Performance enhancement through psychological skill training
advertisement

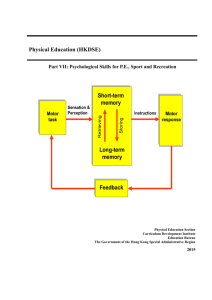
Psychological preparation for Archery Tsung-Min Hung, Ph.D. National Taiwan Normal University A little bit more about myself Ph.D. University of Maryland, College Park. Specialize in Sport & Exercise Psychology, 1996 Professor, Department of Physical Education, National Taiwan Normal University Pesident, SSEPT Treasure, ISSP Member of Sport Science Committee, ITTF Sport psychologist for Chinese Taipei athletes for Olympic and Asian Games Main topics Factors affect sport performance Psychological characteristics of peak performance Introduction to psychological skill training (stress management, concentration, self-confidence) Physiological factors Technique/Strategy Sport performance Psychological factors Psychological characteristics of peak performance Loss of fear Focused on the present Confident/Optimistic In control Enjoyment Total immersion in the activity Effortless performance Psychological skill training Definition:A training process that applies psychological skills to assist athlete’s performance and personal growth. Philosophy:Improvement = win Function:perform to your level realize your potentials Psychological skill training Principles: 1.A long-term training process 2.Education orientation 3.Individualized program 4.Trust and support by coaches and athletes Self-awareness Be aware of your physiological, psychological, technical, strategic, and environmental conditions. Understand your strength and weakness for skill development Understand your emotion states for effective emotion management Understand your arousal level for appropriate arousal management Examine your goal for enhancing motivation Conditions lead to stress Stress: a substantial imbalance b/t demand (physical and/or psychological) and response capability, under conditions where failure to meet that demand has important consequences. Results of stress: muscle tension and deterioration of coordination Narrowing of attention focus Relationship between arousal and performance Cognitive reconstruction Unreasonable reasonable thoughts Self-defeating Self-reinforcement thoughts Negative Positive thoughts Passive Active thoughts Relaxation training Progressive muscle relaxation training Biofeedback training Imagery training Meditation HR biofeedback training 組別 0.00 實驗組 控制組 控制組 8.40 -0.20 瞄 準 時 心 跳 率 減 速 斜 率 組別 8.60 實驗組 平 均 射 箭 成 績 表 現 -0.40 -0.60 -0.80 8.20 8.00 7.80 7.60 -1.00 7.40 -1.20 前測 中測 後測 前測 中測 後測 Attention in game Internal distracters: 1.Attending to past events 2.Attending to future events 3.Overanalyzing body mechanics 4.Fatigue Attention in game External distracters: 1.Visual distracters 2.Auditory distracters 3.Gamesmanship Exercises for improving concentration Learning to shift attention Parking thoughts Learning to maintain focus Searching for relevant cues Learning to shift attention Pay attention to what you hear Become aware of body sensation Turn attention to your thoughts and emotions Open your eyes, pick an object directly in front of you, practice zooming in and out. Parking thoughts This exercise is effective in eliminating negative, intruding thoughts. Use visualization to identify unwanted thoughts, write it down on paper, and place this paper in some other place(parking). Upon completion of the performance, the athlete can go back and deal with the issue by “unparking” it. Searching for relevant cues Searching the number(30/min is good) Tips for improving concentration on site Use simulations in practice Use cue words Establish routine Develop competition plans Practice eye control Stay focus in the present Overlearn skills Dos for building selfconfidence1 Do maintain a high positive precompetitive environment. Do have high expectations of all your participants. Do set realistic but challenging shortand long-term goals.. Dos for building selfconfidence2 Do provide lots of contingent, positive feedback and praise. Do structure the environment to provide early success. Do try to find individuals doing something right (as opposed to just looking for their mistakes). Don’ts for building selfconfidence1 Don’t use sarcasm and put-downs to motivate people. Don’t allow teammates or group members to belittle other team or group members. Don’t criticize individuals for inconsequential mistakes or errors. Don’t embarrass and criticize individuals at the first sight of a mistake. Don’t criticize the person, criticize the behavior. Goal setting Outcome goal: focus on a competitive result of an event, such as winning a game, earning a medal, or scoring more points than an opponent. Vs Performance goal: Focus on achieving performance objectives independently of other competitors, usually making comparisons with one’s own previous performance. Principles of goal setting Set specific goals Set moderately difficult but realistic goals Set long- and short-term goals Set performance and outcome goals Set practice and competition goals Develop goal-achievement strategies Evaluate goals Tsung-Min Hung, Ph.D. Email:ernesthungkimo@yahoo.com.tw Tel:+886-2-77343202