Powerpoint - tesol
advertisement

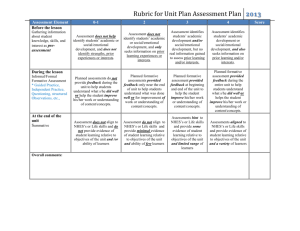
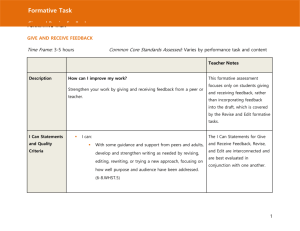
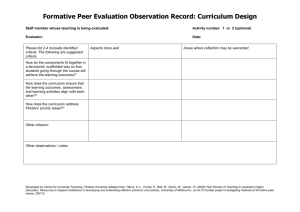
A practical study of formative teacher evaluation tools. Hassen Rached Abstract Formative assessment is of paramount importance for Continuing Professional Development. It aims to support teachers in their development as professionals by providing information about what teachers do in relation to the curriculum and its objectives and the impact of teaching on the learning process. This paper presents what teacher formative assessment is, why it is important, evaluation tools and procedures, the role of the various concerned parties in the evaluation process, evaluation outcomes, and limits. Common strategies used in teacher evaluation by self and others are explored. Tools of formal and informal evaluation processes are suggested to reflect upon teaching beliefs, knowledge, and effectiveness of teaching techniques. Tools for formative evaluation are discussed spanning teacher-specific activities: awareness-raising activities of the teaching process; means of gathering data; and an experimental checklist for self and peer evaluation. Evaluation of the efficiency of the formative tools themselves sums up the paper. Continuing Professional Development Options • • • • • • Option 1: Conference Plan Option 2: Peer Coaching Option 3: Action Research Option 4: Collaborative Study Groups Option 5: Individual Development Plan Option 6: Dialog Journals Definition Formative assessment is an ongoing process. It compromises observations, summaries, and reviews that inform teacher instruction and provide students feedback on a daily basis. (Fisher & Frey, 2007) Definition Formative assessment is a process used by teachers and students during instruction that provides feedback to adjust ongoing teaching and learning to improve students’ achievement of intended instructional outcomes.” (Johnson, 2007) It inhibits open and productive discussions about teaching; in essence, it marginalizes the types of activity that Identifies teacher’s needs could lead to better teaching. It examines instructional practices but often ignore how those practices influence students' learning, thinking, and development. Summative, It is intended to judge the overall quality of teaching performance. Setting Objectives Summative Assessment (Assessment OF develpment) Formative Assessment (Assessment FOR development) Why? • An eclectic Communicative approach towards teaching leaves teachers with a host of options at hand. Ongoing evaluation of those options is necessary. • FA makes the teachers autonomous professionals. • Ongoing development in the world implies continuing research. Evaluation tools • • • • • • • • • • Questionnaires Multiple choice questions Viva Students’ assessment Peer evaluation Self assessment Student evaluation Class discussion Written reflective journals Clinical supervision Teacher Development Projects 2010 - 2011 Monastir Region Mr Brahim Aloui Monastir Pioneer School Teacher formative assessment process Planning. Specifying objectives and crtiteria for success. Improved teaching and Learning experience. Formative assessement tools. Collect and analyze evidence. Change in teaching practice Planning. Specifying objectives and criteria for success. • To foster teaching skills. • To help identify gaps in the teaching learning process. • To enhance the motivation to learn. • To improve students test results. • To provide a better class environment. Which tools are to be used? Student feedback Teacher critical reflection Video recording and analysis Peer observation and staff meetings Advantages of multiple perspectives • Provide a more complete picture of teachers’ contributions to student learning. • Contribute to greater confidence in the results of teacher evaluation. • Create opportunities for teachers to learn from their colleagues. • Provide teachers with greater insights into how their instruction affects student learning. Self-Evaluation questions Nolan and Hoover (2013) suggest that teachers ask themselves five key questions: 1. What am I doing? 2. Why am I doing it in this way? 3. What impact is it having on learners? 4. How might I do things differently? 5. If I did things differently, what impact might it have on learners? 1. What am I doing? - Focus on teaching for Bac exam preparation. Design handouts and follow-up activities. Enrich the lessons with audio and video materials. Ensure that the students’ copybooks contain all the data necessary for exams and to give a positive impression about oneself. 