psychology - World of Teaching
advertisement

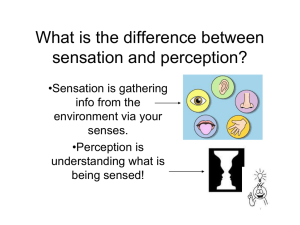
Organizational Behavior / Perception 1 When you change the way you look at things, the things you look at change. Perception “ The study of perception is concerned with identifying the process through which we interpret and organize sensory information to produce our conscious experience of objects and object relationship.” MEANING: Perceptions differ from person to person. Each individual perceives the same situation differently. Perception is a unique interpretation of the situation, not an exact recording of the situation. Perception is than sensation. more complex and much broader NATURE OF PERCEPTION It is a cognitive and psychological process. The manner in which a person perceives the environment affects his behaviour. There can be no behaviour without perception and perception lies at the base of every human action. Perception is the process by which an individual gives meaning to the environment. It occurs whenever stimuli activate the sense organs. A stimulus that is not perceived has no effect on behaviour. Perception is a process that operates constantly between us and reality. Organizational Behavior / Perception 6 IMPORTANCE OF PERCEPTION Perception plays a very important role in shaping the personality of an individual. Perception is central in interpreting the world around us. Perception affects the outcome of our behavior because we act on the basis of what we see. An understanding of perception is important to understand and control the human behavior. Because people’s behavior is based on their perception of what reality is, not on reality itself. PERCEPTUAL PROCESS Perception is an intellectual process. Perception is the basic cognitive or psychological process. Perception is subjective process. Perception is subjective because person beliefs or cultural background shape their perception. Perception consists of several sub-processes. Organizational Behavior / Perception 8 CONT… Perceptual inputs Perceptual throughputs Stimuli Receiving->Selecting->Organising>Interpreting Perceptual Outputs Actions Organizational Behavior / Perception 10 PERCEPTUAL PROCESS Perceptual inputs: Objects, Events and people. All those things in the setting where events occur or contribute to the occurrence of events can be termed as Perceptual inputs. Perceptual Mechanism: involves three elements viz. selection of stimuli, organization of stimuli and interpretation of stimuli. Perceptual Values. outputs: Attitudes, Opinions, Feelings & The result is the “ BEHAVIOUR” Organizational Behavior / Perception 12 Perceptual Error Halo effect The process by which the perceiver evaluates another person solely on the basis of one attribute, either favorable or unfavorable. Expectancy effects Extent to which expectations bias how events, objects, and people are actually perceived Organizational Behavior / Perception 13 Continue… Projection The assignment of one’s attributes to other individuals. Primacy: First impressions personal Organizational Behavior / Perception 14 Improving Perceptual Accuracy Empathize(share feelings) with others Postponed Impression Formation Compare perceptions with others Know Yourself Organizational Behavior / Perception 15 Organizational Behavior / Perception 16 Factors that Influence Perception Perception is influenced by a variety of individuals and situational factors. Physiological Differences Cultural Differences Social Roles Occupational Roles Previous Experiences Organizational Behavior / Perception 17 CONT… Self Esteem Expectations/Wishes Tunnel Vision Intense Feelings & Attitudes Stereotyping Group Pressure Organizational Behavior / Perception 18 Organizational Behavior / Perception 19 Organizational Behavior / Perception 20 Stereotype: A fixed, commonly held notion or image of a person or group, based on an oversimplification of some observed or imagined trait of behavior or appearance. The use of stereotypes is a major way in which we simplify our social world; Organizational Behavior / Perception 21 Organizational Behavior / Perception 22 Organizational Behavior / Perception 23 Basic Elements For Perception Any perceptual event has three components that are: 1.) Perceiver Any individual perceiving from event 2.) Target Thing which is being perceived 3.) Situation ATTRIBUTES OF THE PERCEIVER Several attributes unique to our personalities can affect how we see others. These include the following : i) ii) iii) Self concept Cognitive structure Previous experiences CONT… SELF-CONCEPT A person with a positive self-concept tends to perceive the positive characteristics of others. Conversely, a person with a negative self-concept is likely to focus on negative characteristics. The more accurate a person's self-concept, the more accurate his or her perceptions of others will tend to be. Organizational Behavior / Perception 26 CONT… COGNITIVE STRUCTURE: Cognitive structure, an individual's pattern of thinking, also affects perception. Some people have a tendency to perceive physical traits, such as height, weight, and appearance, more readily. Cognitive complexity allows a person to perceive multiple characteristics of another person rather than attending to just