Ecosystem Energy Pyramid
advertisement

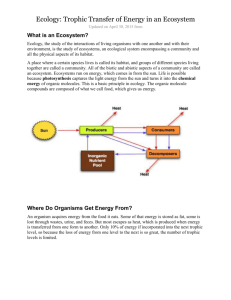
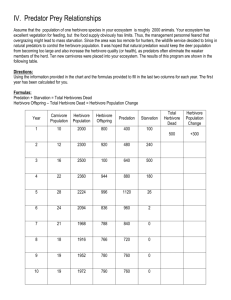
Happy Block Day New spot in notebook: Ecosystem Energy Pyramid Number 1 -5. You’re sick Jerry! Sick, sick, sick! Learning Target: With my team, we will explain why the ecosystem pyramid HAS to be shaped like a pyramid. Now stay calm...Let’s hear what they said to Bill. Ecosystem Pyramid Which energy type(s) are shown in the following pictures? Which Type of Energy? 1) Mechanical Which Type of Energy? 2) The glacier is warming up. It is turning to water. Which Type of Energy? 3) A nice TV What is powering the TV? Which Type of Energy? 4) Use this SOLAR CELL to power your home. Use the power of the sun. Which Type of Energy? 10) Announcements: Science Boards due a week from Friday! Science fair 2/28 After school until 2/22 – lab open for science fair work AND support. ASAP can also help. Supplies and computers! On two pages of your notebook: Definitions for the diagram Ecosystem Energy Pyramid Diagram Definitions: Energy – the ability to cause change. Ecosystem – all of the living and nonliving parts working together in a community. Examples include a pond, Silverton, and the world. Ecosystem Energy pyramid - A graphic organizer demonstrating the flow of energy through an ecosystem. Def: Sun – source of electromagnetic energy for earth. How do you know it’s a chemical change and not a physical change? Sun Chemical Energy Light Travels to Earth Light Energy Most of the sunlight is lost…. It misses the earth entirely or It hits a spot on the earth without a plant. The spot warms up and that thermal energy floats up into the sky. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r MFw5Fhiq24 Sun Chemical Energy Light Travels to Earth Light Energy Most of Light Energy goes into space or does not hit a plant. It is out there but not useful to us. DEF: PRIMARY PRODUCERS Plants Convert sunlight to glucose (sugar) PHOTOSYNTHESIS All life on earth is dependent on them. Sun Chemical Energy Primary Producers Light Travels to Earth Light Energy Chemical Energy DEF: HERBIVORES Animals that EAT PLANTS for their energy. Another example of an Herbivore... *Animal uses energy to move (lost as friction) or to keep warm (heat goes off into space) – all of that energy is hard to use ever again – ENERGY FLOWS Herbivore Thermal Energy* Floats Off Into Space Chemical Energy in body CARNIVORES! Well, they are all not dangerous. ANIMALS that EAT OTHER ANIMALS to obtain energy. *Animal uses energy to move (lost as friction) or to keep warm (heat goes off into space) – all of that energy is hard to use ever again – ENERGY FLOWS Herbivore Thermal Energy* Floats Off Into Space Carnivores Chemical Energy in body Energy is Flowing through from level to level – most of it is lost as it floats into space. Only 10% of usable energy flows onto the next level. Thus, the higher on the pyramid you are… The less efficient is your eating. It takes a lot plants to feed the insects and rodents to feed a hawk. Upper Carnivores You know what I am talking about. LIONS, TIGERS, AND BEARS. Oh My! Last in the chain – DEF: DECOMPOSERS They recycle materials THEY EAT DEAD ORGANISMS to obtain their energy. Mushrooms Buzzards Oh My! Ecosystem Pyramid Consider this choice: 1) You can eat 1 pound of fruits and vegetables or 2) You can eat one pound of hamburger. CONSIDER: It takes ten or more pounds of vegetables to make that one pound of hamburger. Copy and Answer this question and then make a pyramid Haiku. The ecosystem pyramid has a wide bottom and small top because _______. HAIKU is 5 – 7 – 5. And/or a bumper sticker describing why you can help the world if you eat less red meat. Haiku For a cow to live Thousand pounds of plants must DIE Vegetarian Energy Floats Up Not much left when you eat meat Many plants must die