Chapter 3: What You Will Learn
advertisement

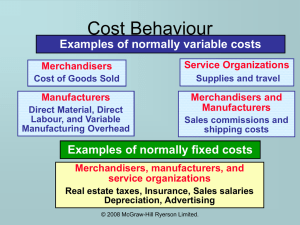
Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Chapter 3: Learning Objectives What Do Financial Institutions Do? Functions of Intermediaries Financial Institutions and Market Types The “four pillars” The role of technology & government regulation How Important is the Financial System? Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Financial Institution An institution that provides financial services for its clients or members The most important financial service provided by financial institutions is acting as financial intermediaries Most financial institutions are highly regulated by government Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited The Function of Financial Institutions Intermediation transforming assets Brokerage an “agency” function: bringing would-be buyers and sellers together Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Financial Intermediary A financial institution that connects surplus and deficit agent Bank, trusts, credit union Channel funds, resources from people who have extra money (savers) to those who do not have enough money to carry out a desired activity (borrowers) Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Financial Intermediaries Provide 3 Major Functions Maturity transformation Risk transformation Converting short-term liabilities to long term assets (banks deal with large number of lenders and borrowers, and reconcile their conflicting needs) Converting risky investments into relatively riskfree ones (lending to multiple borrowers to spread the risk) Convenience denomination Matching small deposits with large loans and large deposits with small loans Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited The Functions of Intermediaries Facilitate the acquisition/payment of goods & services via lower transactions costs Facilitate the creation of a “portfolio” economies of scale & scope Ease liquidity constraints Reallocate consumption/savings patterns Provide security Reduce asymmetric information problem Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited A Legacy from the Past: The “Four-Pillars” •Chartered •personal, •Trusts banks commercial loans, and deposits company and credit unions •fiduciary deposits •Insurance responsibilities and personal loans and company •underwriting •Investment dealers •underwriting Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited insurance contracts and brokering securities Conflict in Regulation Regulation prevented banks to sell insurance Currently, much blending between all “Pillars” due to ease of legislation and financial innovations Protect the public if the institutions go bankruptcy Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Types of Financial Institutions 1. Deposit-taking institutions – accept deposits and make loans chartered banks, trusts, credit unions 2. Insurance Companies and Pension Funds RRSPs (individual); RPPs (employer); CPP (Public) 3. Investment Dealers and Investment Funds Mutual funds, underwrite corporate and government securities 4. Government financial institutions Alberta Treasury Branch (ATB), Business Development Bank, CDIC Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Types of Financial Markets: A Selection of Types Primary vs Secondary Term to maturity open auction, private, public Sectoral classification Retail vs Wholesale Organization brokerage vs intermediation functions Size short vs long term, money vs capital Direct vs Indirect newly-issued vs previously issued Households and unincorporated businesses Nonfinancial corporations The financial The government or public The Rest of the world Complexity Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Assets as a Percent of total assets Non-Financial Assets 42.2% 57.8% Financial Assets Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Most important Financial Instruments, 2004 Percent of total financial assets 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Currency Mortgages Insurance Bank loans Corporate Bonds Foregin Currency The Relative Importance of the Financial Sector Non-Financial Sector Financial Sector 40.98% 59.02% Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Key Financial Sector Institutions in Canada Percent of total assets, financial sector 50 40 30 Insurers Non-deposit-taking instituions Investment Funds Deposit-taking instituion 20 10 0 1990 1992 Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited 1994 1996 Year 1998 2000 2002 What Future for Banking? Non-bank firms are increasingly offering financial services Are banks better at spreading risks? The threat & opportunities from technology Banks: One-stop shopping for all financial services Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Summary Intermediation is a central concept Financial institutions can be classified by type, size, function Financial markets can be classified by size, term, organization, type of assets issued Banks are the most adept at the intermediation function Financial systems should strive for efficiency Copyright (c) 2006 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited