Arousal - Weebly
advertisement

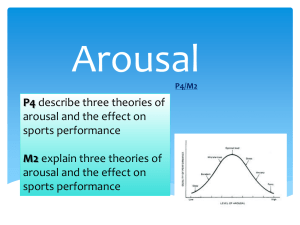
Psychology for sport performance: Anxiety & Arousal BTEC National Miss McLaren Objectives Identify the 3 theories of arousal Describe and explain the 3 theories of arousal and it’s effect on sports performance. P3 describe stress and anxiety, their causes, symptoms and effect on sports performance P4 describe three theories of arousal and the effect on sports performance M2 explain three theories of arousal and the effect on sports performance What need to be included 2 Know the relationship between stress, anxiety, arousal and sports performance Stress: definition; types (eustress and distress); causes (internal, external, personal, occupational, sports environments); symptoms (cognitive, somatic and behavioural); effects on sports performance (nervous system responses, negative mental state, loss of self-confidence and concentration) Anxiety: definition; types (state and trait anxiety); cause (negative effect of stress); symptoms (cognitive, somatic and behavioural); effects on sports performance (negative mental state, loss of self-confidence and decreased expectations of success, fear of failure) Arousal: definition; theories eg drive theory, inverted U hypothesis, catastrophe theory, individual zones of optimal functioning; effects on sports performance (improvements and decrements in performance level, changes in attention focus, increases in anxiety levels, choking 3 Theories of Arousal 1. Drive Theory 2. Inverted U Theory Catastrophe theory 3. Catastrophe Theory A Optimum arousal Extreme D Decline B Arousal C Inverted U Theory Performance increases but only when arousal is at moderate levels – any higher then it will fall away. Performance is bad if: Arousal levels are low Arousal levels are high A persons arousal level depends on 3 factors: Types of skill: Gross skill – kicking a ball requires higher levels of arousal than a simple skill e.g. throwing a dart. Which needs lower levels of arousal. Ability of the performer: expert performers need greater levels of arousal to perform at their best. Personality of the performer: extroverts need higher levels of arousal to perform well. Introverts need lower levels of arousal to perform well. Catastrophe Theory Catastrophe theory suggest a much more dramatic decline. Cognitive anxiety – worries in the mind Somatic anxiety – sweating, increased heart rate etc. Cognitive anxiety is more important than somatic anxiety in determining a performer’s reactions to high levels of stress. Catastrophe theory . Increased levels of cognitive anxiety will help performance if somatic anxiety is low A Optimum arousal Extreme D Decline B Arousal C Key features Point A- Cognitive anxiety - reaching this threshold creates a catastrophic effect Point B – performers continue with deterioration caused by over arousal May continue to Point C Point B- they get to grips with the problem performance will move towards Point D http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xG9T0z NsQqw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Eozhq5 JVhMc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TDEIUR zds1o Individual Zones of Optimal Functioning (IZOF) Individual Zones of Optimal Functioning (IZOF) states that each person has different optimal levels of arousal and can remain in that zone of arousal for a period of time. The difference between this inverted U theory and IZOF is that it is seen as bandwidth. Effects of Arousal on Sports Performance Improvements & decrements in performance level: Arousal can have a positive and negative effect on sports performance – it can be positive depending on the perception of the athlete. If changes due to arousal are seen as positive then this will have a positive effect on performance. If changes are viewed as negative this can negatively effect performance. Changes in attentional focus: During heightened states of arousal, the attentional field which focuses attention and concentration, becomes narrowed. This means that the more aroused you become, the lower the number of relevant cues you can concentrate on. Foe example, In a game of netball, when at optimal states of arousal, the centre will be able to focus on opposing player in possession of the ball as well as her position on the court and the position of other players. During heightened states of arousal, the centre maybe able to focus only on the opposition player who has the ball and may disregard other important cues. They may become more concerned with crowd noise rather than cues from the game. Effects of Arousal on Sports Performance…. Increases in anxiety levels Choking: Increases in arousal levels can lead to an increased awareness of symptoms of state anxiety, which leads to increases in both somatic and cognitive state anxiety. Whether this becomes a positive or negative influence is dependent on how the individual reacts. Occurs in high-pressure situations, such as important events like waiting to putt in the open. It is an extreme form of nervousness that negatively affects performance. It can be more apparent in presence of significant others (peers or parents). http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VyhkaBl yrOU Task Produce a poster that includes the following: A diagram and explanation of each theory Practical, sport-based examples of each theory The key differences between each theory A note about which theory you think is most likely to explain the relationship between arousal and performance and why. Peer Assessment! Swap your computer with a partner. Using the following criteria you are going to highlight where they have achieved the pass or do what they need to include to achieve the pass. Criteria definition; types (eustress and distress); causes (internal, external, personal, occupational, sports environments); symptoms (cognitive, somatic and behavioural); effects on sports performance (nervous system responses, negative mental state, loss of self-confidence and concentration) Sport specific examples of eustress and distress Hand it back 10 minutes to improve your work What is arousal? Arousal is ‘ a general physiological and psychological activation varying on a continuum from deep sleep to intense excitement’ (Gould and Krane, 1992) BORED, RELAXED, SLEEP = Low state of AROUSAL EXCITED, ANGRY, ANXIOUS = High state of AROUSAL Task Describe: Arousal Drive theory – positives and negatives Inverted U Theory – positives and negatives Catastrophe Theory – positives and negatives Include sporting examples to support your conclusions. Task: P3 – Describe stress, it’s causes and symptoms and effect on sports performance Describe: Distress & Eustress How stress is caused? What are the symptom of Stress? What are the potential positive and negative of stress on sports performance? Tip: Use examples from different types of sport e.g. rugby, snooker, cricket etc.