here - deBuren
advertisement

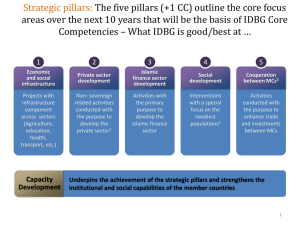
Islamic Finance: Principles and practice It is the Economy, Stupid 5: over Gharar, Riba en Murabaha | 9 October 2012 Rachida Talal-Azimi PhD Candidate Financial crisis “What we need is the application of Islamic finance principles, in particular a strong preference for profit-, loss- and risk-sharing arrangements and a rejection of ‘riba’ or interest-bearing debt instruments.” Willem Buiter Chief Economist, Citigroup (US) Development 2000 and beyond 1990s 1980s 1970s Commercial Banking Commercial Banking + Project Finance + Syndicates Commercial Banking Project Finance Syndicates + Equity + Sukuk al-Ijara + Fund Management Source: Thomas et al.(2005) Structuring Islamic finance transactions Commercial Banking Project Finance Syndicates Equity Sukuk al-Ijara Fund Management + Several Sukuk models + Islamic Microfinance Development What is Islamic Finance? What is Islamic finance? ‘The discipline to perform financial transactions in accordance with the principles of Islamic law.’ Establishment of an Islamic Economic Thought Fundamentals of Islamic financial products QUR’AN Ribā (interest) SCHOLARS Gharar (unnecessary risk / avoidable uncertainty) Prohibited goods Maysir (i.e. Alcohol) (gambling) SUNNAH Other prohibitions / principles • No investments in prohibited companies and/or products • Encouragement of trade • All transactions must be asset backed • Mandatory independent Sharia board (Islamic supervisory board) • Islamic Window! Wat is islamitisch financieren? Handel drijven Winst- & verliesdeling Onafhankelijke shari’araad Asset based Islamic financial instruments Partnership contracts • Muđāraba (type of limited partnership) • Mushāraka (type of equity participation) Islamic financial instruments Mushāraka (type of equity participation) 4 Real estate Bank 2 1 3 Customer 5 6 7 1 Down payment 10.000 2 payment 90.000 3 10 % of the units 4 90% of the units 5 rent* 6 Unilateral commitment to purchase remaining units 7 purchasing contract / sales contract re units Islamic financial instruments Mark-up contracts • Murābaħa (mark-up contract) • Bayc Salam (sale by advance payment for future delivery, i.e. buyer credit) • Istisnāc (production contract) Islamic financial instruments Murābaħa basic contract Purchase Goods for cash sale Islamic financial instruments Murābaħa finance seller buyer 1 3 2 4 financier 1 3 Islamic financial instruments Other contracts • Qarđ al-Ħasan (no-interest loans) • Ijāra (leasing) ijāra wa iqtinā’ (hire-purchase) • Şukūk (Islamic investment certificate) Conclusion What is Islamic finance? ‘The discipline to perform financial transactions in accordance with the principles of Islamic law.’ In other words, more than just a ban on interest! A system based on a completely different approach to the trading of money than the traditional system Conclusion Rapid development of Islamic financial sector Niche market Not yet fully developed Growth is undermined by a number of tough challenges, including: •Lack of standardisation •Lack of qualified staff Financial crisis has both a positive and a negative impact Thank you for your attention!