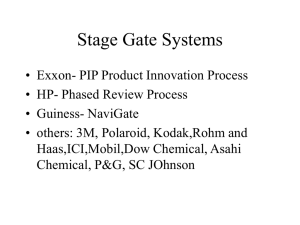
Stage Gate Development
advertisement

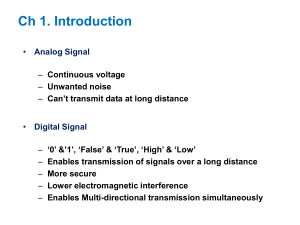
Stage Gate – Lecture 1 Technology Development © 2009 ~ Mark Polczynski Stage Gate - Lecture 1 1 This Course: Strategic Technology Management Strategic Technology Planning • Scenario Planning • Voice of the Customer • Intellectual Property Generation • Ideation • Technology Roadmapping Strategic Technology Development • Stage Gate Development • Stage Gate Review Stage Gate - Lecture 1 2 Scope of This Lecture Set: • We focus on technology development, • But the same basic principles apply to product development. • This is about technology development and project review. • It is about a system where project review is an integral part of technology development. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 3 Integrating the development and review process • Often, project execution and project review are two separate processes. • It is desirable to integrate these two processes, because you get: - Better project results, - Better project review decisions, - Faster decisions – projects move faster, - Happier people: - Everyone knows the rules of the game beforehand, - Everyone follows the rules all the time, - Everyone’s expectations are kept realistic. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 4 Stage Gate Process: 1. What problem are we trying to solve? 2. Stage gate development process. 3. Stage gate review process. 4. Review process cultural issues. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 5 What Problem We Are Trying To Solve? Example: Eaton Corporation - • ~ 10,000,000,000 ~ $10 billion annual sales, • Goal: 10% increase in sales per year, • Driven by stock market expectations, • And stock market is “main customer” in capitalistic system. That equates to $1B in new products per year – every year! (compounded!) Stage Gate - Lecture 1 6 What’s The Problem We Are Trying To Solve? • Need new products that can “move the needle”. • Hard to get to $1B by adding $1M at a time. • You need 1,000 new products! • Significant growth in many small increments is difficult to manage. • Many low-impact products are difficult to support. • Solution: Fewer high-impact projects. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 7 What about small businesses? • It doesn’t matter if you are one of 10,000 engineers trying to add $1B in sales for Eaton Corporation. • Or Joe of Joe’s Garage Shop trying to add $1,000 in sales. • Trying to grow by $1,000 in $10 increments is hard to manage and hard to support when you are done. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 8 What’s the MAIN Problem We Are Trying To Solve? New Product Pipeline Many Low-Impact Products Out Many Small Projects In Before: Difficult to manage many small projects. After: Difficult to support many small products. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 9 What’s do we want to have? New Product Pipeline Many Small Projects In Few High-Impact Products Out Question: How do we figure out which projects to keep? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 10 Ideation Process: 1. Planning 2. Preparation 3. Ideation Event Need to keep only the best 4. Post-Processing Large number of good ideas Project Proposals Stage Gate Process Stage Gate - Lecture 1 11 Overall Goal: Weed out projects that have low impact. Average IMPACT Per Project Total NUMBER of Projects Problem: We don’t know the winners at the start of their life. Goal: Survival of the best. Early Project Life Stage Gate - Lecture 1 Late 12 We must kill many of these projects… Many Small Projects In Few High-Impact Products Out …but how do we discover which are the best? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 13 Total NUMBER of Projects Feed the winners well Kill losers before you spend lots of money on them Early Project Life Stage Gate - Lecture 1 Averagee COST Per Project Overall Goal: Maximize Bang-For-The-Buck. Late 14 Possibly the biggest cause for failure of good projects: • Under-funding Lack of adequate resources. Stage Gate Development Process • Inability to ruthlessly focus on only the best opportunities. • Inability to identify best opportunities early in life. Stage Gate Review Process Stage Gate - Lecture 1 15 Stage Gate Process: 1. What problem are we trying to solve? 2. Stage gate development process. 3. Stage gate review process. 4. Review process cultural issues. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 16 Product Development Stage Gate Process Stage Gate - Lecture 1 17 Technology Development Stage Gate Process Balance Opportunity (Why?) and Technology (What?) Stage Gate - Lecture 1 18 Note: This first gate could be part of ideation process Stage Gate - Lecture 1 19 Ideation Process: 1. Planning 2. Preparation 3. Ideation Event Stage Gate Initial Screen 4. Post-Processing Project Proposals Stage Gate Process Stage Gate - Lecture 1 20 Technology Development Stage Gate Process Begin with the end in mind: What do we need to support stage gate product development? To Stage Gate Product Development Stage Gate - Lecture 1 21 Begin with the end in mind... What do we need to support stage gate product development? By the end of Stage Gate technology development, we will be able to answer Yes or No to these questions: 1. Does our technology actually work under real world conditions? 2. Can products based on this technology actually be designed and manufactured at an acceptable cost? 3. Can the technology provide a unique competitive advantage? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 22 Technology Development Gate Process End gameStage : • Technology works in field? • Designable - manufacturable - profitable? • Unique? Moving to the basics: Stage Inputs and Goals Stage Gate - Lecture 1 23 Questions to answer at the end of Stage A A: Problem Statement • What problem are we trying to solve? • How would this provide value for the customer? A: Identification • What technologies might solve the problem? (long list) • Which technologies will we investigate in Stage B? (short list) • Is there a chance to create Intellectual Property? