Blue-oceans
advertisement

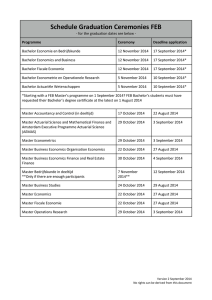
Blue Oceans BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Part Two:Formulating Blue Ocean Strategy 1 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Formulation Principles Risk Factors Reconstruct market boundaries Focus on the big picture, not the numbers Reach beyond existing demand Get the strategic sequence right Lowers Search risk Lowers Planning risk Lowers Scale risk Lowers Business model risk innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Reach Beyond Existing Demand 3 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Reach Beyond Existing Demand The Three Tiers of Noncustomers 1st Tier 2nd Tier 3rd Tier Your Market 4 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Reach Beyond Existing Demand The Three Tiers of Noncustomers First Tier : “Soon-to-be” noncustomers On the edge of your market 1st Tier Your Market Waiting to jump ship.Minimally use the current market offerings to get by as they search for something better. 5 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Reach Beyond Existing Demand The Three Tiers of Noncustomers Second Tier: “Refusing” noncustomers Consciously choose against your market.Their needs are either dealt with by other mean or ignored. 2nd Tier Harboring within refusing noncustomers, however, is an ocean of untapped demand waiting to be released. 6 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Reach Beyond Existing Demand The Three Tiers of Noncustomers Third Tier : “Unexplored” Have not been targeted or thought of as potential customers by any player in the industry 3rd Tier Their needs and the business opportunities somehow always been assumed to belong to other markets. 7 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Get the Strategic Sequence Right 8 innovation.uccs.edu Buyer utility Is there exceptional buyer utility in your business idea? BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ No-Rethink Yes Price Is your price easily accessible to the mass of buyers? No-Rethink Yes Cost Can you attain your cost target to profit at your strategic price? No-Rethink Yes Adoption What are the adoption hurdles in actualizing your business idea? Are you addressing them up front? No-Rethink Yes A commercially Viable Blue Ocean Idea 9 innovation.uccs.edu Buyer Experience Cycle BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ A buyer’s experience can usually be broken into a cycle of six stages, running more or less sequentially from purchase to disposal. Each stage encompasses a wide variety of specific experiences. At each stage, managers can ask a set of questions to gauge the quality of buyer’s experience. Purchase How long does it take to find the product you need? Is the place of purchase attractive and accessible? How secure is the transaction environment? How rapidly can you make a purchase? Delivery How long does it take to get the product delivered? How difficult is it to unpack and install the new product? Do buyers have to arrange delivery themselves? If yes, how costly and difficult is this? Use Does the product require training or expert assistance? Is the product easy to store when not in use? How effective are the product’s features and functions? Does the product or service deliver far more power or options than required by the average user? Is in overcharged with bells and whistles? Supplements Do you need other products and services to make this product work? If so, how costly are they? How much time do they take? How easy are they to obtain? Maintenance Disposal Does the product Does use of require external the product maintenance? create waste items? How easy is it to maintain and How easy is it upgrade the to dispose of product? the product? How costly is maintenance? Are there legal or environmental issues in disposing of the product safely? How costly is disposal? innovation.uccs.edu Uncovering Blocks to Buyer Utility BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Uncovering blocks to buyer utility can identify the most compelling hot spots to unlock exceptional utility. By locating your proposed offering on the thirty-six space of the buyer utilit map, you can clearly see how, and whether the new idea not only creates a different utility proposition from existing offerings but also removes the biggest blocks to utility that stand in t way of converting noncustomers into customers. Purchase Delivery Use Supplements Maintenance Disposal Customer Productivity: In which stage are the biggest blocks to customer productivity? Simplicity: In which stages are the biggest blocks to simplicity? Convenience: In which stage are the biggest blocks to convenience? Risk: In which stage are the biggest blocks to reducing risks? Fun and Image: In which stage are the biggest blocks to fun and image? Environmental In which stage are the biggest blocks to environmental friendliness? Friendliness: innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Buyer Utility Map The buyer utility map helps managers look at this issue from the right perspective. It outlines all the levers companies can pull to deliver exceptional utility to buyers as well as the various experiences buyers can have with a product or service. The Six Stages of the Buyer Experience Cycle 1. 