Cells in Action
advertisement

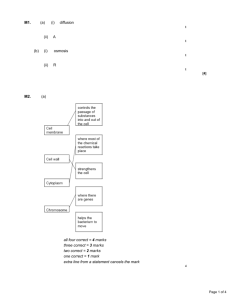
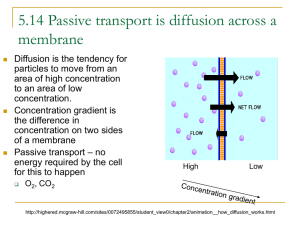
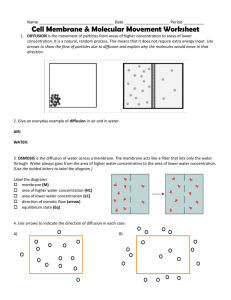
Movement of Materials in the Cell Diffusion Osmosis • Each individual cell exists in a liquid • environment. The presence of the liquid environment makes it easier for materials such as food, oxygen, and water to move into and out of the cell. The exchange of materials between a cell and its liquid environment takes place at the cell’s membrane. Diffusion: Passive transport • The process by which molecules of a substance • move from areas of higher concentration of that substance to areas of lower concentration. Since molecules are in constant motion, the cell does not have to use any energy during diffusion (passive transport). What factors determine whether diffusion occurs across a membrane? • First Factor: If two substances are present in unequal amounts on either side of a membrane, the substance will tend to move toward the area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. - concentration for both are the same. • Factor 2: Permeability. If a particular substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, then that membrane is permeable to that substance. • Permeable: substance can pass through • Impermeable: substance cannot pass through. • Semi-permeable membrane - a physical barrier which only allows certain particles to pass through it; membranes of organelles and cells are semi-permeable. Osmosis • Osmosis is defined as the diffusion of water through a • selectively permeable membrane which separates two solutions of different solute concentrations. Water always flows from a higher water concentration to a lower water concentration. • Water molecules pass through most cell membranes very rapidly. Solution: two parts • Solvent: Universal solvent is water. It is what the substance is dissolved into. The lab: solvent = water • Solute: The substance that is being dissolved. The lab: salt = solute Three types of solutions: • Always compare two solutions against each other. – Isotonic: both solutions are equal. Same concentration of both substances – Hypotonic: lower concentration of the dissolved substance – Hypertonic: higher concentration of dissolved substance The Lab: • Diffusion, Osmosis or both? • Questions: • What do you see happening in the water when you first place the pig intestine into the beaker? • You should have observed the sugar moving from the inside of the intestine into the beaker. • Did you observe any change in the color of the water? If yes, what does that prove? • Water may have gotten cloudy, however based on 10 minutes may not have observed. It proves that sugar diffused through membrane. After heating the test tube and adding Benedict’s solution, did you observe any change? If yes, what was the change and why did this change occur? • The solution turned orange. Proved the presence of sugar. Darker the orange = more sugar. After placing iodine into the beaker, was there any change in either the pouch of the beaker solution? If yes, what was the change and why did it occur? • Iodine diffused into the membrane and turned the starch purple/black. If the solution in the beaker changed from a cloudy precipitate into a dark purple/black then starch was in the beaker. • Pouch not tied tightly or not rinsed off well enough. Conclusion: • The sugar diffused out and the iodine diffused in. The starch molecules were to large to pass through. The water molecules are classified as a polar covalent bond that has a certain electronegativity that did not allow the water molecule to pass. • Selective permeability. Quiz Tomorrow: • Know the 3 types of solutions. • Know the 3 types of permeability. • Osmosis/Diffusion • Carrot/egg lab • Pig intestine lab Energy in the Cell Photosynthesis Cellular respiration Producers: green plants • Change light energy into chemical energy that the plant could use. • To carry out photosynthesis , plants take in water and carbon dioxide. Light energy is captured by chlorophyll (contained in the chloroplast) to aid in the chemical change. Light Water + Carbon dioxide --------------Sugar + Oxygen Chlorophyll • Oxygen is a waste product for the plant. • Some sugar used rest is stored. Cellular respiration • Once the food is made it must be broken down. Respiration is that process. • The breakdown of food occurs in the mitochondria. During respiration, oxygen combines with glucose to release stored energy.