Works Contract
advertisement

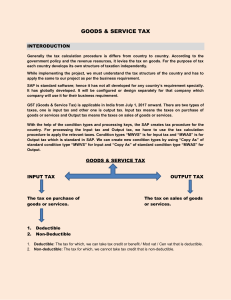
Presented By CA Swatantra Singh, B.Com , FCA, MBA Email ID: singh.swatantra@gmail.com New Delhi , 9811322785, www.caindelhiindia.com, www.carajput.com WORKS CONTRACT TAX Rajput Jain & Associates Background Works contract under VAT Inter-State Works contract Works contract under Service Tax Upcoming Legislation – GST 3 Contents Background 4 Constitutional Amendment 46th Amendment made to the Constitution from February 2, 1983 Outcome of the above: • Permitted the States to levy tax on the Sale of goods involved in execution of all work contract. • States have been given power to separate the contract between work and the labour and services • Identifying whether the goods retained their original identity after the work was executed or had been merged, integrated or becoming part and parcel of the works, buildings etc. All the States to power under this Constitution Amendment and made Amendments in their respective Sales Tax Law to levy tax on such sale either by making separate legislation or by amendment in existing sales tax law 5 Basic Sale of Goods vis-à-vis Works Contract Sale of Goods Works Contract Taxed as actual Sale : Seller & Buyer Taxed as Deemed Sale : Contractor & Contractee Absolute property of the maker when produced / manufactured. Later on sold to buyer In WC, it is never an absolute property of the maker. Materials used in WC – may be makers absolute property The sale is ‘chattel as a chattel’ i.e. ‘goods’ are sold as ‘goods’ In WC, article produced becomes the property of buyer without first becoming property of the maker. Primary function - supply of materials Incidental - work or service Primary function - work and labour Incidental - materials are supplied TDS provisions are not applicable TDS provisions are applicable 6 Types of contract • Supply of Materials and Labour – Works Contract (e.g. Construction of a building, roads, bridges, dams etc.) • Supply of labour and supply of materials is incidental to the contract – Not a Works contract (e.g. Painting, cleaning, overhauling, lubricating, greasing of an old machinery etc.) • Pure Labour Contract – may involve materials for executing contract – Not a Works contract (e.g. Semi-finished material supplied to Jobworker for further processing, tailor doing stitching work) WCT under VAT 8 Works Contract under Gujarat VAT • Section 2(23) : Definition of Sale includes transfer of property in goods, (whether as goods or in some other form) involved in the execution of a works contract Government of Gujarat has notified list of works contract Notified works contractList_of_Works_Contract.pdf Works Contract under Gujarat VAT Act Valuation options under Works Contract Actual Labour deduction Composition Standard Labour deduction Calculation of Sale Price of Works Contract Actual labour deduction – Following deductions are allowed in case books of accounts are maintained (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Labour charges & Service charges Sub-contract charges Planning, designing and architect's fees Machinery on hire and tools used Cost of consumables, the property in which is not transferred Cost of establishment to the extent to it is relatable to the supply of labour and services (g) Other similar expenses relatable to the supply of labour and services (h) Profit earned by the contractor to the extent it is relatable to the supply of said labour and services Intention of the government is to levy tax ONLY on Material component Calculation of Sale Price of Works Contract Indivisible Contract – in case separate books of A/c’s are not maintained – Lump sum deductions are allowed Description of Works Contract Percentage of Deduction Construction, improvement, repair of any building, road, bridge, dam, canal or other immovable property 30% Installation, fabrication, assembling, commissioning or repair of any P&M 15% Installation, fabrication, assembling, commissioning of Air conditioner, air cooler 10% Assembling, fitting, re-assembling, improving, producing, repairing, furniture, fixtures (interior decoration) 20% Construction, fabrication, assembling, commissioning, repairs of bodies on chassis of motor vehicles 20% Overhauling or repairing or dismantling of any motor vehicles, vessels of every description meant for plying on water or any vessel propelled by mechanical means, any air craft, etc 20% * Amount to be deducted from the contract price (expressed as a percentage of contract 12 Calculation of Sale Price of Works Contract Indivisible Contract – in case separate books of A/c’s are not maintained – Lump sum deductions are allowed Description of Works Contract Percentage of Deduction Fitting out, assembling, altering, ornamenting, re-assembling, blending, finishing, furnishing, improving, processing, otherwise treating, adapting or fabricating of any goods 15% Erection, installation and commissioning of wind turbine generator 30% Fixing of marble, slabs, polished granite stones and tiles other than mosaic tiles 20% Fixing of sanitary fittings and plumbing 15% Painting and polishing 20% Laying of pipes excluding plumbing 20% Tyre retreading 30% * Amount to be deducted from the contract price (expressed as a percentage of contract pri 13 Calculation of Sale Price of Works Contract Indivisible Contract – in case separate books of A/c’s are not maintained – Lump sum deductions are allowed Description of Works Contract Percentage of Deduction