2. 3. Purchase Delivery Use 4. 5. SupplementsMaintenance 6. Disposal The Six Utility Levers Customer Productivity Simplicity Convenience Risk Fun and Image Environmental friendliness innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Price Corridor of the Mass This tool helps managers find the right price for an irresistible offer, which, by the way, isn’t necessarily the lower price. The tool involves two distinct buy interrelated steps. The first step involves identifying the price corridor of the mass which deals with customer price sensitivity and pricing strategies of products offered outside the group of traditional competitors. The second step deals with specifying a level within the price corridor which factors in legal protection and exclusive assets. Step 1: Identify the price corridor of the mass. Three alternative product/service types: Same form Different form, same function Step 2: Specify a price level within the price corridor. Different form and function, same objective High degree of legal and resource protection Difficult to imitate Mid-level pricing Price Corridor of the Mass Some degree of legal and resource protection Low degree of legal and resource protection Easy to imitate innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries 14 BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries The first principle of blue ocean strategy is to reconstruct market boundaries: break from the competition create blue oceans. Challenge: successfully identify $ compelling blue oceans 15 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Six Approaches that Look Across: Alternative Industries Strategic Groups Within Industries The Chain of Buyers Complementary Product and Service Offerings Functional or Emotional Appeal to Buyers Look Across Time 16 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries Broader than substitutes Products & Service Substitutes: different forms but same functionality Products & Service Alternatives: different functionality and forms but same purpose 17 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: QUESTION: Name the 2 examples the book uses? 18 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: FIRST EXAMPLE CLUE: Sorting out personal finances 19 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: FIRST EXAMPLE: Sorting out personal finances Installing financial software packages on a computer: hiring a CPA using pencil and paper What is it?: different forms but same functionality different functionality and forms but same purpose 20 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: FIRST EXAMPLE: Sorting out personal finances Installing financial software packages on a computer: hiring a CPA using pencil and paper What is it?: different forms but same functionality Helps people manage financial affairs 21 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: SECOND EXAMPLE CLUE: Cinemas vs. Restaurants 22 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: SECOND EXAMPLE: Cinemas vs. Restaurants Restaurants: offer conversational & gastronomical pleasure Cinemas: visual entertainment What is it?: different forms but same functionality different functionality and forms but same purpose 23 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: SECOND EXAMPLE: Cinemas vs. Restaurants Restaurants: offer conversational & gastronomical pleasure Cinemas: visual entertainment What is it? CLUE: Same objective but its not a substitite: about enjoying a night out - therefore they are alternatives of each other: 24 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: SECOND EXAMPLE: Cinemas vs. Restaurants Restaurants: offer conversational & gastronomical pleasure Cinemas: visual entertainment What is it?: different functionality and forms but same purpose 25 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: RECAP: Sorting out personal finances different forms but same functionality Cinemas vs. Restaurants different functionality and forms but same purpose 26 innovation.uccs.edu Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: QUESTION: What was the deal with NetJets? BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ What was Netjets’ Blue Ocean? 28 Reconstructing Market Boundaries BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ fractional jet ownership 29 BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: NetJets: Blue ocean of fractional jet ownership In less than 20 years, it was the fastest growing airline company Over 500 aircraft - Operating in over 40 countries Purchased by Berkshire Hathaway in 1998 Revenue growth from 30-35% each year 30 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: NetJets SUMMARY: NetJets reconstructed market boundaries to create their blue ocean by looking across alternative industries 31 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ How did they reconstruct market boundaries to create their blue ocean? BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries They asked: Why do corporations use commercial airlines for their travel? What are the Costs. 