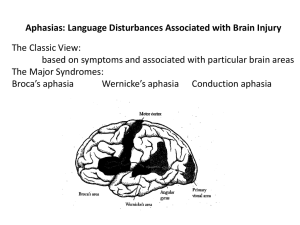
The Stroke & Aphasia Quality of Life Scale (SAQOL-39)
advertisement
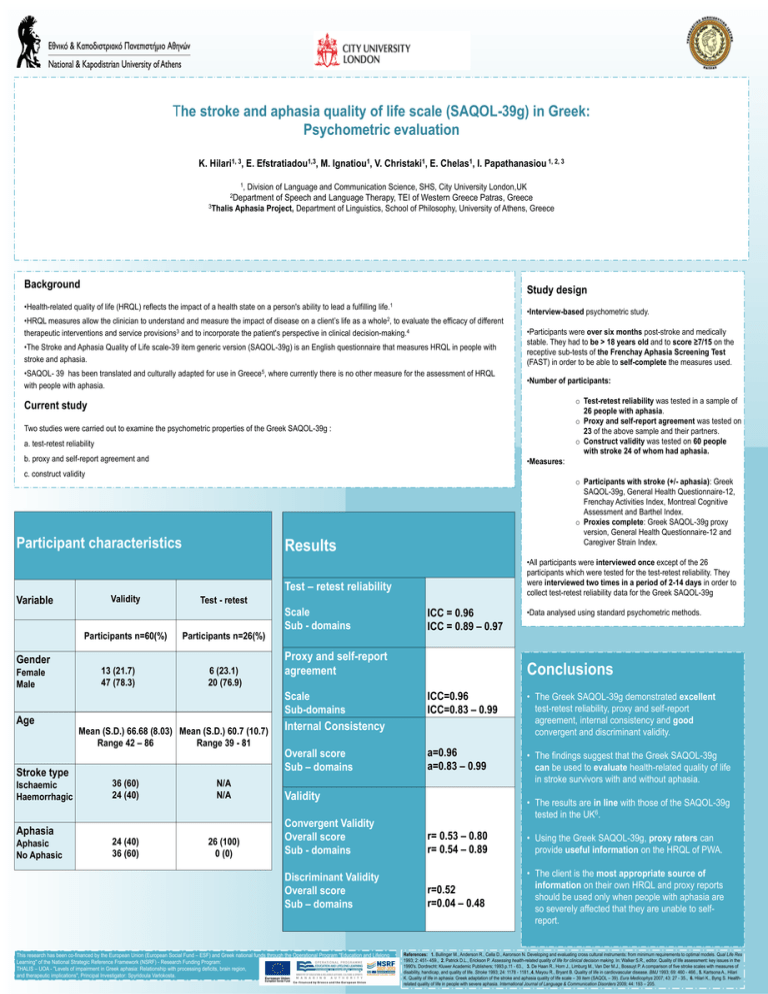
The stroke and aphasia quality of life scale (SAQOL-39g) in Greek: Psychometric evaluation K. Hilari1, 3, E. Efstratiadou1,3, M. Ignatiou1, V. Christaki1, E. Chelas1, I. Papathanasiou 1, 2, 3 1, Division of Language and Communication Science, SHS, City University London,UK 2Department of Speech and Language Therapy, TEI of Western Greece Patras, Greece 3Thalis Aphasia Project, Department of Linguistics, School of Philosophy, University of Athens, Greece Background Study design •Health-related quality of life (HRQL) reflects the impact of a health state on a person's ability to lead a fulfilling life.1 •HRQL measures allow the clinician to understand and measure the impact of disease on a client’s life as a whole2, to evaluate the efficacy of different therapeutic interventions and service provisions3 and to incorporate the patient's perspective in clinical decision-making.4 •The Stroke and Aphasia Quality of Life scale-39 item generic version (SAQOL-39g) is an English questionnaire that measures HRQL in people with stroke and aphasia. •SAQOL- 39 has been translated and culturally adapted for use in Greece5, where currently there is no other measure for the assessment of HRQL with people with aphasia. •Interview-based psychometric study. •Participants were over six months post-stroke and medically stable. They had to be > 18 years old and to score ≥7/15 on the receptive sub-tests of the Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test (FAST) in order to be able to self-complete the measures used. •Number of participants: o Test-retest reliability was tested in a sample of 26 people with aphasia. o Proxy and self-report agreement was tested on 23 of the above sample and their partners. o Construct validity was tested on 60 people with stroke 24 of whom had aphasia. Current study Two studies were carried out to examine the psychometric properties of the Greek SAQOL-39g : a. test-retest reliability b. proxy and self-report agreement and •Measures: c. construct validity Participant characteristics o Participants with stroke (+/- aphasia): Greek SAQOL-39g, General Health Questionnaire-12, Frenchay Activities Index, Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Barthel Index. o Proxies complete: Greek SAQOL-39g proxy version, General Health Questionnaire-12 and Caregiver Strain Index. Results •All participants were interviewed once except of the 26 participants which were tested for the test-retest reliability. They were interviewed two times in a period of 2-14 days in order to collect test-retest reliability data for the Greek SAQOL-39g Test – retest reliability Variable Validity Test - retest Scale Sub - domains Participants n=60(%) Participants