Cultural Change
advertisement
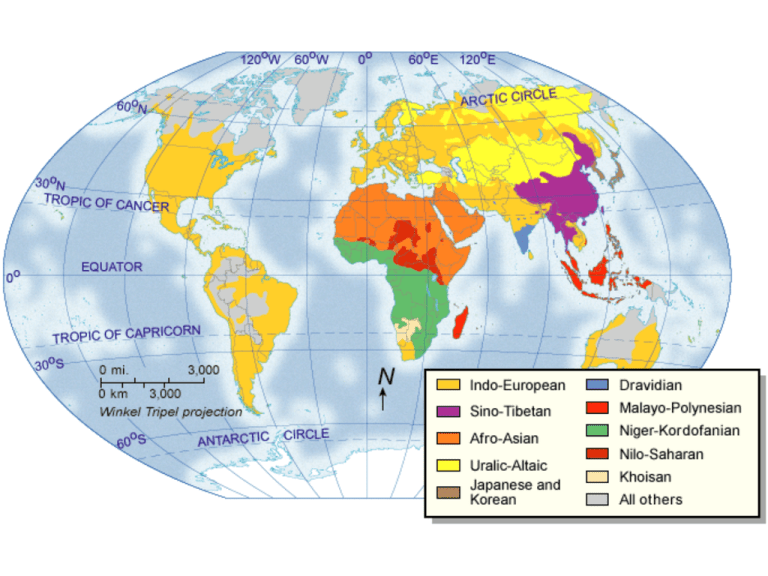
Cultural Change Culture Regions • Includes diff. countries that share common traits like…? – Economic systems – Forms of govn’t. – Social groups – History – Religion Cultural Change • New ideas, lifestyles, and inventions Δ w/in cultures (internal Δs) • Δ also comes from external influences – Trade, migration, war This is called cultural/spatial diffusion Cultural Change • Cultural Divergence – Occurs when diff. cultural influences cause an area to divide into separate parts • Eastern vs. Western Roman Empires • Ancient India India & Pakistan • Cultural Convergence – Occurs when diff. cultures x∆ ideas and become more similar – More common now with globalization 1) Agricultural/Neolithic Revolution • Earliest humans were nomads= hunters and gatherers (no fixed home) • Then they settled in river valleys and plains began farming & had permanent home • This shift then spread throughout the world’s regions 2) Civilizations • By 3500 B.C., the farming villages then shifted into civilizations… – Highly organized – City-based – Advanced farming, trade, govn’t, art & science innovations • But how did this way of life spread?... Culture Hearths • Early centers of civilization • Ideas & practices spread out from these first as nomads passed thru • Where were the most influential culture hearths? Culture Hearths • What did those 5 places have in common? – Fertile land from river valleys/water sources – Made canals/ditches to irrigate land Allowed ppl to grow surplus crops… 3) Specialization • Surplus food allowed fewer ppl to farm develop new jobs – Metalworking & shipbuilding more trade • More trade led to more cities • Now need complex govn’t – Coordinate harvests, plan projects, manage army • Able to create writing systems share info. Cultural Contacts • Civilizations affect each other when permanent migration occurs – Why do ppl migrate? • By CHOICE- for better education, jobs, more $ • By RELUCTANCE- harsh govn’t, wars, persecution, famines • By FORCE- slavery, exiled – Practices & ideas then blend with one another 4) Industrial Revolution • In 1700s, after centuries of cultural diffusion, countries began to industrialize – Used power-driven machines & factories economy boost • Faster and cheaper production • Less labor (cost) – Ppl moved from farms to cities (term?) 5) Information Revolution • At the end of 1900s: computers brought a turning point – Able to store huge amts. of info and share it all over world instantly this links the cultures even more closely & quickly