33 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries They responded: Offerering customers 1/16th ownership of an aircraft shared with 15 other customers who all Receive 50 hrs of flight time per year for $375,000 Private jet at the price of a commercial airline ticket Due to NetJets smaller airplanes, use of smaller regional airports, and limited staff, their costs are kept to a minimum 34 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ What are dead head fees? BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Dead head fees are: Additional client costs, calculated per mile, that apply when the pick up, drop off location, or The service area is not within 25 miles of the bus company, or Charters where the mileage fee is greater than the hourly fees. innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Functional or Emotional Appeal to Buyers What Industries should compete on Rational appeal Emotional appeal Appeal usually a result of how companies have competed in the past Ex: Functionally oriented companies become more functionally oriented 38 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Functional or Emotional Appeal to Buyers Change Emotionally oriented industries offer extras at extra price without enhancing functionality By stripping those extras it would create a fundamentally simpler business model Functionally oriented industries can add emotion to their products to stimulate demand 39 innovation.uccs.edu Reconstructing Market Boundaries BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Look Across: Functional or Emotional Appeal to Buyers Example: Quick Beauty House Traditional Japanese haircuts - took around an hour because of rituals Price was around $27 to $45 -Reduced to around $9 Decided working professionals did not want to waste an hour Stripped the emotional service of the haircut - focused on basic cuts 40 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Functional or Emotional Appeal to Buyers Look Across: Buyers’s Utility and how they purchase Example: Cemex World’s 3rd-largest cement producer: Blue ocean: functional to emotional Cement houses were the dreams of the people of Mexico - unaffordable Foundation of tandas While competitors were selling cement, Cemex was selling dreams 41 innovation.uccs.edu What defines the “Bottom of the Pyramid”? Annual per capita income (1) More than $20,000 $ 1,500 - 20,000 Less than $ 1,500 (1) Based on purchasing parity in US $ BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Population in millions 75-100 1,500 – 1,750 4,000 Source: U.N. World Development Reports innovation.uccs.edu Six Assumptions You May Be Making BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ 1. The poor are not our target customers because with our current cost structures, we cannot profitably compete for that market. 2. The poor cannot afford and have no use for the products and services sold in developed markets. 3. Only developed markets appreciate and will pay for new technology. The poor can use the previous generation of technology. 4. The bottom of the pyramid is not important to the long-term viability of our business. We can leave Tier 4 to governments and nonprofits. 5. Managers are not excited by business challenges that have a humanitarian dimension. 6. Intellectual excitement is in developed markets. It is hard to find talented managers who want to work at the bottom of the pyramid. Source: C.K. Prahalad and Stuart L. Hart, The Fortune at the Bottom of the Pyramid, strategy + business, Issue 26 Every single one of these assumptions is generally wrong. innovation.uccs.edu Cemex Launched the Patrimonio Hoy Project for the Poor People of Guadalajara (Mexico) BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ “How can we give poor people access to the home-owning experience faster?” innovation.uccs.edu The Challenge for Poor People: Building Their Home One Room at a Time Cement bag BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ “Selfconstruction” market “How can we accelerate access to the cement bag for poor people?” innovation.uccs.edu Patrimonio Hoy Builds on an Existing Community Called a Tanda BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Tanda concept A tanda is a traditional Mexican community savings scheme. Every five months, the accumulated savings is won in a lottery by one of five people, who receives 50 pesos. For example, 10 people save 1 peso per month. All participants win the 50 pesos one time only. Traditionally, the tanda money goes toward festive events. With Patrimonio Hoy, the winner receives a bag of cement from Cemex. The value is in the acceleration of access to the larger sum, and in the discipline of savings that is created (community peer pressure). Communities nearly always play a role in solving bottomof-the-pyramid problems innovation.uccs.edu A win-win solution for Cemex and tandas BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Microcredit lending to the tanda: Based on solidarity of a group of at least 3 people. No collateral required. $4 credit for each $1 saved. Security of supply: Frozen prices for 70-week periods. Warehousing services to store materials according to customer needs. Technical advice: Customized house growth project for each family, phased one room at a time. innovation.uccs.edu Results from the customer’s standpoint More than 75,000 families have participated. Customers in 23 cities served by 48 Cemex offices. BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Families have built the equivalent of 33,000 additional 11square meter rooms. Accelerated access to home-owning: 1 room in 16 months vs. 48 months historically. 