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 24 B: Functional Requirements • What is the specific application? • What functions does the customer need? B: Feasibility • Which technology will we use? (select one) • Does technology work in the lab? • What is our strategy to create IP? Questions to answer at the end of Stage B Stage Gate - Lecture 1 25 Technology Development Stage Gate Process C: Demonstration • Does technology work in real world conditions ? • Can we make/sell a product? (tech transfer) • What is our IP? C: Physical Requirements • Under what real world conditions must the functions be provided? Questions to answer at the end of Stage C Stage Gate - Lecture 1 26 Stage A Technology Development Work • What technologies might solve the problem? (Make long list) • “Ideation” sessions and literature search, including patents, to: • Expand understanding of the Problem Statement. • Reveal prior art. • Identify possible technologies. • Which technologies should we investigate? (Make short list) • Analyze technical feasibility - why might these solutions work?. • Assess technical risk - why might these solutions not work? • Is there an opportunity to create Intellectual Property? • “Ideation” sessions - to identify novel potential solutions. • Document concepts - to establish prior art for all novel solutions. Note: Stage A does not include experimental work. Stage Gate - Lecture 1 27 Stage B Technology Development Work • Which particular technology will we use? (select one) • Analyze technical feasibility - why should the selected solution work? • Assess technical risk - why might this solution not work? • Assess technology transfer issues • Why might it be difficult to design products? • Why might it be difficult to manufacture products? • What might jeopardize cost targets? • Can we meet the functional requirements? (lab conditions) • Construct lab models - can we make it work in the lab? • Perform lab tests - how does it perform in the lab? • Establish “proof of concept”. • What is our strategy to create Intellectual Property? • Assess novelty - do we have a new solution? • Document inventions - describe our solution (invention disclosures). • Initiate IP strategy - what is the opportunity to create a proprietary position? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 28 Stage C Technology Development Work • Can we meet the physical requirements? (field conditions) • Demonstrate field operability - does it work under field conditions? • Test under field conditions - how will it function in the field? • Can the division make a product? (tech transfer) • Assess technology risk - what problems might occur in the field? • Assess technology transfer issues • What are all the things needed to design products? • What are all the things needed to manufacture products? • What are all the things that drive cost? • What is our Intellectual Property? • Describe claims - what, exactly, have we invented? • Document IP - “teach” others how our technology works. • Complete IP strategy - who will do what by when to create proprietary position? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 29 Comparison of Technology Development Work IP Experiments Analysis Ideation Stage A What technologies might solve problem? - “Ideation” sessions and literature search - Expand understanding of problem. - Identify possible technologies. Stage B (Need new Stage A projects?) Stage C (Need new Stage A projects?) Which technologies should we investigate? Which technology will we use? - Analyze technical feasibility - Analyze technical feasibility - Assess technical risk - Assess technical risk - Assess technology transfer - Potential design issues? - Potential manufacturing issues? Can we actually make a product? (No experimental work) Does technology work in lab? - Construct lab models - Perform lab tests Will it work in field conditions? - Demonstrate field operability - Test under field conditions Is there a chance to create IP? - “Ideation” sessions to ID new solutions - Scan for prior art - Document concepts - establish prior art What is our plan to create IP? - Assess novelty - is it new? - Document inventions - what is it? - Initiate IP strategy What is our IP? - Describe claims - what is new? - Document IP - how does it work? - Complete IP strategy Stage Gate - Lecture 1 - Assess technical risk - Assess technology transfer - Who will design? - Who will manufacture? 30 Comparison of Technology Development Work IP Testing Analysis Ideation Stage A Stage B Stage C What technologies might solve problem? - “Ideation” sessions and literature search - Expand understanding of problem. - Identify possible technologies. Which technologies should we investigate? Which technology will we use? - Analyze technical feasibility - Analyze technical feasibility - Assess technical risk - Assess technical risk - Assess technology transfer - Potential design issues? - Potential manufacturing issues? Can we actually make a product? (No experimental work) Does technology work in lab? - Construct lab models - Perform lab tests Will it work in the field? - Demonstrate field operability - Test under field conditions Is there a chance to create IP? - “Ideation” sessions to ID new solutions - Document concepts - establish prior art What is our plan to create IP? - Assess novelty - is it new? - Document inventions - what is it? - Plan IP strategy What is our IP? - Describe claims - what is new? - Document IP - how does it work? - Execute IP strategy Stage Gate - Lecture 1 - Assess technical risk - Assess technology transfer - Who will design? - Who will manufacture? - Technology roadmapping 31 Build Patent As We Execute Stages Stage A Patent Section Purpose • Field of Use • What’s the problem? • Prior Art • What have others done? • Why is this inadequate? B • Description of Invention C • Claims • What is our solution? • Why is it better? • What do we claim exclusive rights to? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 32 Specific Stage Gate IP Elements These three IP-related elements are addressed at Stage Gate reviews: A B C 1. Problem/Solution Statement: • What problem are we trying to solve? Required Required Required • How will we solve it? Required Required Required 2. IP/Literature Scan: • Who has done what to solve this problem? Not Required Required Required 3. IP Strategy: • How will we protect our IP? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 33 Begin with the end in mind... What do we need to support stage gate product development? By the end of Stage Gate technology development, we will be able to answer Yes or No to these questions: 1. Does our technology actually work under real world conditions? 2. Can products based on this technology actually be designed and manufactured at an acceptable cost? 3. Can the technology provide a unique competitive advantage? Stage Gate - Lecture 1 34