secondary industry secondary industries
advertisement

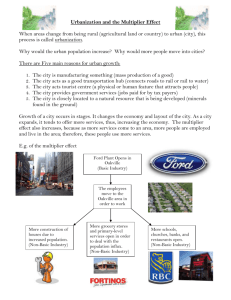
CANADA: ECONOMIC CONNECTIONS SECTORS OF THE ECONOMY INTRO WORK Answer the following question, as an introduction to this unit. Imagine you’re walking along a street with your friends. You get a craving for some fast food, so you drop in at a fast-food outlet. You decide on a hamburger, fries, and pop. As you wait for your order, your mind wanders and you start thinking about what you’re about to eat. What goes into a hamburger anyway, and where does it come from? List as many ingredients/materials as you can (for the food and the packaging) that were required to produce the combo meal. Next, try to identify the location where each of these items came from. Where’s That Burger From? ECONOMIC CONNECTIONS This mini-unit examines how the physical components of Canada are tied to the people who live in it – primarily through their work. TYPES OF INDUSTRIES The jobs that people do can be placed into one of three categories: PRIMARY INDUSTRIES SECONDARY INDUSTRIES TERTIARY INDUSTRIES PRIMARY INDUSTRY Primary Industry: Industries that take raw materials from the environment Usually located where resources are found. E.g. farming, forestry, fishing, and mining PRIMARY INDUSTRY primary industries make a critical contribution to Canada’s wealth A small percentage of Canada’s labour force works in primary industries A greater percentage of Canada’s labour force worked in primary industries before machinery replaced human labour for many tasks SECONDARY INDUSTRY Secondary Industry: involve the processing of primary industry products into finished goods The most important secondary industry is manufacturing Secondary industries employ far more Canadians than do primary industries - three times as many workers Takes raw materials and changes them into things that we can use. E.g. Automobile production plant, Oil refinery, Steel mill SECONDARY INDUSTRY Manufacturing often involves more than one stage of processing For example, iron ore, coal, limestone, and other metals all products of primary industry - are used to make steel This is called primary manufacturing In the secondary manufacturing stage, the steel may be used to make a car, a refrigerator, nails etc. Manufacturing industries are located in towns and cities and in most cases in more densely populated areas SECONDARY INDUSTRIES Uses the products of primary manufacturing (e.g. paper to make newspaper and books). TERTIARY INDUSTRY Tertiary Industry: Tertiary industries provide a wide range of services that support primary and secondary industries These industries DO NOT manufacture products. They provide SERVICES such as transportation and retail outlets. E.g. Airline, retail, sales, government, tourism and other services LET’S SEE IF YOU GET IT SECTORS OF THE ECONOMY A simple product like skates involves all sectors of the economy HOW MANY PEOPLE ARE EMPLOYED IN EACH SECTOR? In Canada, which sector do think employs the most people? CHANGE IN EMPLOYMENT IN CANADA *Most Canadians are employed in the tertiary sector CANADA’S ECONOMIC STRUCTURE COMPARED TO OTHER COUNTRIES OF THE WORLD (1998) BASIC & NON-BASIC INDUSTRIES Basic Industries: provide the money to support the local economy (e.g. mining, logger, paper mill, steel mill) – Industry that sells products outside of the local community – Money comes primarily from outside the economy of the local town – Without them, there would be no money entering the town and it could not exist. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) dec ompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. BASIC & NON-BASIC INDUSTRIES Non-Basic Industries: • Recycle the existing money. (e.g. cook, teacher, bank teller). • Industry that sells within the community • Do not bring new money into the local economy. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Unc ompressed) decompress or are needed to s ee this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Homework 1. Define, in your own words, and give three examples of each of the following: primary industry, secondary industry, tertiary industry. 2. From the following list, indicated whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary industries. raw materials manufacturing factory mining civil servant natural resources ski resort steel mill construction farming car dealership 3. What is the difference between a basic industry and non-basic industry. 4. a) b) c) d) Which of the following are basic and which are non-basic jobs? Explain each answer. An assembly line worker in the Ford factory in Oakville A fire fighter in your community A wheat farmer in Saskatchewan The artist who illustrated this book 5. Describe a situation in which each of the following jobs can be basic in nature and a situation in which it can be non-basic: a) A doctor b) A bus driver c) A golf professional