8 2 2 2 2 innovation.uccs.edu Results for Cemex BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Results from Cemex’s standpoint Excellent credit results: Demand expansion: Accelerated cement use. Creation of a new market valued at $500-600 MM. Growing quickly. Branding: On-time payments better than 99%. Increased brand loyalty. Brand preference in other segments based on demonstrated socially responsible programs. Generating its own growth resources: Customers become Cemex cement salespeople. innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Curves 50 BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Strategic Groups Within Industries: CURVES Blue ocean demand for women failing to keep in shape Built on two strategic groups: traditional health clubs and home exercise programs eliminated everything else Asked: What makes women trade either up or down from these two strategic groups? Curves’ low-cost business model makes its franchises easy to afford and are profitable within the first couple of months Curves facilities now exist in most towns all over the U.S. 51 and North America and have expanded into Europe innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Strategic Groups Within Industries: CURVES Asked: What makes women trade either up or down from these two strategic groups? Makes its franchises easy to afford profitable within the first couple of months All over the U.S. / North America and Europe 52 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Strategic Groups Within Industries: Group Others Polo Ralph Lauren Toyota’s Lexus as a Luxury Car Sony’s Walkman in the late 1970s Champion Enterprises prefabricated housing 53 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: The Chain of Buyers Typically, industry focuses on who the target buyer is. In reality, there is a chain of “buyers” purchasers, users, and influencers Each hold different definitions of value 54 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: The Chain of Buyers Individual companies in an industry often target different customer segments. large vs. small customers An industry typically converges on a single buyer group Pharmaceutical industry - influencers Office Equipment industry - purchasers Clothing industry - users 55 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: The Chain of Buyers Novo Nordisk created a blue ocean in the insulin industry and transformed from an insulin producer to a diabetes care company. Industry focused on doctors - shifted to users (patients) rather than doctors. NovoPen = 1st user-friendly insulin delivery system NovoLet = prefilled disposable insulin pen Innovo = electronic memory records 56 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: The Chain of Buyers Industry focused on purchasers (IT managers) Bloomberg saw traders & analysts making the crucial decisions for their employers -Designed system to offer users better value with a easy-to-use, broker-friendly computer system -Also added information and purchasing services to enhance their personal lives In return the traders & analysts exerted their power within the firm to drive IT managers to purchase from Bloomberg. 57 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Complementary Product & Service Offerings What is the context in which your product or service is used? What happens before, during, and after? Can you identify the pain points? How can you eliminate these pain points through a complementary product or service offering? Untapped value is often hidden in complementary products and services. Define the total solution buyers seek when they choose a product or service. 58 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Complementary Product and Service Offerings Examples Virgin Entertainment’s Megastores Dyson Vacuums Zeneca’s Salick Cancer Centers 59 innovation.uccs.edu Reconstructing Market Boundaries BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ Alternative Industries: QUESTION: What was the deal with NTT DoCoMo’s i-mode? 60 Reconstructing Market Boundaries BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ What was DoCoMo’s Blue Ocean? 61 BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: DoCoMo: Largest telecommunications company in Japan Changed the way people communicate and access information Created blue ocean by thinking of why people trade across alternatives of mobile phones and the internet 62 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Alternative Industries: DoCoMo: Largest telecommunications company in Japan - Changed the way people communicate and access information Created blue ocean by thinking of why people trade across alternatives of mobile phones and the internet Deregulation of telecommunication industry in Japan, it was easy for new competitors to enter the market Result: rising costs, and the average revenue per consumer fell Broke out of red ocean by creating wireless transmission of voice, text, data, and pictures innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Strategic Groups Within Industries Companies in an industry that pursue similar domain: Mercedes, BMW, and Jaguar all focus on outcompeting one another in the luxury car segment versus Economy car makers who focus on excelling over one another in their strategic group. 