a few traits Organizational Behavior / Perception 27 ATTRIBUTES OF THE TARGET The first major influence on perception is of the target. In particular, the following attributes of target can be identified: i) Physical appearance ii) Verbal and non verbal communication iii) Intentions CONT… PHYSICAL APPEARANCE Physical appearance pals a big role in our perception of others. Extremely attractive or unattractive individuals are more likely to be noticed in a group than ordinary looking individuals. Motions, sound, size and other attributes of a target shape the way we see it. Organizational Behavior / Perception 29 VERBAL AND NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION Verbal Communication from targets also affects our perception of them. Nonverbal communication conveys a great deal of information about the target. The perceiver deciphers eye contact, facial expressions, body movements, and posture all in a attempt to form an impression of the target. Organizational Behavior / Perception 30 CONT… INTENTIONS: How we interpret the intentions of others influences our perceptions of their personality. For instance, if you assume that your professor is going to criticize your work, you may perceive your instructor to be a negative and critical person. Organizational Behavior / Perception 31 ATTRIBUTES OF THE SITUATION Elements in the surrounding environment also influence perception process. Some of these are as follows : i) ii) iii) Social context Organizational role Location of event Organizational Behavior / Perception 33 Types of perception Color perception Visual perception Speech perception Size perception Motion perception Color Perception: The ability to interpret information about something on the basis of the effects of colors. Color perception is subjective. COLOR PERCEPTION While perceptions of color are somewhat subjective, there are some color effects that have universal meaning. Several ancient cultures, including the Egyptians and Chinese, practiced chromotherapy(referred to as light therapy ), or using colors to heal. Red was used to stimulate the body and mind and to increase circulation. Yellow was thought to stimulate the nerves and purify the body. Orange was used to heal the lungs and to increase energy levels. Blue was believed to soothe illnesses and treat pain. Indigo shades were thought to alleviate skin problems. Organizational Behavior / Perception 37 Visual perception Visual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. Visual perception is a function of our eyes and brain. Organizational Behavior / Perception 39 Size Perception: The ability to interpret information about the size of objects It includes: Size constancy Shape constancy Color constancy Organizational Behavior / Perception 40 Size constancy: When we know that an object is of a certain size,we tend to perceive it as being same size,regardless of how far it is from our eyes. Organizational Behavior / Perception 41 Shape Constancy: When we know that the object is a certain shape,we tend to perceive it as the same shape,regardless of the viewing angle. Organizational Behavior / Perception 42 Organizational Behavior / Perception 43 Color Constancy: Colors of the objects tend to remain constant in perception when we know their actual color. Organizational Behavior / Perception 44 Organizational Behavior / Perception 45 A perception that occurs when a sensory stimulus is present but is incorrectly perceived and misinterpreted, such as hearing the wind as someone crying. Most of the illusions are optical illusions i.e An object causing a false visual impression • IMPOSSIIBLE FIGURE ILLUSION: The figures for which our brain is able to take sensation that is two dimensional and produce perception that is three dimensional. Reversible figures present ambiguous infarmation tha can be interpreted in more than one ways. The Mueller-Lyer Illusion is an optical illusion involving two lines and arrowheads at the ends of each line. When two lines and arrowheads of equal length are used, the one with ends pointing out is thought to be longer than the one with ends pointing in. The variation in the apparent size of the Moon (smaller when overhead, larger when near the horizon) is another natural illusion; it is not an optical phenomenon, but rather a cognitive or perceptual illusion Some times the objects at rest seem to be moving while those that are moving seem to be at rest. E.g train at railway station. Abnormal condition or defects of the sense organs. Illusion due to odd arrangements of stimuli. Illusion due to appreciation,interests, expectations etc. Illusion due to limitations of the sense organs. Social factors such as needs, motives,past experiences and expectations about the world and the way we percieve it. “If a tree falls…” If a tree falls in the forest and there is nobody around to hear it… Does it make a noise? Organizational Behavior / Perception 61 Answer NO…Sound (like color) is all in your head! Can you believe that this is a picture and not an animation? To check, just focus on one leaf for 5 seconds Organizational Behavior / Perception 63 Organizational Behavior / Perception 64 Organizational Behavior / Perception 65 Organizational Behavior / Perception 66