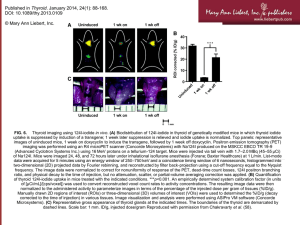
The Philippine Thyroid Disorder Prevalence Survey (PhilTiDeS)
advertisement

The Philippine Thyroid Disorder Prevalence Survey (PhilTiDeS) A project of the Philippine Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism in cooperation with the Food and Nutrition Research Institute-Department of Science and Technology and the Philippine Council on Health and Research Development National Prevalence of Goiter • • • • • 1987 and 1993 National Nutrition Surveys National prevalence of goiter based on PE 1987 - 3.7% 1993 - 6.7% in 1993 Highest prevalence rate seen in pregnant women 13-20 yo - 27.4% • This study will be the first national survey in the Philippines on the prevalence of thyroid disorder based on thyroid function tests. Phil. F&F, 2001 Significance of the study • This study is the first national survey in the Philippines on the prevalence of thyroid disorders based on thyroid function tests. Phil. F&F, 2001 Objectives • To determine the prevalence of: – – – – Overt Hyperthyroid and subclinical hyperthyroid disorders Overt Hypothyroid and subclinical hypothyroid disorders Thyroid nodules Iodine deficiency disorders • To evaluate the sufficiency of iodine nutrition based on urinary iodine excretion • To determine the relationship between abnormal thyroid function and: – Lipid levels – Clinical symptoms and signs as assessed by the modified Wayne's index Population • 7th National Nutrition Survey 2008 • National Statistics Office Labor Force Survey Sample • Non-pregnant, non-lactating adults > 20 yo Sampling design • stratified multi-stage sampling design • 17 regions, 80 provinces Primary sampling units (PSUs) Barangays with > 500 households Enumeration areas 150-200 households Household Household members N=5000 Methodology • PhilTiDeS questionnaire administered by trained field personnel – Demographics – Clinical history – PE for goiter grading • Biochemical assays – Serum TSH (microparticle immunoassay Abott) • Ref range 0.47-4.64 – Serum free T4 (ELISA) • Ref range 0.71-1.85 – Urinary iodine – Total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL WHO-UNICEF-ICCIDD 2001 consensus Median value (UIE ug/L) Iodine intake (ug/day) Iodine status < 20 Insufficient Severe iodine deficiency 20-49 Insufficient Moderate IDD 50-99 Insufficient Mild IDD 100-199 Adequate Adequate iodine 200-299 Above requirements Adequate for pregnant, lactating, more than adequate for others >300 excessive Risk of adverse health consequences Thyroid Function Biochemical Status Operational definition Overt hypothyroidism Elevated TSH (>4.64) and low FT4 (<0.71) & no intake of meds On current LT4 therapy Any TSH, any FT4 and intake of LT4 and Post-thyroidectomy and Post-RAI Overt hyperthyroidism Low TSH (<0.47) and elevated FT4 (>1.85) and no intake of meds Any TSH, any FT4 and current intake of ATD Subclinical hypothyroidism elevated TSH (>4.64) and normal FT4 and no intake of meds Subclinical hyperthyroidism Low TSH (<0.47) and normal FT4 and no intake of meds Classification based on thyroid status Classification Count Percentage Normal Current ATD Biochemical hyperthyroid Subclinical hyperthyroid 4481 4 26 258 91.49 0.08 0.53 5.27 Current LT4 Biochemical hypothyroid Subclinical hypothyroid 2 17 110 0.04 0.35 2.25 Total N (with blood tests) 4898 100 Goiter grading and thyroid status Classification Grade 0 Grade 1 Grade 2 Total Freq (%) Freq (%) Freq (%) Normal 4025 (90.51) 324 (7.29) 98 (2.2) 4447 Biochemical hyperthyroid 14 (46.67) 10 (33.3) 6 (20) 30 Subclinical hyperthyroid 216 (84.71) 20 (7.84) 19 (7.45) 255 Biochemical hypothyroid 16 (84.21) 2 (10.53) 1 (5.26) 19 Subclinical hypothyroid 96 (88.07) 10 (9.17) 3 (2.75) 109 Total 4367 (89.86) 366 (7.53) 127 (2.61) 4868 Population with goiter by PE Classification Count Percentage Goiter 675 9.34 7229 100 Grade 0 Grade 1 Grade 2 Total