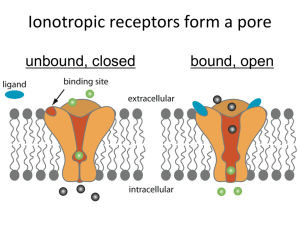
Drainage System Design and Layout
advertisement
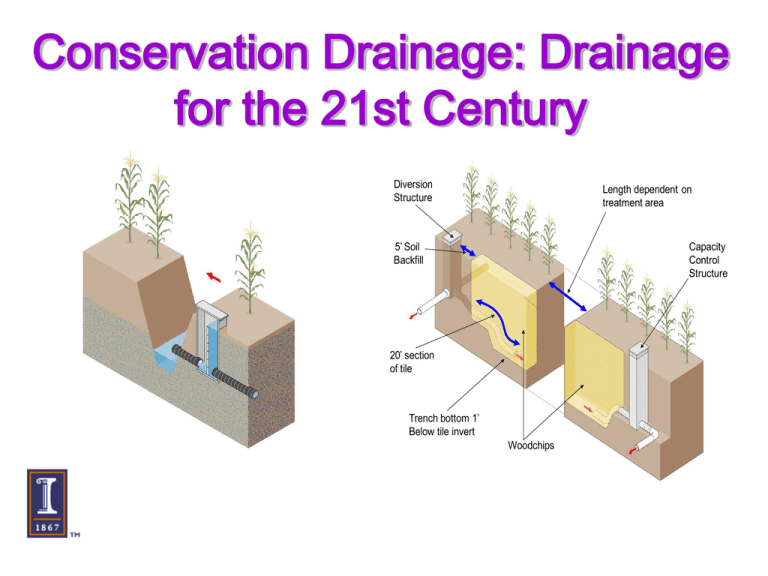
Conservation Drainage: Drainage for the 21st Century Diversion Structure Length dependent on treatment area 5’ Soil Backfill Capacity Control Structure 20’ section of tile Trench bottom 1’ Below tile invert Woodchips The Nitrate Saga 1890s Scientists sound alarm about need for new source of nitrates Fritz Haber Carl Bosch Nutrient contributions to the Gulf, by State Distribution of Subsurface Tile Drainage in Illinois 3-4 million ha (6-10 million acres) drained with subsurface tile in Illinois This comprises some of the most productive agricultural land in the US. HYDROLOGIC CYCLE (with tiles) 7.2 km/km2 Mutabaruka The solutions that you seek will not be found in the streak of a pen, or even one thousand words of mine. Nitrate Reduction Techniques Altering Nitrogen Application Amounts Altering Nitrogen Application Timing Edge-of-Field Treatment Optimizing Drainage System Conservation Drainage The incorporation of environmentally friendly practices and structures into existing drainage infrastructure Minnesota Department of Agriculture Conservation Drainage The optimization of drainage systems for crop production, water quality and water harvesting benefits Drainage Water Management Conservation Drainage Subsurface Bioreactors Depth/Spacing Modifications Convenient and Cost-Effective Golden Rule of Drainage • Only release the amount water necessary to insure trafficable conditions for field operations and to provide an aerated crop root zone – any drainage in excess of this rule likely carries away nitrate and water that is no longer available for crop uptake Drainage Water Management Manual Gate Structure Automated Gate Structure Float Structure Drainage Water Management Guidelines Period Production Activity Control Setting* (inches) Nov.1-Mar.15 Fallow 6-18 Minimize drainage outflow and encourage denitrification Mar. 15 – Apr.15 Tillage, corn seedbed preparation, planting 36-48 Just deep enough to provide trafficability and good conditions for seedbed preparation. Corn establishment, early growth 24 – 30 Deep enough to promote good root development. Comments** Apr. 15 – May 15 Nitrogen sidedressing Just low enough to allow trafficability 24-36 May 15 - Aug. 15 Corn development and maturity 18-24 Temporary adjusting during wet periods Aug.15 - Oct. 31 Harvesting, tillage 36-48 Lower enough to provide trafficabilty – in an unusually dry season, control can be 3 to 6 inches higher; – in an unusually wet season, control should be 3 to 6 inches lower; – in coarse-textured soils, trafficability can be provided with the water table approximately 6 inches higher. Managed Drainage - Winter Conservation Mode for Fallow Season Managed Drainage - Spring Full Drainage Mode for Planting Season Managed Drainage -Summer Shallow Drainage Mode for Growing Season Managed Drainage - Fall Full Drainage Mode for Harvest Season Drained Volume (inches) . Potential Water Available from Drainage Management 3 Sable 2.5 2 ~ 1.5 inches 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 12 24 36 48 Depth to Water Table (inches) . Source: Based on DRAINMOD Simulations 60 Water Deficit Stress DWM Benefits • Reduces Nitrate Concentrations in Effluent – 30-95% reductions annually • Increased Yield – 76% higher yield in a dry year • Lower Concentrations of Other Pollutants Required Information for Economic Analysis of DWM System •Drainage Costs •Added Revenue •Capital Costs •Timeliness Benefits Drainage Water Management Hume 2004 Flow Depths (cm) From a Paired Drainage Site 14 13.4 12 10 FreeDrainage Drainage 8 Free Managed ManagedDrainage Drainage 6 10 4 2 3.9 3.4 3.6 0.3 0 Mar.-Oct . Nov.-Feb. Annual Hume 2006 1.4 20 18 1.2 1.0 14 12 Flow (cm/day) 0.8 10 0.6 8 6 0.4 4 0.2 2 0.0 11/19/05 0 1/8/06 Free Drainage 2/27/06 4/18/06 Managed Drainage 6/7/06 Cumulative Flow (cm) 16 Long Term Nitrate Trends: 2005 2005 T ile Nitrate C onc entrations at Hume Nitrate-N C onc entration (ppm) 25 20 15 10 5 0 11/9 12/29 2/17 F ree Drainage 4/8 Managed Drainage 5/28 7/17 Long Term Nitrate Trends: 2008 2008 T ile Nitrate C onc entrations at Hume Nitrate-N C onc entration (ppm) 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 2/2 2/22 3/13 4/2 F ree Drainage 4/22 5/12 Managed Drainage 6/1 6/21 7/11 Free Drainage 11.3 acres 50-70 ft Spacing Managed Drainage 13.1 acres 50-70 ft Spacing Nitrate-N (mg/L) Kinderhook Site System Layout for Drainage Water Management Layout Costs Cost Differential: $50/acre