Supply of goods in providing know-how, designs, labour, supervision, inspection, training or other services with any of the operations specified above 20% Dyeing and printing of textiles 30% Printing contracts 30% Any other works contract 20% To arrive at Taxable turnover above rates are applied after deducting payment made to specialised contractor, sub contractor (discharging liability separately) 14 Calculation of Sale Price of Works Contract Composition Scheme – For contractors who do not wish to pay tax based on the specific formula or after considering the lump sum deductions •Rate of tax is 0.6% or 2% of the total contract value as under: 0.6%- Construction contracts relating to roads, buildings, bridges, pipeline laying, dams, etc. 2% - Other contracts including contracts for erection, installations etc. • Restrictions: ITC not available on purchases Contractor not eligible to issue VAT Invoice and also can not charge tax in the invoice - Therefore, no ITC is available to the employer Cannot import goods on interstate basis or branch transfer basis TDS Rate under GVAT Person responsible for payment exceeding Rupees 1 crore for works contract is responsible for deduction of tax at prescribed rates TDS Rate : 0.6% in case of construction contract and 2% in case of others Works Contractor is mandatorily required to obtain TAN No. from Commercial Tax Department. Pay the tax to the Government within statutory due date in Form-207 and issue certificate in Form-703 to the contractor evidencing the deduction of tax at source. File a return within 30 days of end of quarter in Form-704 and also file a annual statement within 30 days from end of financial year. Gujarat VAT – Compliance at a Glance TDS Rate 0.6% in case of construction contract and 2% in case of others Remittance of tax deducted To be deposited to within 22 days in Form 207 from the end of the respective month TDS Certificate to be issued Certificate to be issued in ‘Form 703’ Records to be maintained for TDS by Contractee In ‘Form 705’ on monthly basis TDS Return to be submitted In ‘Form 704’ within 30 days from the end of the quarter Monthly Return to be submitted In ‘Form 201’ within 30 days including e return for specified dealers Annual Return to be submitted In ‘Form 205’ within 9 months from the end of the year including e return for specified dealers 17 Gujarat VAT – Input Tax Credit • ITC available on all inputs used in works contract other than composition method subject to fulfilment of conditions • Broad Restrictions on ITC: ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ CST purchases Capital goods used in works contract Lease goods Goods purchased from Lump sum dealer Goods not connected with business Vehicles, equipments, accessories or spare parts Fuel used in motor vehicles Goods used as fuel in generation of electrical energy • ITC to be reversed by 4% in case of branch transfer 18 Inter State Works Contract 19 Inter-State Works Contract • Finance Act 2002, had made certain amendment in the Central Sales Tax Act 1956, to include inter-state sales of goods involved in the execution of works contract taxable from May 11, 2002 clause (ja) in Section 2 of the CST Act was inserted which define work contract as:A contract for carrying out any work – Which includes assembling, construction, building, altering, manufacturing, processing, fabricating, erection, installation, fitting out, improvement, repair or commissioning of any movable or immovable property. • Citus of taxation will come only when: (a) Contractor executes works in another states and 20 (b) The property over the goods passes from him to his customer either by transfer of document of title over the goods when they are in transit from his state to another state or directly on their incorporation in the works. How to determine the taxable turnover? Proviso to Section 2(h) of the CST Act provides the meaning of sale price as under:‘sale price’ in relation to transfer of property in goods (whether as goods or in some other form) involved in the execution of a works contract, shall be determined in the prescribed manner by making such deduction from the total consideration for the works contract as may be prescribed and such price shall be deemed to the sale price for the purpose of this clause. However no deductions has been prescribed under the CST Act . Section 8A of the CST Act does not prescribe any mechanism regarding how to determine the turnover in case of a works contract. Section 13 (1)(aa) of the CST Act empowers the Central Government to make rules providing for “the manner of determination of the sale price and the deductions from the total consideration for a works contract under the proviso to Section 2(h)”. However no rules has been framed by the Central Government in this regard. Section 13 (3) the CST Act empowers the State Government to make Rules, not inconsistent with the provisions of this Act and the Rules made under sub-section (1), to carry out the purpose of this Act 21 How to determine the taxable turnover? However no specific rules have been made by the State Government in respect of an inter-state works contract. So, what are the remedies available in this matter Recourse needs to be taken to the Supreme Court judgment in the case of “M/s. Mahim Patram Private Limited v. Union of India (2007)”. 