chapter five
Communication
and Consumer
Behavior
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Essentials of Contemporary Advertising
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Objectives_1
Explain how advertising differs from the
basic communication process
Outline the consumer perception
process and explain why advertising
people say “perception is everything”
Describe the fundamental motives
behind consumer purchases
5-2
Objectives_2
Discuss the various influences on
consumer behavior
Explain how advertisers deal with
cognitive dissonance
Describe how a consumer’s level of
involvement with a product influences
the decision-making process and the
advertising approach
5-3
Consumer Behavior
HomeGrocer
sought to
change how
people
shopped
for groceries
5-4
Exhibit 5-1
The Human Communication Process
5-5
Perception is Reality
5-6
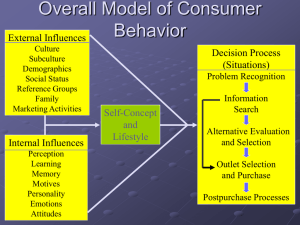
Exhibit 5-2 The Consumer Decision Process
5-7
Exhibit 5-3 Consumer Perception Process
5-8
Perceptual Screens
5-9
Consumer Self-Concept
Advertisers may
capitalize on
consumers’
concepts of
themselves
5-10
Theories of Learning
Cognitive Theory
Conditioning Theory
5-11
Exhibit 5-5 Elaboration Likelihood Model
5-12
Peripheral Processing
Typical when
consumers have
low involvement
with a product
category
5-13
Habits
What is a habit?
The acquired
behavior pattern that
becomes nearly or
completely
involuntary
A natural extension
of learning
What do advertisers
want consumers to
do about habits?
Break habits
Acquire habits
Reinforce habits
5-14
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Physiological
Safety
Social
Esteem
Self-Actualization
5-15
Exhibit 5-7 Rossiter and Percy’s Fundamental
Purchase and Usage Motives
Negatively originated
Positively originated
Problem removal
Problem avoidance
Incomplete
satisfaction
Mixed approachavoidance
Normal depletion
Sensory gratification
Intellectual
stimulation or
mastery
Social approval
5-16
Interpersonal Influences
Family
Society
Culture
5-17
Societal Influences
Social Class
Reference
Groups
Opinion
Leaders
5-18
Culture
This ad from the Ai Sin Foot Reflexology Centre
capitalizes on the notion of
Asian expertise in holistic therapies
5-19
Postpurchase Evaluation
High involvement
purchases result in
highly involved
postpurchase
evaluations
People seek to
avoid cognitive
dissonance
5-20
Exhibit 5-9 The FCB Grid
High
Involvement
Thinking
Feeling
Informative
Affective
Low
Habit Formation
Involvement
Self-Satisfaction
5-21
Exhibit 5-10 The Kim-Lord Grid
5-22
Key Terms_1
Attitude
Brand interest
Brand loyalty
Central route
Channel
Cognition
Cognitive
dissonance
Cognitive theory
Conditioning theory
Consumer behavior
Consumer decision
process
Culture
Decode
Elaboration
Likelihood Model
Encoded
5-23
Key Terms_2
Evaluation of
alternatives
Evaluative criteria
Evoked set
FCB grid
Feedback
Habit
Hierarchy of
Needs
Informational
motives
Interactive media
Interpersonal
influences
Kim-Lord grid
Learning
Mental files
Message
Motivation
5-24
Key Terms_3
Needs
Negatively
oriented motives
Noise
Nonpersonal
channels
Nonpersonal
influences
Opinion leader
Perception
Perceptual screens
Peripheral route
Personal channels
Personal processes
Persuasion
Physiological
screens
5-25
Key Terms_4
Positively originated
motives
Postpurchase
evaluation
Psychological
screens
Receiver
Reference groups
Selective perception
Self-concept
Semiotics
Social classes
Source
Stimulus
Stimulus-response
theory
Subculture
Transformational
motives
Wants
5-26