Journalism 614: Communication and Public Opinion

Journalism 614:
Opinion and Perception II:
Spiral of Silence
What is Public Opinion?
Any opinion held by a majority of citizens?
– Democratic view - The General Will
Any opinion about public affairs?
– Liberal Democratic view - All are valid
Only reasoned opinion about issues?
– Elitist view - Only informed opinions count
Each of these is about forming preferences and expressing those views
Another definition…
Public opinion is any opinion that can expressed publicly without sanctions
– Can state without fear of social isolation
• Here, public opinion is a matter of visibility
• Minority opinions must be seen for those who hold them to feel comfortable expressing themselves
This is about the perceptions of the opinion climate and the ability to speak out without risks
Media Influence
Direct Method - Communication events, arguments, and opinions that change the mind of audience members
Indirect Method - Present indicators of what already seems to be public opinion
– Media convey an impression of how accepted an opinion may be now or in future
Spiral of Silence
Societal norms can be intimidating
Understand public opinion as a tangible force
– Intense social pressure can be brought to bear on the person who dares to test the boundaries
Perception of distribution of opinion shapes willingness to express opinions
– People express opinions more confidently when they see they are in the majority or “gaining ground”
– People are unwilling to express opinions that run counter to their perception of majority view
Opinion Expression
What opinions can be expressed?
– Opinions that do not risk fear of social isolation
– Opinions that are publicly visible
• Can be a minority opinion, but minority must speak out and act as if it is, or will be, majority
People have a “quasi-statistical organ”
– A sixth sense that provides information about what society is thinking and feeling
– Constantly scan the environment to gauge the climate of opinion and future trends.
Fear of Isolation
Fear of social isolation is the key force that drives the spiral of silence
– Group pressure has tremendous influence
– We don’t like to be excluded for our views
Theory about obedience to authority in
World War II - citizens in Nazi Germany
– Noelle-Neumann was Nazi Party member
• She worked for Goebbels, head of Nazi Propaganda
• Wrote for Das Reich, but later withdrew/recanted
Social Influence
Considers effects of group settings on attitudes, opinion expression, behavior
Largely based on experimental research
– Solomon Asch’s work on social conformity
• When do we go along with the group?
– Stanley Milgram’s work on social compliance
• When do we obey authority?
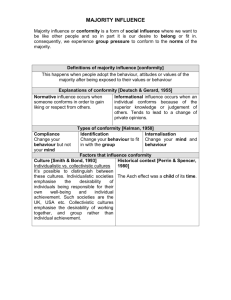
Asch – Conformity
Conformity
The Asch studies
Unambiguous situation
Small group setting (10-12)
Uniform incorrect assessment
Over one-third concur with incorrect assessment - go along with the group
Minority Influence
Judgments about color of slides
Consistent incorrect assessment by minority
Portion of subjects agree in error
Implication:
– Minority opinion can exert power
– Bandwagon vs. Siding with the underdog
Milgram – Obedience
Obedience
Subjects “randomly” assigned the role of
"teacher" and asked to administered shocks to
"pupils” for incorrect responses
Pupils were actually part of the experiment.
– Act out the effects of progressively higher “shocks”
– What proportion will continue to the highest level when prodded by the supervisor?
• Highest voltage switches (450 volts) were marked with labels of “Danger: Severe Shock” and then “XXX”
Setup and Scenario
QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.
Voltage
75
120
150
200
300
330+
Confederate Response
Grunts
Shouts in pain
Refuses to continue
Blood-curdling screams
Refuses to answer
Silence
Objection Supervisor’s response
First "He's fine. go on.”
Second "The experiment requires you to go on.”
Third
Fourth
"It is absolutely essential to go on.”
"You have no choice. You must go on."
Response of Subjects
Milgram’s Obedience
Experiment
Different subjects, locations (~)
Decrease proximity of authority (-)
Increase connection to student (-)
Involve obedient others (+)
Involve disobedient others (-)
When to Speak or Keep Silent
Conformity and compliance have great social power over individuals
– Those in minority positions tend to keep quite if they do not sense support
– Not that they change their minds
• “Duck their heads and keep their own council”
Summary
People have the ability to gauge trends of public sentiment
People justifiably fear social isolation
People are hesitant to express minority viewpoints, especially if “losing ground”
But where do they get their perceptions?
Media Influence
Mass media work jointly with majority opinion to silence minority views
– Mass media, particularly TV, suggest what others are thinking through portrayals
– People look to the media to see if there is support and legitimization for views
• Index the media to gauge current climate
• Provide the words and phrases that people can use to defend a certain point of view
Critiques of Spiral of Silence
Hardcores - the minority that remains vocal in defiance of threats of isolation
– Bill Maher, Dixie Chicks, War Protesters
Pluralistic ignorance and Projection - we tend to misestimate the prevalence of our views
– Quasi-statistical organ doesn’t work so well
Weak support outside of WW II Germany
– Maybe only operates in totalitarian regimes
– The ability to find like-minded views online