4-Agustin Sanchez_session_4
advertisement

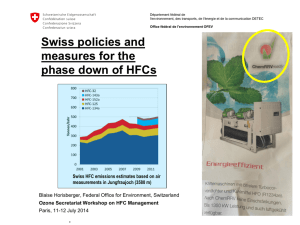
HFC WORKSHOP Agustín Sánchez Guevara Ozone Unit Coordinador.- México PARIS, FRANCE JULY 2014 HCFC and HFC Consumption in México HFC Consumption Inventory in 2012 (t) HFC-152a 7.39% HFC-125 0.09% R410A 30.66% HFC-134a 40.17% R407C 0.91% HFC-245fa 13.91% R404A 6.86% HFC-23 0.01% • In 2012, the total consumption of HFC in México was 17,223 Metric tonnes. •HFC-134a, R-410A and HFC -245fa are mostly consumed HFCs. Reference: Proklima -Consumption & emission inventory of fluorinated greenhouse gases (CFC, HCFC and HFC) in Mexico Potential Emissions of HFC in 2012 (MtCO2eq) HFC-152a, 0.6 HFC-125, 0.1 R410A, 22.9 R404A, 7.1 HFC-134a, 26.5 HFC-245fa, 8.1 R407C, 0.6 HFC-23 , 0.01 Total Potential emissions in 2012: 65.9 MtCO2 eq Reference: Proklima -Consumption & emission inventory of fluorinated greenhouse gases (CFC, HCFC and HFC) in Mexico Direct and Indirect Emissions Base line 2010 HFC emissions HFC & HCFC emissions 4.5 MtCO2eq 9 MtCO2eq Unitary air conditioning Unitary Chillers air conditioning Chillers Mobile AC Mobile ACrefrigeration Domestic Total emissions 43 MtCO2eq Indirect emissions Domestic refrigeration Commercial Refrigeration Commercial Refrigeration Industrial Refrigeration Industrial Transport Refrigeration Transport Refrigeration 34 MtCO2eq • 43 MtCO2 out of 750 MtCO2eq • Contribution of HFC emissions to overall GHG emissions: 5.7 % National Policies for the Control of HFC’s GENERAL LAW OF CLIMATE CHANGE INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK NATIONAL SYSTEM OF CLIMATE CHANGE PLANING National Strategy of Climate Change FINANCE Climate Change Fund INSTRUMENTS • Emissions Inventories • Financial instruments National Standards National Emission Registry • • Special Program of Climate Change State Program of Climate Change ASSESSMENT Coordination and Assessment LAW ENFORCEMENT Penalties NATIONAL STRATEGY OF CLIMATE CHANGE, 10, 20, 40 Energy generation form clean sources www.encc.gob.mx Resilience in Social Groups Energy efficiency Sustainable Cities: Mobility, Waste, Buildings Resilience un Production Systems Best practices: agriculture and forestry Medium and Long term 10, 20, 40 years Resilience in ecosystems Phase Down of Short Life Climate Pollutants ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION OF CLIMATE CHANGE PILLARS OF CLIMATE POLICY Transverses Policies Fiscal Policies, Economic Instruments I&D Climate Culture MRV International Cooperation Addressing effects of Climate Change and Develop a Competitive , sustainable and low-carbon economy. Action Lines M5.1 To promote the elaboration of regulations in order to reduce the emissions of short-lived climatic pollutants such as CFCs, HCFCs and HFCs. M5.5 To accelerate the penetration of refrigerant with low global warming potential in different sectors including conditioning airs, refrigeration, foams, handling and final disposition of HFCs. M5.6 To reduce leaks and encourage the correct handle and final disposition of HFCs. Special Program of Climate Change PECC 2013- 2018 Objective 4. To reduce the emissions of short-lived climate pollutants, promoting co-benefits of health and wellness. Strategy 4.3 To control the emission of refrigerant with high global warming potential. 4.3.1 Contain and destroy HFCs refrigerants by replacement programs. 4.3.2 Develop a national inventory of HFC consumption by substance and by sector. 4.3.3 Develop technological feasibility projects for the sectors of commercial air conditioners and domestic and commercial refrigeration. Strategy 4.3 Develop and promote policy instruments to regulate the issuance of shortlived climate pollutants. 4.4.10 To Issue standards to control the emission of ozone depletion substances. Strategy 4.5 Promote de development of National Appropriate Mitigation Actions that reduce SLCP. 4.5.2 To encourage NAMA projects for F-Gases in domestic and commercial RAC. Grac ias Agustín Sánchez Guevara Ozone Unit Coordinador- México Tel. +52 (55) 5624 3552 agustin.sanchez@semarnat.gob.mx