Plant cell and Animal cell – Cell membrane and

Plant cell and Animal cell
–
Cell membrane and
Mitochondria
Cell Membrane
What is a cell membrane?
The cell membrane is the very thin outermost layer of the cell that functions to keep the cytoplasm and organelles in the cell and other particles out.
It is semi permeable meaning that it only allows certain particles through.
The purpose of this is to be able to let molecules in that the cell needs, like nutrients, but to keep particles out that could harm the cell.
Cell Membrane
What is the function of cell membrane?
The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell and, in animal cells, physically separates the intracellular components from the extracellular environment.
The cell membrane also plays a role in anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape to the cell, and in attaching the extracellular matrix to help group cells together in the formation of tissues.
The barrier is selectively permeable and is able to regulate what enters and exits the cell, thus facilitating the transport of materials needed for survival.
Cell Membrane
What is the structure of a cell membrane?
• The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer
• It is composed of proteins and lipids
• The structure consists primarily of a thin layer of amphipathic phospholipids which arrange so that the hydrophobic "tail" regions are shielded from the surrounding polar fluid
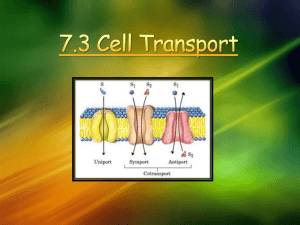
A cross section of the cell membrane.
You should notice two different structures; the phospholipids are the round yellow structures with the blue tails, the proteins are the lumpy structures that are scattered around among the phospholipids.
Cell Membrane
Transport Proteins:
Carrier proteins are proteins which do not extend all the way through the membrane. They move specific molecules through the membrane one at a time
Carrier proteins bond and drag molecules through the bilipid layer and release them on the opposite side.
Mitochondria
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are organelles found inside most eukaryotic cells.
They generate the energy that the cell need, so they are sometimes compared to power plants.
The mitochondria make adenosine triphosphate, which the cell can use as an energy source.
The synthesis of ATP is done through the citric acid cycle, which uses glucose, pyrovate and NADH as the input molecules.
Mitochondria
What is the structure of mitochondria?
• Mitochondria have two membranes
• The outer membrane covers the organelle and contains it
• The inner membrane folds over many times; folding increases the surface area inside the organelle
• The increased surface area allows the small organelle to do as much work as possible
• Many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane of the mitochondria
Mitochondria
• The mitochondria is the power plant of the cell.
• The more active the organism is, the more mitochondria it will have in its cells.
• It is the part that turns food into energy.
• Think of the mitochondria as the part of the cell that burns the fuel to keep the organism running.
Bibliography
1. Harweb 2001 – 2011, Josh bomstein United States of America, veiwed 5 August
2011, http://www.harweb.com/cell/animal.htm
2.
Plant cell structures 2008, admin United States of America, veiwed 6 august 2011, http://plantcellstructures.com/plant-cell-structures/cell-membrane-and-cell-wall/
3. EnchantedLearning 2001-2010, EnchantedLearning United States of America, viewed
7 august 2011, < http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/plants/cell/ >
4. Buzzle 2000-2010, 2011 Puja Lalwani United States of America, viewed 6 august
2011,< http://www.buzzle.com/articles/labeled-plant-cell-diagram-andfunctions.html
>