Managing Change
advertisement

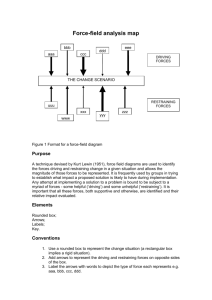
Managing Change Upul Abeyrathne, Dept. of Economics, University of Ruhuna, Matara Kurt Lewin’s Model • He is a social psychologist • He developed his theory 50 years ago. • He name it as the “Force Field Analysis”. This model is composed of two sides • Driving Forces: They push organizations towards a new state of affairs. • Restraining Forces: It maintains the status quo. Driving Forces • They are of two varieties. 1. External environment E.g. Globalization, Virtual work and changing work 2. Internal: Leaders create driving forces within organizations so the organization anticipates the external forces. Remember that the internally originated driving forces are difficult to apply because they lack external justification. Effective transformational leadership as well as structural change mechanism are necessary to legitimate and support internal driving forces. Restraining Forces • They are called resistance to change. • It is because that employees behaviour is something that block the change. Stability • It happens when driving forces and restraining forces are roughly in equilibrium. That is when they are approximately equal strength in opposite direction. What does this model emphasizes? • Effective change occurs by unfreezing the current situation and moving to a desired condition and refreezing the system so that it remains in the desired state. What is Unfreezing? • It is the producing disequilibrium between driving forces and restraining forces. • It can be achieved by either increasing the driving forces or reducing the Restraining forces. Refreezing • It occurs when organization system and structures are aligned with the desired behaviour. • They must support and reinforce the new role pattern and prevent organization from sliping back into the old ways of doing things Restraining Forces • “People likes to keep things the way they are”. Forms of Resistance: Passive noncompliance, complaints, absenteeism, turnover and collective actions. Resistance is a symptom of deeper problem in the change process. It is better for managers to understand the reasons for not changing the behaviour by employees. Restraining Forces • Direct Cost: People resists actions that result in higher direct cost or lower benefits than the existing situation. • Saving Face: Some people resist change as a political strategy to prove that the decision is wrong or the person encouraging the change is incompetent. Restraining Forces • Fear of the Unknown: People resist changes out of fear that they could not adjust to new work requirements. • Breaking Routines: People are creatures of habit. Routine makes life more predictable. Restraining Forces • Incongruent Organizational System: Rewards, selection, training and other control systems ensure that employees maintain desired role pattern. However, organizations that maintains stability discourage employees from adopting new ways. • Incongruent Team Dynamics: Teams develop and enforce conformity to a set of norms that guide the behaviour. Conformity to the present norms may discourage employees accepting organizational change. Team norms conflict with desired changes need to be altered. What a manager shall do? • He should increasing the driving forces and reduce the resistance forces simultaneously. How to create urgency for Change • It is cliché that organizations operate in more dynamic, fast-paced environment. • Environment pressure represent the driving forces for change. It pushes employees out of their comfort zones. • Change process has to begin by ensuring employees feel an urgency to change: Informing of the competitors, changing consumer needs, impending government regulations and other driving forces. How to create urgency for Change • Customer –driven change • Urging change without external forces Reducing the restraining forces • • • • • • Communication Learning Employee involvement Stress Management Negotiation coercion Change Agent • Every Organization Requires change agent. • Change agent is anyone who possesses knowledge and power to guide and facilitate the change effort. • Change agents form a vision for a desired future, communicate it in meaningful manner to others, behave in a manner consistent with that vision. Approaches to organizational change • Action Research Approach • Appreciative Inquiry Approach • Parallel Learning Structure Approach Action Research • Pioneer: Kurt Lewin • Action Research takes the view that meaningful change is a combination of Action Orientation (Changing Attitudes and Behaviour) and Research Orientation(Testing Theory). • On the one hand change process needs to be action oriented because the ultimate goal is to bring about change. Action Research • Action orientation involves diagnosing problems and applying interventions to resolve the problems. • On the other hand, change process is research study because change agents apply a conceptual framework( such as team dynamics and organizational culture) to a real situation. • As with any good research, it involves data gathering to diagnose problems more effectively and systematically evaluate how well theory works in practice. • It involves organizational learning and knowledge management. Action Research • Action Research assumes change agent originate outside the organization. • 1. Form Client-consultant Relationship. • 2. Diagnose the need for change • 3. Introduce interventions • 4.Evaluate and stabilize change. • This approach takes a negative approach to organization. Appreciative Inquiry Approach • It tries to break out the problem solving mentality of traditional change management practices by reframing relationships around the positive and the possible. • It search for organizational strengths and capabilities • Adapts or applies that knowledge for further success or well-being. Appreciative Inquiry Approach • It highlights the importance of positive traits and qualities of individuals and organization. • It directs inquiry to successful events, units and organizations and strives to make them models. • It increases open dialogue by redirecting the groups attention away from its own problems • It helps organization by way of focusing on what is possible for better future. Appreciative Inquiry Approach 1. Discovery: Identifying the best of “What is” 2. Dreaming: Envision “What might be” 3. Designing : Engage in dialogue about “What should be” 4. Delivering: Develop objectives about “What will be” Parallel Learning Structures • Highly Participative • Follow action research model to produce meaningful change. • They are social structures developed alongside the formal hierarchy with purpose of increasing the organization’s learning. Ethical Issues • Privacy rights of individuals • Increase managers power. • Change undermines self-esteem Thank You