Stress and Coping - Bukal Life Care & Counseling Center
advertisement

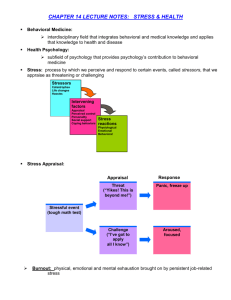
Stress and Coping Presented by Mrs. Tess Leones Lecture Objectives 1. To know the basic facts about stress and its sources. 2. To understand the effects of stress in our life. 3. To identify and learn different coping strategies DOH Facts about Stress 75-90% of visits to physicians are stressrelated Stress-related disorders are a major cause of rapidly increasing health care costs. According to the World Health organization (WHO), by year 2020, five (5) of the top ten medical problems world-wide will be stressrelated DOH Facts about Stress Stress is a major cause of Low productivity High absenteeism Misallocation of resources Poor morale, which may lead to suicide. One fact seems certain: Stress is on the increase! Stress is derived from the Latin word “Stringi” which translates as “to be drawn tight.” That state of increased arousal necessary for an organism to defend itself at a time of danger. The “wear and tear” our bodies experience as we adjust to our continually changing environment. A dynamic state of imbalance in response to demand, threat, or unmet needs. Sources of Stress (Stressors) 1. Stress of change: -major life changes like starting a new job -getting married -moving to a new house Sources of Stress (Stressors) 2. Environmental -Noise -Overcrowding -Natural disasters -Traffic Sources of Stress (Stressors) 3. Family and Relationships -Marital Conflicts -Disagreement with Other Persons -Stress of Bereavement Sources of Stress (Stressors) 4. Occupational/Work Stresses -Loss of job and mounting bills -Long work hours -Short-term contracts -Task demands -Promotion/demotion Stress Symptoms: Physical headaches (often termed tension headaches) palpitations skin problems/ rashes sleep problems high blood pressure indigestion muscle twitches (tics) colds/ flu increased bowelmovements (nervous diarrhea) excessive sweating (palms/ armpits) Stress Symptoms: Emotional/Psychological sadness irritability nervousness mood swings depression (common pathway to prolonged periods of stress) angry outburst negative thoughts, including suicidal ones nightmares Stress Symptoms: Behavioral decreased productivity poor appetite resulting in weight loss. overeating (bulimia) self-care is neglected social activities curtailed substance abuse-- excessive alcohol or cigarette smoking excessive day-dreaming Stress Symptoms: Cognitive trouble concentrating forgetfulness poor memory and recall increased number of errors difficulty making decisions, confusion Stress Scale TOO LITTLE STRESS OPTIMAL STRESS TOO MUCH STRESS Boredom lethargy passive vegetate Life is balanced happy in control confidence Tense Depression always tired exhaustion feeling 'tied up in a knot' constant feeling of having too much to do BURNOUT Stress “Thermometer” 0 30 50 70 100 little moderate high extreme stress stress stress stress <----------------------------------------------------------------> Life Change Index Scale According to Dr. Thomas Holmes. Utilizes an Index Number 1-100 for stress from different life events. Events Stress Index Death of Spouse Divorce/Separation Detention in jail/other institution 100 73 63 Major personal injury/illness Marriage 53 50 Being fired at work 47 Retirement from work Pregnancy Gaining a new family member (birth, adoption, older member moving in) Child leaving home (marriage, college) 45 40 In-law trouble 29 Vacation 13 39 29 Dr. Thomas Holmes and his colleagues have shown a relationship between recent life changes and the onset of illness. 0-149 No significant problem 150-199 Mild life danger with 37% chance of illness 200-299 Moderate life crisis level with a 51% chance of illness 300+ Major life cricis level with a 79% chance of illness ACCORDING TO HANS SELYE, A PERSON UNDERGOES 3 STAGES WHEN EXPERIENCING A STRESSFUL EVENT. Stage 1: Alarm Chemical substances called hormones are released into the blood in increased amounts. Body is trying to ready itself to cope with a stressor. Stage 2: Resistance Increased bodily activity to leave stressor or resist it. Stage 3: Exhaustion If exposure to the stressor continues, the body loses its ability to adapt to the situation. The person's energy is depleted and the result is exhaustion. Doctors believe that several kinds of illnesses may be caused by prolonged periods of stress. NOTE: Almost no one is able to maintain a normal existence under continued high level of stress. When the stage of exhaustion lasts for a long period of time, it develops into “burnout”. NOTE: If anyone is experiencing any of the following, consider seeing a doctor: -Depression/ desperation -Loss of appetite/ weight loss/ insomnia -One feels that life is not worth living. -Feel overwhelmed by anxiety -Loss of energy -Withdrawal. Stress Management A. Build your physical reserves because good health increases tolerance to stress. -Eat well-balanced/nutritious foods -Get enough rest and sleep -Get enough exercise -Avoid drugs such as tobacco and alcohol. They contribute to wear and tear on the body. -Take a warm bath/shower before going to sleep. -Avoid caffeine Stress Management B. Maintain and strengthen your emotional reserves. Have a network of friends and family to provide a support system in terms of: -tangible assistance -giving information -emotional support NOTE: Physical contact like a hug is a great stress buster. Stress Management C. LOL (laugh out loud). A good laugh reduces the level of stress hormone cortisol, and epinephrine and boosts immunity Stress Management D. Stress Innoculation. A good amount of stress comes from the irrational and self-defeating beliefs about oneself. If you can remove them from your system, it helps you to develop some kind of “immunity” against uselessness. Example Situations Negative Selfstatement Positive Selfstatement Losing one's job I'll never get another job Maybe my next job will be a better deal It's not the end of the world. I'll meet someone else someday. There are other things I can do with my life other than grad school. Breaking up with I have nothing to the person you live for. He/she is love all that I have. Not getting into graduate school I'm really dumb. I don't know what I'll do Stress Management E. Avoid crowding activities into a short period of time. Learn to priorize tasks. One step at a time. Do not expect too much of yourself. Delegate some tasks if there are other responsible people who can help you. “We are not superheroes!”. Learn to say “NO” Stress Management F. Learn to relax. Plan restful vacations once in a while. Schedule regular recreation into your life. Take on a hobby (“All work and no play makes Juan a dull boy!”) Follow your bliss. Listen to sweet music Gardening, if you enjoy it. Go to spa for a massage Treat yourself to a beauty parlor (girls) Shop for things you like (stress buster) Meditate and/or do yoga Go ballroom dancing Travel (take a short trip if money is the problem) Use “de-stress visualization/relaxation” exercises De-stress Visualizaiton/ Relaxation Exercises? Sit in a quiet corner of your room. Close your eyes. Imagine you are in a dream vacation mountain get-away, on top of the Eiffel Tower, Great Wall of China, Boracay, Cruse ship. Hold the thought for 10 minutes and see your self happy Remember… Stress is unavoidable. Not all stress is bad. “Spice of Life” Life with no stress would be BORING. “Eustress” versus “Distress” When or should all the coping strategies I had discussed with you fail, Let God... Rest in Him... for He said, “Come to Me you who are weary and I will give you rest.” Stress and Coping Presented by Mrs. Tess Leones www.bukallife.org