ES10 Halogenoalkanes
advertisement

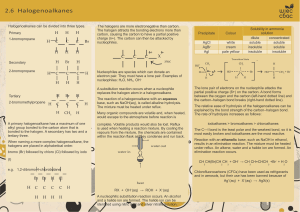
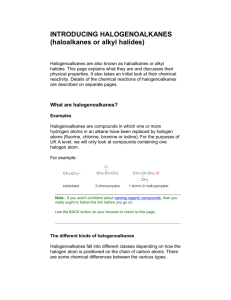
Which is the odd one out? Ions in solution Ionic Formulae Manufacturing Halogenoalkanes Redox Bonding Atoms and Ions Halogens Dipoles Elements of the sea Content • Nomenclature of halogenoalkanes • Physical and chemical reactions of halogenoalkanes including hetrolytic fission Process • Carry out an experiment Benefit • Explain reaction mechanisms Nomenclature Homologous series (actually one for each halogen!) 1. Location of halogen (smallest possible) 2. Prefix of halogeno – with an o (i.e chloro/flouro/bromo – if more than 1 – alphabetically) 3. Root is parent C chain Name these/draw these 2,3-dichloropentane CHCl3 3-bromobut-1-ene 2,3-dibromo-1-chloro-2-methylbutane Physical properties Halogen makes gp polar – but not sufficient to make it miscible with H2O Complete this worksheet 1. Explain the physical properties if astatine was attached. Chemical Reactions • Try to break Hal-C bond (hal short for halogen) • Bond breaking (fission) can be either hetrolytic or homolytic. H3C-Cl • Guess what do you think they mean? Homolytic fission • Can occur by visible/UV radiation (hv) hv + H3C Cl H3C + Cl • Each of the bonding e- goes to each of the atom. • Creating a highly reactive atom/gp of atoms with an unpaired e- are called a radicals. HOT question Should there be a charge here? • This causes ozone issues in stratosphere Heterolytic fission • Reactions depend on conditions (nonpolar solvent/gas phase with high temp HOT question homolytic fission) Give an example of a polar solvent • Common in lab conditions (polar solvent) H3C Cl H3C + Cl • Both of the bonding e- goes to one of the atom/groups of atoms. • Forms a –ive halide ion and a +ive carbocation (carbon + ca+ion). ES 6.2 • Do these Hal-C bonds break at the same time? • Remember to answer the questions. ES 4.5 If a precipitate appears, this means that hydrolysis has taken place – the carbon–halogen bond has broken and halide ions have been released from the halogenoalkane. 1. Which halogenoalkane underwent the fastest hydrolysis? • Which was slowest? 2. Student X suggests that the rate of hydrolysis depends on the polarity of the C–Hal bond, and that the halogenoalkane with the most polar bond will hydrolyse most quickly. • Student Y suggests that the rate of hydrolysis depends on the strength of the C–Hal bond, and that Which the halogenoalkane with the weakest bond will hydrolyse most quickly. • Use your Data Sheets to find data that you think will help • you and write it down. Use the data to decide whether • bond polarity or bond enthalpy is more important in • determining the relative reactivity of halogenoalkanes. 3. What result would you predict for 1-fluorobutane? Explain your answer. 4. Why was this experiment done using halogenobutanes rather than halogenomethanes? Which is more important in reactivity of halogenoalkanes bond enthalpy or bond polarity? Extension – predict how would fluorobutane react? ES 4.5 Enthalpy more influential – so fluoroalkane would happen slower/less reactive than chloroalkane as higher bond enthalpy for fluroalkane. • Remember to answer the questions. CFCs CFC’s release – hang around in the troposphere and then ....... CFCs 1. Complete ES6.2 2. Read 13.1 and make notes – we will cover nucleophilic substitution but reading ahead will help you understand it better.