Integumentary Power Point
advertisement
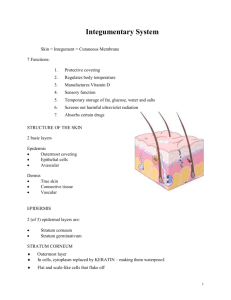
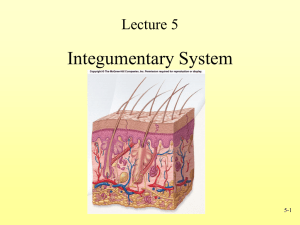
Integumentary System Facts about your Skin • Inegument = means covering • Integumentary System- skin, nails, hair, membranes, sweat, & oil glands • • • • Surface Area = 1.2 to 2.2 square meters Weight = 4 to 5 kg Thickness 1.5 - 4.0 mm 7% of average body weight for an adult Functions of Skin Protection Cushions and insulates and is waterproof Protects from chemicals, heat, cold Not helpful against organic solvents, heavy metals or plant oils from poison oak Screens UV Acid Mantel keeps down bacteria ~pH 5 Macrophages gobble up invaders Synthesizes vitamin D with UV Functions of the Skin Regulates body heat Prevents unnecessary water loss Sweat 500ml a day if about 31-32 C vessel dilate & constrict But Lipid soluble – Vitamins and steroids in Sensory reception (nerve endings) Thermoreceptors Pacinian receptors • Bumps and deep pressure Meissner’s corpuscles & Merkel disks • Aware of caress of clothing Layers of the Skin 1) Epidermis 2) Dermis 3) Hypodermis 1) Epidermis • Epi = Upon • Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium • nutrients reach by diffusion/ avascular • Outer layer of dead skin cells called cuticle with living level underneath . “Ashiness” is caused by this layer of dead skin cells being very rough and raggedy • DUST you see around is made up of dead skin cells! Epithelium: layers (on left) and cell types (on right) Remember… • Four basic types of tissue – Epithelium – epidermis just discussed – Connective tissue - dermis – Muscle tissue – Nervous tissue 2) DERMIS Thick, tough, leathery, flexible layer Made of connective tissue Vascularized – contains blood vessels Anchors the epidermis Critical in Temperature regulation – contract and expand In the dermis: • Oil glands • Sweat glands • Hair follicles • Fat tissue • Nerves • Connective tissue • Blood vessels Two layers Papillary – areolar connective tissue; includes dermal papillae Reticular – “rticulum” (network) of collagen and reticular fibers Fingerprints, palmprints, footprints Dermal papillae lie atop dermal ridges Elevate the overlying epidermis into epidermal ridges Are “sweat films” because of sweat pores Genetically determined Flexion creases • Deep dermis from continual folding Finger Print 3) HYPODERMIS • Subcutaneous Tissue /Hypodermis / superficial fascia – not really part of skin, but helps with protective functions – superficial to connective tissue around bones – loose enough for free movement – Adipose tissue – different patters of accumulation for men and women (grows when we gain weight) – shock absorber & insulator – Deep pressure receptors Cells of the Epidermis • Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium • Four distinct cell types – – – – Keratinocytes Melanocytes Merkel Cells Langerhans’/ Epidermal Dendrite Cells Keratinocytes o Most epidermal / superficial cells o Produce keratin – “kera”= horn . Fibrous protein that gives stretch o Constantly in mitosis & pushed upwards o By the time they are on the surface they are dead o New epidermis every 25-45 days o Friction= keratin formation is accelerated therefore callus- a thickening of the epidermis Melanocytes o Spider shaped epithelial cells that make Melanin o Deepest layers of the epidermis o Melanin made & collects in granules called melanosomes o Actin filaments move them along till they are taken up by Keratinocytes o Granules accumulate on the superficial “sunny side” of the Keratinocytes nuclei & protect nucleus from harmful UV rays Merkel Cells o Shaped like a spiky hemisphere o Help with sensory of touch Langerhans’ Cells / Epidermal Dendrite Cells Macrophages (pac mans) that help activate our immune system Layers of the Epidermis • Thick skin= covers palms, fingertips, and soles of the feet – FIVE layers/ strata • Thin Skin= rest of the body – FOUR layers (no stratum lucidum) Deep to Superficial: stratum basal stratum spinosum strata granulosum strata lucidum strata corneum Epidermis and dermis of (a) thick skin and (b) thin skin (which one makes the difference?) Stratum basale/ stratum germinativum/ Basal Layer – – – – Deepest epidermal layer Single row of cells Attached to dermis w/ a wavy boarder line 10-25% of cells are melanocytes & their branches – undergoing mitosis stratum spinosum/ Prickly Layer • several cell layers thick • keratinocyte in this layer are spiny strata granulosum/ Granular Layer • 3-5 cell layer • keratinocyets flatten & start to die – not enough oxygen and nutrients b/c pushed away from blood source strata lucidum/ Clear Layer o o o thin translucent band only in thick skin start making distinct layer strata corneum/ Horny Layer • 20-30 cells thick • ¾ of epidermal thickness • thickened plasma membrane of cells protects from abrasion & penetration • glycolipid acts as a “water proof” • protects body from heat and water loss • “dandruff” 18kg= 40 lbs in a lifetime Skin Color 1. Melanin • same # of melanocytes • kind + amount of melanin made & retained – Darker = more darker melanosomes & retain longer • Freckles & pigment moles are accumulation of melanin • Sunlight causes melanin buildup – to protect from UV Skin Color 2. Carotene – – – – Yellow-orange pigment Accumulate in the stratum corneum Palms of hands, soles of feet Eat lots of rich carotene foods- becomes more obvious 3. Hemoglobin – Pinkish hue of light skin b/c can be seen through light skin Skin Appendages • Derived from epidermis but extend into dermis • Include – Hair and hair follicles – Sebaceous (oil) glands – Sweat (sudoiferous) glands – Nails HAIR • Hair growth: averages 2 mm/week – Active & Resting phase then Shed – At the base of the follicle, hair papilla • Contains blood vessels and nerves Bulb • Contains matrix – epithelial cells responsible for growth – Contains melanocytes • Functions of hair – Warmth – Sense light touch of the skin – Protection – scalp • Hair color – Amount of melanin for black or brown; distinct form of melanin for red – White: decreased melanin and air bubbles in the medulla – Genetically determined though influenced by hormones and environment Hair and hair follicles: complex Derived from epidermis and dermis Everywhere but palms, soles, nipples, parts of genitalia * Hair papilla is connective tissue________________ *“arrector pili” is smooth muscle Hair bulb: epithelial cells surrounding papilla Nails • hard keratin • Corresponds to hooves and claws • Grows from nail matrix Sebaceous (oil) glands • Entire body except palms and soles • Oils and lubricates Sweat Glands • Entire skin surface – except nipples and part of external genitalia • Prevent overheating • 500 ml to 12 L /day! • Humans most efficient (only mammals have) • Produced in response to stress as well as heat