n=26(%) Gender Female Male 13 (21.7) 47 (78.3) 6 (23.1) 20 (76.9) Proxy and self-report agreement Scale Sub-domains Age Mean (S.D.) 66.68 (8.03) Mean (S.D.) 60.7 (10.7) Range 42 – 86 Range 39 - 81 Ischaemic Haemorrhagic 36 (60) 24 (40) N/A N/A Aphasia Aphasic No Aphasic 24 (40) 36 (60) 26 (100) 0 (0) ICC=0.96 ICC=0.83 – 0.99 • The Greek SAQOL-39g demonstrated excellent test-retest reliability, proxy and self-report agreement, internal consistency and good convergent and discriminant validity. a=0.96 a=0.83 – 0.99 • The findings suggest that the Greek SAQOL-39g can be used to evaluate health-related quality of life in stroke survivors with and without aphasia. Validity Convergent Validity Overall score Sub - domains Discriminant Validity Overall score Sub – domains This research has been co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund – ESF) and Greek national funds through the Operational Program "Education and Lifelong Learning" of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF) - Research Funding Program: THALIS – UOA - "Levels of impairment in Greek aphasia: Relationship with processing deficits, brain region, and therapeutic implications", Principal Investigator: Spyridoula Varlokosta. •Data analysed using standard psychometric methods. Conclusions Internal Consistency Overall score Sub – domains Stroke type ICC = 0.96 ICC = 0.89 – 0.97 • The results are in line with those of the SAQOL-39g tested in the UK6. r= 0.53 – 0.80 r= 0.54 – 0.89 • Using the Greek SAQOL-39g, proxy raters can provide useful information on the HRQL of PWA. r=0.52 r=0.04 – 0.48 • The client is the most appropriate source of information on their own HRQL and proxy reports should be used only when people with aphasia are so severely affected that they are unable to selfreport. References: 1. Bullinger M., Anderson R., Cella D., Aaronson N. Developing and evaluating cross cultural instruments: from minimum requirements to optimal models. Qual Life Res 1993; 2: 451- 459., 2. Patrick D.L., Erickson P. Assessing health-related quality of life for clinical decision making. In: Walker S.R., editor. Quality of life assessment: key issues in the 1990's. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1993.p.11 - 63., 3. De Haan R., Horn J., Limburg M., Van Der M.J., Bossuyt P. A comparison of five stroke scales with measures of disability, handicap, and quality of life. Stroke 1993; 24: 1178 - 1181.,4. Mayou R., Bryant B. Quality of life in cardiovascular disease. BMJ 1993; 69: 460 - 466., 5. Kartsona A., Hilari K. Quality of life in aphasia: Greek adaptation of the stroke and aphasia quality of life scale – 39 item (SAQOL – 39). Eura Medicophys 2007; 43: 27 - 35., 6. Hilari K., Byng S. Healthrelated quality of life in people with severe aphasia. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders 2009; 44: 193 – 205.