Chapter10: Agriculture
advertisement

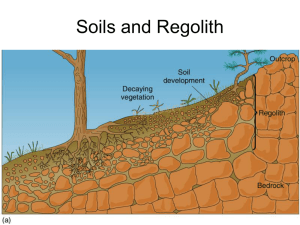
Chapter 10: Farming: Conventional and Sustainable Practices 10.1 Resources For Agriculture • Soils are complex ecosystems • Healthy soil fauna can determine soil fertility • Your food comes mostly from the A horizon Soil Formation Young Soils • Strongest Influence Is Parent Material Mature Soils • Strongest Influences: Climate, Vegetation, Drainage Never Safe From Weathering Soil Formation Processes Leaching from Surface • K, Mg, Na • Ca • Si • Al, Fe Accumulation beneath Surface • Al, Fe in Humid Climates • Ca in Arid Climates • Clay (Mechanical Movement) Soil Horizons and Profiles • Soil Horizons – Layers in Soil – Not Deposited, but Zones of Chemical Action • Soil Profile – Suite of Layers at a Given Locality • Some CSI myths – You can’t generally identify a soil from surface material – You can’t generally pinpoint a location from a soil sample Principal Soil Horizons • O: Organic (Humus) – Often Absent • A: Leaching – K, Mg, Na, Clay Removed • B: Accumulation – Absent in Young Soils – Distinct in Old Soils – Al, Fe, Clay (Moist) – Si, Ca (Arid) • C: Parent Material Limits of Soil Formation • Balance Between: – Downward Lowering of Surface – Downward Migration of Horizons • If erosion rapid or soil evolution slow, soils may never mature beyond a certain point. – Soils on Steep Slopes – Soils in Arid or Cold Climates • Extremely ancient soils may have lost everything movable Soil Classification • May be the most difficult classification problem in science • Varied Bases for Classification – Age – Parent Material – Climate and Drainage • Multiple Objectives – Scientific – Agricultural – Engineering "The 7th Approximation" • U.S. Soil Conservation Service • 12 Soil Orders "The 7th Approximation" Degree of Weathering and B Horizon Development Little Slight Moderate Large Extreme Entisols Aridisols 10,000 yrs. 100,000 y 1 m.y. Inceptisols Alfisols Spodosols Ultisols 100 years 1000 yrs. Mollisols Oxisols Soils Defined by Special Constituent Materials Andisols Volcanic Ash Histosols Peat, Organic Matter Vertisols “Self-Mixing” Clay Soils Gelisols Soils on Permafrost Mollisols Feed The World Aridisol, Kuwait Ultisols: Alabama Tennessee Soils of the U.S. Oxisol, California (a Paleosol) Soils and Organisms • • • • • Bacteria Fungi Nematodes Springtails Earthworms (not always good?) – Aerate and Mix Soil, but…. – In northern U.S. and Canada, most are exotic – Consume Organic Matter 10.2 Ways We Use And Abuse Soils • • • • Arable land is unevenly distributed Soil losses reduce farm production Wind and water move most soil Deserts are spreading around the world The Counterfeit Paradise • Year-round growing season – but --• Tropical Soils are nutrient poor • Tropical ecosystems ruthlessly recycle nutrients • Agriculture rapidly depletes nutrients – Slash and burn agriculture – Need for Fertilizer for intensive agriculture – Hardpan development 10.3 Water And Nutrients • All plants need water to grow • Plants need nutrients, but not too much – "Brawndo's got what plants crave. It's got electrolytes" • Farming is energy-intensive – Global Food Production = 6 x 1015 cal/yr = 25 x 1018 J/yr – Global Energy Use = 474 × 1018 J/yr Farming is energy-intensive • Global Food Production = 6 x 1015 cal/yr = 25 x 1018 J/yr • Global Energy Use = 474 × 1018 J/yr • Direct Agricultural Energy Use = 1% of Total or about 5 x 1018 J/yr • By Some Estimates We Use More Energy Than We Get Out • We Cannot Grow Enough Crops to replace Fossil Fuels 10.4 Pests And Pesticides • People have always used pest controls • Modern pesticides provide benefits, but also create problems – Kill beneficial organisms – Toxic to humans – Resistance • There are many types of pesticides People have always used pest controls People have always used pest controls 10.5 Environmental Effects Of Pest Controls • Pesticides accumulate in remote places • Many pesticides cause human health problems • Hormone Disruptors • “Organic” Pest Control Can Backfire – Mongooses in Hawaii to Control Rats – Cane Toads in Australia to Control Beetles – Mosquito Fish (Worldwide) 10.6 Organic And Sustainable Agriculture • • • • What does “organic” mean? Careful management can reduce pests Useful organisms can help us control pests Integrated Pest Management uses a combination of techniques 10.7 Soil Conservation • • • • Contours reduce runoff Ground cover protects soil Reduced tillage leaves crop residue Low-input agriculture can be good for farmers and their land • Consumers’ choices play an important role Natural and Human Processes • Most human processes are “natural” • What’s unnatural: – Rate of human processes – Scale of human processes – We Now Move More Material Than Natural Erosion Soil Depletion • Wind • Water • Remedies – Windbreaks – Contour plowing – Strip Cropping – No-till Agriculture Contour Plowing Strip Cropping