrative Action - Overview Chinese administrative body enforces intellectual property rights. Administrative bodies: – Intellectual Property Offices (e.g. Yongkang IPO): – Patents (inc. designs) – Administration for Industry and Commerce (AIC): – Trade marks and unfair competition – National Copyright Administration: – Copyright Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Administrative Action - Remedies The administrative body may: – Raid premises and seize and destroy infringing items – Order infringing party to cease infringement – Fines (low) – Compile evidence Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Administrative Action - Advantages Administrative actions have the following advantages: – Cost effective – Efficient – ‘Immediate’ enforcement – Evidence gathered can be used in civil action – Can be used as leverage for settlement Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Administrative Action - Disadvantages Administrative actions have the following disadvantages: – Idiosyncratic – No damages – Decision does not bind the court in any subsequent civil litigation – Subject to appeal Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Civil Litigation (1 of 4) Features of the court systems: – Civil law system – No doctrine of binding precedent – Four levels of courts – Basic People’s Court – Intermediate People’s Court – Higher People’s Court – Supreme People’s Court Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Civil Litigation [2 of 4] Injunctions: – Court can issue interim injunctions (rare) Two tier approach: – Court determines infringement – SIPO determines invalidity of trade mark / design / patent Stay (pending invalidation proceedings): – Depends: Less likely to stay infringement actions involving invention patents Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Civil Litigation (3 of 4) Timeline: – First instance: 6 – 9 months – Second instance: 3 months Damages: – Typically low but signs of increasing – 2007: Schneider Electric: Ordered to pay US$46 million (appealed and settled for US$23 million) – 2008: Samsung: Ordered to pay US$7.3 million – 2009: Neoplan: Awarded US$3 million – 2010: Strix: Awarded US$1.5 million Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Civil Litigation (4 of 4) Remedies: – Injunction – Seizure and destruction of infringing goods – Damages Costs: – Only small proportion of costs recoverable Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Criminal Sanctions - Overview Public Security Bureau (PSB Can be referred if liability is over a certain threshold: – Individuals: – Turnover: RMB 50,000 or illegal profit of RMB 30,000 – Companies: – Turnover: RMB 150,000 Consequences: – Up to 3 years imprisonment – Higher punishment of 3 – 7 years if value is 5 times the threshold – More sever penalty if crime relates to substandard goods that affect people’s health and safety Antony Craggs, Associate Enforcement of China IPR Rights: Conclusions Implement the following steps: – Register your intellectual property rights – Perform due diligence on your business partners /licensees – Ensure your contracts protect your intellectual property rights – Make scheduled and unscheduled visits to your operations in China – “Guanxi”: Build up contacts with local government authorities – Patrol trade fairs – Enforce your intellectual property rights Antony Craggs, Associate Antony Craggs, Associate Dr. Jian Xu, Associate Email: DDI: Email: jian_xu@wragge.com DDI: +86(0)2038103782 Mobile: +86(0)13 902 297 469 antony_craggs@wragge.com + 86 (0)203 810 3783 + 44 (0)207 664 0341 Mobile: + 44 (0)792 188 1397 Antony Craggs, Associate QUESTIONS & ANSWERS