2. Why am I doing it in this way? - Teach for summative assessment. - Teach to please the parents view of learning. - Teach to show up some proof of work. 3. What impact is it having on learners? - Mechanical process of teaching. Loss of motivation. Back to ‘old’ standards of teaching. Poor or no communication. Absence of challenge. 4. How might I do things differently? - Collect data about students’ concerns and expectations. - Devise an action remedial plan. 5. If I did things differently, what impact might it have on learners? - Better lesson outcomes. More motivated students. More productive and satisfying teaching Free ourselves “from impulse and routine behavior.” Develop the skills of considering the teaching process thoughtfully. Make and review on audio or video • Laptop webcam was used to record lessons. • Videos were viewed and analysed in a staff meeting. • Remarks were agreed on in a report. Review on audio or video findings • Lessons are usually carried out in a hasty manner. • Despite everyone’s belief in communicative principles, lessons were highly structured and monopolized by the teachers. • Only some students jumped into answers before questions are asked. We were usually pleased with that. • Grammatical mistakes were corrected on the spot at the expense of communication. Student feedback • • • • • Learning logs One-minute paper Questionnaire Student journal entry Exit cards Student feedback findings • The class is just boring. We are always doing the same thing. • The questions are not challenging enough to attempt an answer. • We are never given the chance to communicate in class. • You (teacher) insist to interfere in debates and set way for ‘your’ opinion. Teaching portfolio As a powerful Tool for Continuous Improvement of Teaching and Learning, it is used to • document and assess more fully the substance and complexity of teaching. • connect assessment of teaching with assessment of learning. Change in Practice • Identifying the problems • Better practice • Better teaching-learning experience. Searching for better practice. • • • • • Literature search. Ask seniors for advice. Ask for the help of supervisors. Share experiences on the net. Forum topics. Challenge and motivation 1 • Design activities that are more complex, abstract, independent, require mutual accountability. • Require more complex expression of ideas. Challenge and motivation 2 • Ask students to tell the story from a different point of view rather than display questions. • Supplment the program with more challenging textual input rather than task handouts. • Have students use the information in a completely new way. Questioning techniques • Prepare questions in advance. • Vary questions. • Give enough time before allowing answers. • Set clear rules for class participation. • Don’t interrupt answers to correct grammar and vocabulary. Note down frequent mistakes and then design a remedial plan. Primary Results • Ongoing self-reflection, peer assessment and students’ feedback. • Data proved better practice and better outcomes. • Comments on improvements were sketchy: Good, better, feel more comfortable, more participation. Next Step We noticed the need for setting standards, an assessment reference to assess and measure improvements. Assessement Table Focus Poor Basic Skilled Excellent Challenge Tasks do not motivate the learners. Little relevance. Low cognitive challenge. Tasks vary between more and less motivation. Rapid rhythm. No space for different learning styles Lesson procedure and teaching techniques are highly challenging. Students work in pairs and groups to construct meaning Lessons interest the learners. Students lead the discussion and production. Students are given opportunities to reflect upon their work: peer correction. Conclusion • Professional development is an ongoing process, one that evolves as teaching beliefs and practices are assessed and reexamined. Following the evaluation standard set in the table, teaching practice evolved gradually but surely. • There is no recipe for professional development that works for everyone. It is a matter of reflection and adaptation. What is paramount is discovering the many options we have for directing our own learning about teaching. • Effective professional development is self-empowering. • New assessment tools do not necessarily duplicate each other but assess and evaluate different components of the teacher’s performance.