Arab Nationalism
advertisement

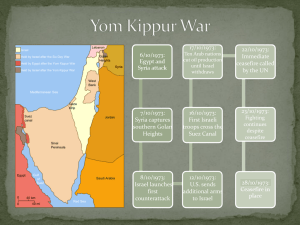
Emergent Nationalism in the Middle East Arab Nationalism and the Suez Crisis OVERVIEW In this lesson we examine: • The background of Arab nationalism • Nasser and ‘Pan-Arabism’ • International involvement in the Suez Crisis • Factors for long-term conflict Background of Arab Nationalism • At the beginning of the 20th century, the Ottoman Empire was in decline • European states took over outer territories such as the British takeover of Egypt • During WWI, Arabs with British support led a revolt against the ottoman Empire in return for sovereignty • Egypt, Iraq, Palestine and Transjordan were under British control • Lebanon and Syria were French mandates • By the end of WWII, most of the mandates had become kingdoms under Arab rule Nasser and Pan-Arabism Pan-Arabism: • Called for unity of all After the ArabArab states in North Africa and the Middle Israeli War of 1948, East Gamal Abdel Nasser • Was intended to be seized power in secular (religion & government separate) Egypt. What were and suppressed Muslim the key parts of his extremism ‘Pan-Arab’ • Was influenced by Marxist socialist ideals platform? but wanted to be nonaligned during the Cold War International involvement in the Suez Crisis Several key actions by Nasser began to agitate Britain, France and Israel: • Purchased arms from Czechoslovakia in 1955 • Forced British forces out of the Suez Canal in 1956 • Condemned the anti-Soviet, Baghdad Pact of Turkey, Iraq, Iran and Pakistan Up until 1956, the US and the World Bank offered loans for Egypt’s Aswan hydroelectric dam project. The West withdrew financial support and in response, Nasser… How did Britain, France and Israel • nationalized the Suez Canal react? • forced foreign engineers out of the country • bought out British and French shareholders In a secret meeting at Sevres, Britain, France and Israel decided: • Israel would invade Egypt on the pretense of opening the Gulf of Aquba Why was the Suez Canal still valuable • Britain and France would offer a to Britain and France 1956? ceasefire, leaving Israel inin Egyptian territory • Britain and France would invade Egypt after it rejected the ceasefire • Britain, France and Israel had successfully invaded the Suez Canal and Sinai Peninsula • The USSR threatened to attack Britain and France. The US supported UN resolutions for a ceasefire and threatened to withdraw financial support to Britain • Britain, France and Israel were forced to withdraw and UN peacekeepers monitored the withdrawal on Egyptian territory – Lester Pearson wins the Nobel Peace Prize for creating the United Nations peacekeepers Factors for long-term conflict • Both the US and USSR increased their influence in the Middle East • Nasser emerged as a In the aftermath of the conflict popular defender of Arab what factors ensured future interests conflict was inevitable? • Israel saw the success of unilateral action in dealing with its neighbours • The Gulf of Aquba and Palestinian refugees were unresolved issues SUMMARY QUESTIONS • Why did Nasser nationalize the Suez Canal and how did Britain and France respond? • What lesson did Britain and France learn about their influence in the post WWII world? • Why were the US and USSR so concerned with their reputations among Arab states?