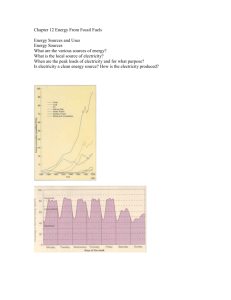
File - tallisA2units
advertisement
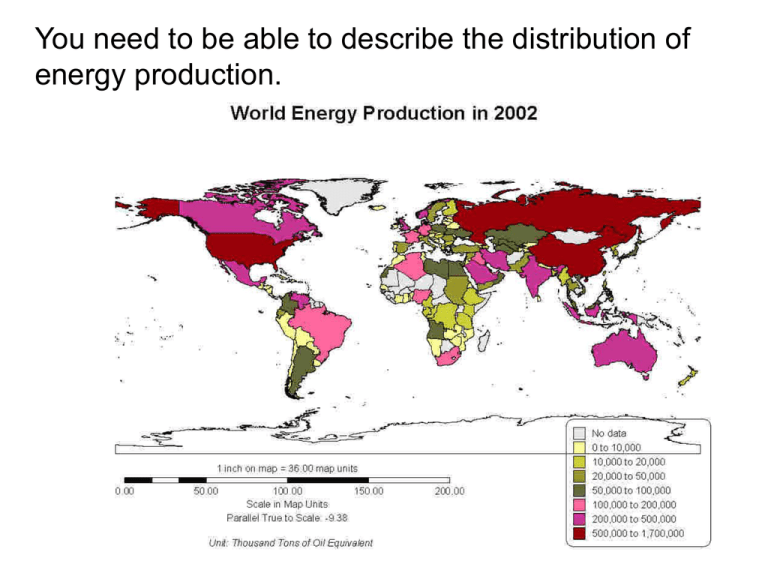
You need to be able to describe the distribution of energy production. Topic 1= Energy Security The topic is split into 3 key questions: 1. To what extent is the world's energy 'secure' at present ? • Energy supply, demand and security 2. What are the potential impacts of an increasingly 'energy insecure' world? • The impacts of Energy Insecurity 3. What might the world's energy future be? • Energy Security and the future Energy-Issues-Contested Economic viability of energy sources Offshore wind Onshore wind European biodiesel USA Corn ethanol Sugar cane ethanol Tar sands Coal to liquids Oil Shale Deep water oil Conventional Oil other Conventional Oil Middle East 0 20 40 60 80 100 Oil price US$ 120 140 160 Planet…. Energy-Issues-Contested Planet…. 1. Supply-demand and security 2. Impacts:environmental and socio economic issues 3. Futures- alternatives, renewables, conservation, efficiency…….. Oil exploration Arctic Expansion nuclear power UK eg Sizewell Energy crisis - oil peak Kingsnorth coal powerstation + Grenpeace protest Economic viability of energy sources Offshore wind Onshore wind Hybrid car- less energy European biodiesel USA Corn ethanol Sugar cane ethanol Alternatives for future? Tar sands Coal to liquids Oil Shale Deep water oil Conventional Oil other Conventional Oil Middle East 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Oil price US$ Renewables: wind farm Thames Estuary ARRAY and wave: Anaconda system Key supply player: OPEC What does it mean to be energy secure? • To have ENERGY SECURITY means to have access to reliable and affordable energy sources • E.g. Russia • Countries that do not have this are said to be ENERGY INSECURE Key terms – learn and use Achieving Energy Security Factors important are: • Control over supplies • Control over prices • Having a variety of energy sources to call on • Political stability (in supply region as well as demand region) Energy security can be threatened by: • Rapid increase in prices (oil 2004) • Instability of suppliers (Georgia 2008) • Manipulation of supply and process • Attack on infrastructure (terrorism) • Competition from expanding economies e.g. China • Environmental legislation which adds to the costs of finding, transporting and processing the resource Energy security can be improved by: • Greater energy efficiency • Greater energy self-sufficiency • Decentralization of energy production • Short term stockpiles (90 days) Energy Issues across the World – which statement goes where? •Rapidly growing demand; use of pollution sources such as high sulphur coal; health impacts; impact on global fossil fuel prices •Reserves; questions of developing these in the Arctic, Antarctic and other sensitive areas •Energy poverty; dependency on foreign TNCs to exploit supply (Nigeria, Sudan) •Dependency; wastefulness; lack of fossil fuel supply (energy insecurity) •Supply security; role of unstable regions in fossil fuel supply; link between nuclear power and weapons. •Huge surplus; inefficient use; energy as a political weapon? Energy Issues across the world Reserves; questions of developing these in the Arctic, Antarctic and other sensitive areas Dependency; wastefulness; lack of fossil fuel supply (energy insecurity) Huge surplus; inefficient use; energy as a political weapon? Key issues for learning Energy poverty; dependency on foreign TNCs to exploit supply (Nigeria, Sudan) Supply security; role of unstable regions in fossil fuel supply; link between nuclear power and weapons. Rapidly growing demand; use of pollution sources such as high sulphur coal; health impacts; impact on global fossil fuel prices