22 Brief facts of the case:• Appellant was engaged in the printing of question papers for various universities and boards situated outside the State of Uttar Pradesh; • As the goods have moved from one State to another, it was an interstate works contract; • The appellant had contended that in absence of the provisions for determining the ‘sale price’; taxable turnover cannot be computed under Section 8A and CST cannot be levied. How to determine the taxable turnover? The learned Supreme Court decided as under: • Section 9(2) of the CST Act empowers the assessing officer to ‘assess, reassess, collect and enforce payment of tax, including any interest or penalty payable by a dealer under this Act as if the tax, interest or penalty payable by such dealer under this Act is a tax, interest or penalty payable under the general sales tax law of the State’. • Thus the powers conferred and the procedures laid down under the State sales tax laws would, therefore be applicable for the purpose of carrying out the assessment under the CST Act. 23 How to determine the taxable turnover? • 24 In view of the above ruling, provisions made in a particular State (from where the goods are moving) for determining the taxable turnover and the sale price in case of a works contract would be applicable accordingly in case of an inter-state works contract . Rate of Tax Applicable After determining the ‘sale price’ and the ‘turnover’ as per the provisions of the State Act, rates of CST prescribed under Section 8 of the CST Act would be applicable. Section 8 of the CST Act provides the following rates in case of an interstate sale • If sale is made to a registered dealer against Form ‘C’ – 2% • If sale is made to a registered dealer without form ‘C’ – rate applicable in the respective State • If the sale is made to an un-registered dealer – rate applicable in the State from where the goods are moving in the course of inter-state trade or commerce. 25 Works Contract under Service Tax 26 Following are relevant taxable services involved in the Works Contract Description of Service Taxable w. e. f Commercial or Industrial Construction services 10/9/2004 Erection, Commissioning or Installation Services 1/7/2003 Construction of Complex Residential services 18/4/2005 Works contract services 1/6/2007 Works Contract service – Inserted from 1st June 2007 Section 65(105)(zzzza) of the Finance Act defines taxable service as: “any service provided or to be provided to any person by any other person in relation to the execution of a works contract, excluding works contract in respect of roads, airport ports, railways, transport terminals, bridges, tunnels and dams” Explanation to this sub-clause defines ‘works contract’ : Works contract means a contract wherein – Transfer of property in goods involved in the execution of such contract is leivable to tax as sale of goods and such contract is for the purpose of carrying out specified works. Works Contract service – Inserted from 1st June 2007 Specified works are: (a) Erection, commissioning or installation of plant ,machinery equipment or structures, whether pre-fabricated or otherwise, installation of electrical and electronic devices, plumbing, drain laying or other installations or transport of fluids. heating ,ventilation on air-conditioning related pipe work, duct work and sheet metal work, thermal insulation, sound insulation, fire proofing or water proofing, lift and escalator ,fire escape staircases or elevators or (b) Construction of a new building or a civil structure or a part thereof or of a pipeline or conduit ,primary for the purpose of commercial or industry or (c) Construction of a new residential complex or a part thereof or (d) Completion and finishing services, repairs, alteration, renovation or restoration of or similar services in relation to (b) and (c) (e) Turnkey projects including, engineering, procurement and construction or commissioning (EPC) projects. Works Contract service – Inserted from 1st June 2007 Two essential conditions for taxability under works contract service are – There must be transfer of property in goods involved in the execution of specified works contracts Such transfer is leviable to tax as sales of goods. Appropriate Classification under Service Tax Legislation If the specified work contract involves transfer of property and on which VAT/Sales tax is payable the service will be taxable under Works contract Service If the Contract is a simple service contract i.e. no material is involved or even if some material is involved, VAT/Sales tax is not payable the service would be classified under respective category of Construction or Erection and Commissioning Service Works Contract Service Valuation options Computation as per Valuation Rules Composition Valuation of works contract service Computation as per Valuation Rules Value of works contract shall be equivalent to gross amount charged for the works contract less value of transfer of property in goods involved in execution of the said works contract. Along with value of Material VAT/CST paid to be deducted. Following to be included : (a) Labour charges & Service charges (b) Sub-contract charges (c) Planning, designing and architect's fees (d) Machinery on hire and tools used (e) Cost of consumables, the property in which is not transferred (f) Cost of establishment to the extent to it is relatable to the supply of labour and services (g) Other similar expenses relatable to the supply of labour and services (h) Profit earned by the contractor to the extent it is relatable to the supply of said labour and