64 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Strategic Groups Within Industries: QUESTION What company does the author focus on? 65 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Time All industries are subject to external trends that effect their businesses over time Internet “Going Green” to protect the planet Most companies adapt incrementally / passively as trends emerge focusing: projecting the trend itself paceing themselves to keep up with the trend. HOW: Get out of Red Oceans and develop a Blue Ocean strategy? 66 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Time Example Internet buying text books online cheaper to purchase books online trend increasing - local stores beware: will have to see how they can create a blue ocean strategy 67 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Time Example protecting the planet. Many companies adapted to consumer needs such as creating hybrid vehicles. however these companies are still competing within the red ocean. 68 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Time Blue oceans arise from seeing how the trend will change value to customers - Three Principles: Trends must be decisive to your business Trends must be irreversible Trends must have a clear trajectory Example: The Asian Crisis of 1997 vs. the Euro 69 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Time Digital music downloading: Apple’s iTunes Legal, easy to use, flexible While more digital music stores enter the market, Apple kept a blue ocean with the iPhone. High-Speed data exchange: Cisco Systems File share downloading by kazaa, limewire, and napster was rapidly growing; however - illegal, sound quality was bad, few complete cds 70 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Reconstructing Market Boundaries Look Across: Time Questions What trends have a high probability of impacting your industry, are irreversible, and are evolving? How will these trends impact your industry? Given this, how to start unprecedented customer utility 71 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ From Head-to-Head Competition to Blue ocean Creation Head-to-Head Competition Blue Ocean Creation Industry Focuses on rivals within its industry Looks across alternative industry Strategic group Focuses on competitive position Within strategic group Looks across strategic groups within industry Buyer Group Focuses on better serving the buyer group Redefines the industry buyer group Scope of product or service offering Focuses on maximizing the value of product & service offerings within the bounds of its industry Looks across to complementary product and service offerings Functional emotional orientation Focuses on improving price performance within the functional-emotional orientation of its industry Rethinks the functional-emotional orientation of its industry Time Focuses on adapting to external trends as they occurs Participants in shaping external trends over time 72 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ The Big Picture, Not the Numbers 73 The Big Picture, Not the Numbers BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ Visual Awakening Compare your business with your competitors’ by drawing your “as is” strategy canvas. See where your strategy needs to change. 74 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR OF INNOVATION™ innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ The Big Picture, Not the Numbers Visual Exploration Go into the field to explore the six paths to creating blue oceans. Observe the distinctive advantages of alternative products and services. See which factors you should eliminate, create, or change. 76 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ The Big Picture, Not the Numbers Visual Strategy Fair Draw your “to be” strategy canvas based on insights from field observations. Get feedback on alternative strategy canvases from customers, competitors’ customer, and noncustomers. Use feedback to build the best “to be” future strategy 77 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ The Big Picture, Not the Numbers Visual Communication Distribute your before-and-after strategic profiles on one page for easy comparison. Support only those projects and operational moves that allow your company to close the gaps to actualize the new strategy. 78 innovation.uccs.edu BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ In My view it should be Big Picture THEN the numbers innovation.uccs.edu The Big Picture, THEN the mumbers BACHELOR BACHELOR OF OF INNOVATION INNOVATION ™ ™ If you are driving innovation from below.. good visuals like value-curves are often key to getting quick buy-in from upper management. But some (what MB type are they??) will quickly want to drill down into supporting data so be ready to back it up. 80 innovation.uccs.edu