Food Chains and Webs
advertisement

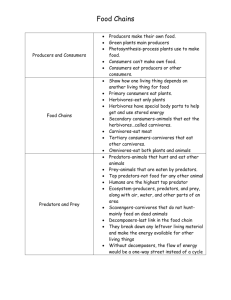
Teacher Information! Necessary materials: PowerPoint Guide Teacher may wish to hand out these note guides: Carbon Cycle Guided Discussion Phosphorous Cycle Guided Discussion Nitrogen Cycle Guided Discussion Food Chains and Webs Principles of Ecology Students will be able to… Describe food chains and webs The flow of energy “Three hundred trout are needed to support one man for a year. The trout, in turn, must consume 90,000 frogs, that must consume 27 million grasshoppers that live off of 1,000 tons of grass.” —G. Tyler Miller, Jr., American Chemist (1971) Ecosystems Definition reviewed: Community + abiotic factors interact to form stable system Depends on: One-way flow of energy Energy input from sun Cycling of materials Nutrient inputs “Biogeochemical” cycles Recycles chemicals Carbon cycle Phosphorous cycle Nitrogen cycle Life on earth depends on these cycles & photosynthesis Producers The base of ecosystems Convert sunlight energy to chemical energy Construct organic compounds from inorganic raw materials Producers Photosynthesis a very fundamental process !! Chlorophyll Producer = autotroph = plants & algae (green organisms) Consumers Organisms that eat other living plants, animals or microbes Get energy from preformed organic molecules heterotrophs Primary consumers eat producers Secondary eat primary consumers Tertiary eat secondary consumers Detrivores Organisms that eat detritus Detritus Dead plants, animals, & microbes & fecal wastes of animals Get energy from preformed organic molecules Decomposers Live on detritus in such a way that it decays Subgroup of detrivores Food chains & webs Food chain pathways of feeding relationships Producer-consumer relationships Parasite-host relationships Food web Complex pattern of interconnected food chains A food chain A food web Review Describe food chains and webs What can happen with a disruption in a food web?