Comprehension Workshop T3

Parent Information Session
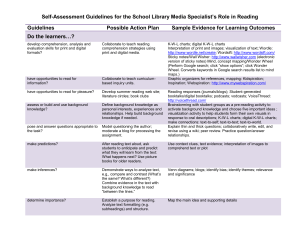
Comprehension –
Monday 19 August 2013
What is comprehension?
Making meaning ……..THINKING
When comprehending, learners strive to process text beyond word-level to get to the big picture.
When they read independently they have moved beyond decoding to understand and think about what they are reading and have read.
When being read to they also need to understand and think……………….
Comprehension
Fluency without comprehension = “Barking at Print”
Reading is a challenging process. It requires skills to be continually built upon and practised throughout life.
Reading comprehension occurs before, during and after reading a text.
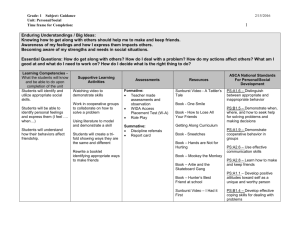
Three levels of comprehension:
• Literal (here)
• Inferential (hidden) Heart
• Evaluative (head)
What do you do when you read?
• Make Connections
• Create images in your head
• Question
• Predict
• Summarise
• Monitoring
• ……….these are the “Super Six”
Making Connections
Learners make personal connections from the text with:
Something in their own life (text to self)
Another text (text to text)
Something occurring in the world (text to world)
Visualising
(students who can visualise as they read show a greater amount of enjoyment)
Learners create a mental image from a text read/viewed/heard.
Visualising brings the text to life, engages the imagination and uses all of the senses.
Questioning
Learners pose and answer questions that clarify meaning and promote deeper understanding of the text. Questions can be generated by the learner, a peer or the teacher.
Predicting
……using information from the text, and background knowledge and understandings to predict what will happen and to actively adjust comprehension and understanding of text……………
Summarising
Learners identify and accumulate the most important ideas and restate them in their own words.
Monitoring
Learners stop and think about the text and know what to do when meaning is disrupted
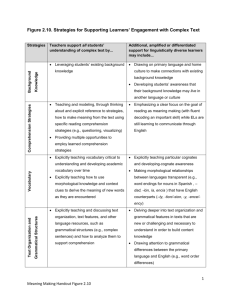
How do we teach/assess comprehension?
All strategies for comprehending are taught through:
Modelled lessons - the teacher explicitly demonstrate and teaches the skill/strategy to be learnt. Students practice set activities
Guided lessons – the students work in small groups or as an individual under the guidance of the teacher. Specific activities are planned to guide students to the next level of learning
Independent lessons – students work in small groups or as an individual to independently apply the skills/knowledge/strategies learnt to demonstrate their learning
P.A.C.T.