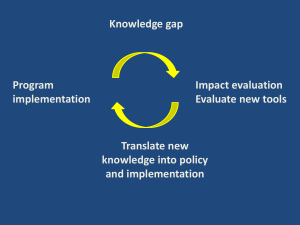
6 Community engagement for malaria elimination
advertisement

Community Engagement for Malaria Elimination Workshop 22-24 November 2011 Centara Duangtawan Hotel, Chiang Mai, Thailand APMEN (asia pacific malaria elimination network) • The Asia Pacific Malaria Elimination Network (APMEN) was established in 2009 to bring attention and support to the under-appreciated and little-known work of malaria elimination in Asia Pacific, with a particular focus on Plasmodium vivax. • APMEN is composed of eleven Asia Pacific countries (Bhutan, China, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Republic of Korea, the Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Vanuatu) that are pursuing malaria elimination, as well leaders and experts from key multilateral and academic agencies. APMEN (asia pacific malaria elimination network) • The mission of this diverse but cohesive Network is to collaboratively address the unique challenges of malaria elimination in the region through leadership, advocacy, capacity building, knowledge exchange, and building the evidence base. Aims and Objectives Workshop • To showcase current/ active examples of community engagement and participation for malaria control/ elimination within the APMEN Country Partners. • To review historical examples of community engagement and participation in infectious disease elimination programs. • To draw lessons from these examples and begin building consensus on good practice for the design of scalable models of community engagement for malaria elimination. • To explore the additional challenges of achieving synchronous cross-border community engagement for malaria elimination. National Malaria Elimination Plan Goal: Malaysia to be certified malaria free (eliminated) by 2020 Objectives: 1. Malaria elimination in Peninsular Malaysia by 2015 and in Sabah & Sarawak by 2020 2. 20% annual reduction of local malaria incidence in Peninsular Malaysia 3. 15% annual reduction of local malaria cases in Sabah/Sarawak 4. Reduction of malaria deaths - 50% annually 24.5% pop. at risk 19.7% pop. at risk 0.4% pop. at risk Malaria cases :Sarawak 42% and Sabah 40% What we want to achieve in Communication and Community Engagement • Improved knowledge and awareness among population at risk • Empowerment community mobilization to control malaria • To assist in case surveillance, vector control, early detection and prompt treatment, and response to outbreak Community engagement for malaria elimination 1 Advocacy to increase awareness and commitment to the elimination program Moving from questions of What and Why to How How? Community engagement for malaria elimination 2 Supportive environment decentralization of resources and local decision making, adequate human resources Community engagement for malaria elimination 3 Identifying and mobilising local stakeholders and social networks through consensus building processes Considering the realities of people Community engagement for malaria elimination 4 Intersectoral collaboration (Agriculture, Education, private sector, development agencies etc.) Community engagement for malaria elimination 5 Local-level action-orientated research (where there are gaps) as part of an initial scoping mission that will build community partnerships and inform community mobilisation and behaviour change communication strategies Intervention planning based on dialogue “world cafe” “world cafe” “world cafe” Community engagement for malaria elimination 6 Integration of malaria interventions with activities addressing other community health and disease priorities (Primary Health Care approach); • Village Health Representative Program (WKK) in Sarawak • Basic Health Care Volunteers Program (SPKA) in Sabah • Primary Health Care Volunteers in Peninsular Malaysia Community engagement for malaria elimination 7 Targeted implementation of locallyappropriate, multi-level behaviour change communication to maintain attention and motivation for participation in malaria elimination Unknown how intervention will be: not based on assumptions! Community engagement for malaria elimination 8 Reporting systems that support community feedback to decision makers and the flow of information on program progress to communities Basic principle: one size does not fit all Community engagement for malaria elimination 9 Monitoring and evaluation of community participation activities Learning from experiences Key BCC achievements • Excellent coordination between two country teams • Harmonized/bi-lingual IEC materials • Cross-border training on innovative approaches • Coordinated activities on special events • Use of innovative BCC approach on mobile and migrant workers i.e. use of malaria corners (engagement of private sector) Successes Malaria Elimination in Malaysia • Involvement and commitment of community leaders • Established and well organized of Village Health Workers Program Challenges Malaria Elimination in Malaysia • Inaccessible area • Sustainability of volunteer • Incentive for volunteer – Monetary incentive due to administrative issue. • Resistance and communication break-down (plantation community) Next Step… • Increasing of volunteer • Increasing the scope of volunteer roles (e.g. microscopy and other aspects of primary health care) • Extend participation within plantation community • Involvement of volunteer in environmental management (e.g. maintenance of drainage system, automatic siphon, subsoil drainage control drains and streams etc for larva control Think out of box THANK YOU