Family-Driven Strategies to Improve Juvenile Justice
advertisement

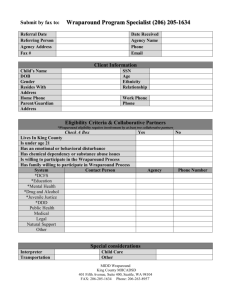
Family-Driven Strategies to Improve Juvenile Justice Santa Cruz County 2008 JDAI results, including a significant drop in detention… Average Daily Population 50 46.7 40 52% decrease 30 22.5 20 10 0 1996 2007 …a significant reduction in DMC… Latino Representation in Juvenile Hall vs. General Population 5% gap 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 64% 30% gap 55% 50% 34% 1997 Latinos in Juv. Hall 2007 Latinos in Gen. Pop. ...along with a drop in placements and institutional commitments … 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Placements Ranch Camp CYA Juvenile Hall ADP* 1996 104 35 11 50.67 2007 61 11 1 22.5 1996 2007 …could not be sustained without home-based and community solutions supported by family focused Juvenile Justice Practices. Premises of Juvenile Justice Practices that Support Youth and Family Centered Practice • The Justice System does not hold the wisdom of youth, families and communities • Youth problems do not develop in isolation, therefore solutions should be context focused not offender focused and retributive. • Reliance on authoritarian and confrontational approaches is unnecessary, unproductive and will produce resistance and mutual disrespect. • Partnerships with youth, families and communities produce better services, outcomes, promote public safety and are more cost effective. Why Include Families ? • Better and more sustainable outcomes are achieved when youth and families are involved in the planning • More informed decision making • Reinforces that caregivers should maintain the lead in raising their children • Transparency encourages trust in the JJ system • Can break destructive intergenerational cycles • Creates a cooperative partnership rather than an adversarial relationship • Meets best practice standards Go Beyond… Satisfaction Surveys Family Engagement Services Create a Family Friendly Culture • • • • • • • • Family Conferencing Court Video Wraparound services Family partners Cara y Corazon curriculum Placement Screening Committee Facilitated crisis intervention Victim – Offender mediation for domestic disputes • Family Resource Center Contracts • Youth Re-entry Team • Services to Children of Incarcerated Parents Require Contractors to Put Families and Youth First • Work with CBO’s who are in the same community as your clients and share your values • Provide training for CBO’s on EBP’s, strength based work, the court system, etc. • Be clear with CBO’s about expected outcomes. Examples from a Santa Cruz contract – “CAA will provide primary attention to youth in secure custody to expedite safe release to a less restrictive environment” – “CAA will provide services in a youth and family centered manner, in the primary language of the family” Youth Re-entry Team • Parents and youth self-refer to services – Four CBO’s – Specializing in gang related issues, career development, family stresses, school barriers, LGBT struggles, and physical and mental health linkages to the community – In conjunction with Children’s Mental Health Involve all Stakeholders in Critical Decisions Placement Screening Committee • Interdisciplinary team meets 2x’s per week • Team consists of: – Children’s Mental Health: • Detention Mental Health Clinician, • Supervising MH Clinicians for Wraparound and Family Preservation Programs – Probation: • Probation supervisors for residential placement and Wraparound and Family Pres Programs • Probation manager • Presenting Probation Officer – Community Based Organization – Youth Services • Parent partner – – – – Parent’s or caregivers and possibly other family Youth Health Educator Other support people – ex: Clergy, school personnel, neighbor What Cases are Screened ? • Any youth who might be escalated to the following dispositions in the system: – – – – Wraparound or Family Preservation Residential Placement Ranch Camp Intensive Mental Health Caseload and Evening Treatment Center SB 163 Wraparound Services – Target population are deeply entrenched interagency involved families – high criminality, dual diagnosis, high need – Key principles: • • • • • • • • Family voice and choice Culturally responsive and community based services Team approach/collaboration Involves natural supports Individualized family plans Outcome based – goals remain at forefront Strength based and needs driven Addresses all life domains Wraparound In Action : • Staff – Child and Family Team: – Child and Family Team Facilitator – coordinator of services – Parent Partner – focus on parent – Family Specialist – focus on youth – Probation Officer as team member – Natural Helpers and family members Lessons Learned • Families know more about themselves than we can ever hope to • Parents need to be supported so they have sufficient resources to care for their children • Don’t ever give up – recovery can be a long, grueling process • There is not a one-size-fits-all solution – responsivity needs to be tied to risk/need • Family centered work is also culturally competent and helps address DMC • Collaboration with other family and child serving agencies is key • It’s not just about family system change – formal system must undergo self examination and change