services (i) Other similar expenses relatable to supply of labour and services (j) Profit earned by the service provider relatable to supply of labour and services. Valuation of works contract service Computation as per Valuation Rules - Tax rate and CENVAT -Service Tax @ 10.3% to be paid on taxable value arrived -CENVAT credit on Input services and Capital goods can be availed Valuation of works contract service Computation as per Composition scheme Optional Composition scheme Service Tax (including Ed. Cess and SHE Cess) is 4.12 % of the total value of the works contract. Intimation to the department for availment of this option prior to execution of Works Contract. Once opted, can not change the option till completion of the contract. Value of free issue items also to be included in Gross Value - CENVAT credit on Input services and Capital goods can be availed Goods & Services Tax(GST) • Indicated roll-out date is April 1, 2011 36 The Gist of Proposed GST: Taxes to be subsumed Central Levies • Excise duty • Additional excise duties • Excise duty under Medicinal and Toiletries Preparation Act State Levies • Value added tax • Entertainment tax • Luxury tax • Tax on lottery, betting & gambling • Service tax • Entry tax • Additional and special additional • Surcharges and cesses customs duties • Surcharges and cesses Central GST 37 State GST What prompted the GST? • Several indirect taxes at Central and State level • Tax on tax in current Central Excise and State VAT mechanism • No harmony in rates of VAT on similar commodities from one State to another • CENVAT credit & VAT input tax set-off not comprehensive due to restrictive provisions • Break in credit chain in inter-State transactions • Multiple taxes leading to complexity in compliance 38 The Gist of GST: Uniformity in structure • 1st Discussion paper on GST released by the Empowered Committee on 10th Nov’2009 • As far as practicable there will be uniform procedures across various statutes concerning: - Chargeability - Taxable event - Taxable person - Valuation - Classification • Rules for taking and utilisation of credit for CGST and SGST would be aligned, but no cross utilisation of credit between these two taxes 39 The Gist of GST: Scope and coverage • CGST and SGST would be applicable on all transactions of goods and except: - Exempted goods and services -Transactions which are below the prescribed threshold Goods outside the purview of GST: Goods Treatment under GST Products containing alcohol Outside the purview of GST, State Government to levy taxes as at present Tobacco Products Central Government to levy excise duty on tobacco products over and above GST Outside the purview of GST, will be subject to sales Petroleum Products tax / value added tax Levied by State Governemnt and to cess, excise duty by Central Government 40 The Gist of GST: Rates and thresholds • Two-tier rate structure for both CGST and SGST - Standard rate for most goods and services - Lower rate for essential commodities and precious metals • Threshold limits: Threshold limits for : Tax CGST SGST Goods Rs. 150 Lakh Rs. 10 Lakh Services Yet to be decided Rs. 10 Lakh • Composition scheme with floor rate of 0.5% to be available for taxpayers having annual turnover below Rs. 50 Lakh 41 The Gist of GST: Input tax credit Mechanism • Input Tax Credits (ITC) CGST CGST against IGST SGST SGST against IGST IGST IGST against CGST SGST 42 The Gist of GST: Inter-State transactions • Inter-State sale of goods and services will be taxed under the innovative Integrated GST (IGST) model • IGST model would work as follows: - The Central Government would levy IGST at the rate of CGST + SGST on all inter-State sale transactions - To pay this IGST, the inter-State seller may use credit of CGST, SGST and IGST on his inputs - The inter-State purchaser may use the credit of the IGST paid on his purchases to discharge the output tax liability on his taxable supply of goods or services 43 The Gist of GST: Exports and imports • Exports would be zero-rated • Exports to processing zones of SEZ will also be zero rated - No benefit would be allowed for the sales from SEZ to Domestic Tariff Area • Imports of goods and services would be subject to CGST and SGST based on destination principle: - SGST revenue will accrue to the State where the imported goods and services are consumed - Both CGST and SGST paid on import of goods and services will be available as credit 44 Impact on businesses: Decision matrices • Product Pricing needs to reflect GST efficiency • Stock level to be maintained as on transition date • Timing of acquisition of assets • Review impact on existing contracts • Focus on core activities vs. backward / forward integration • Ascertain change in documentation and processes • Identify changes to ERP system to be GST compliant • Assess need to re-engineer tax management function 45 New dual GST: Transition matters • Treatment of unutilised tax credit balance as on transition date • Tax credit on capital goods where only partial tax credit taken in pre-GST regime • Treatment of tax already paid on goods lying in stock as on the transition date • Sales return of goods sold in pre-GST period • Taxation of contracts and services spread over pre-GST & post-GST period • ‘Change-in-law’ provisions in existing and new contracts 46 Presented By CA Swatantra Singh, B.Com , FCA, MBA Email ID: singh.swatantra@gmail.com New Delhi , 9811322785, www.caindelhiindia.com, www.carajput.com 47